 January 2019 in “Clinical Dermatology Open Access Journal”
January 2019 in “Clinical Dermatology Open Access Journal” Combining corticosteroids and non-ablative fractional laser therapy may effectively treat extensive alopecia areata.
 85 citations,
February 1989 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
85 citations,
February 1989 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Children with loose anagen hair have easily pluckable hair due to root sheath problems, and it might improve without treatment.
[object Object]  34 citations,
December 1995 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
34 citations,
December 1995 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Congenital Triangular Alopecia is a rare, non-scarring hair loss that can be surgically treated in females for cosmetic reasons.
 4 citations,
March 2006 in “Journal of dermatology”
4 citations,
March 2006 in “Journal of dermatology” A Chinese-Japanese boy had a rare fungal infection on his scalp and skin, likely caught in China.
 2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine”
2 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine” Different hair and scalp disorders cause hair loss or excess hair growth, with various treatments available depending on the specific condition.
 1 citations,
June 2014 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology”
1 citations,
June 2014 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology” A woman with discoid lupus improved with treatment after being misdiagnosed with a different hair loss condition.
 January 2014 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2014 in “International Journal of Trichology” A man had an unusual type of hair loss that didn't match known patterns and didn't improve with treatment.
 6 citations,
February 2016 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology”
6 citations,
February 2016 in “American Journal of Dermatopathology” The boy with woolly hair nevus had thinner hair and abnormal hair follicles, which improved with treatment but worsened when treatment stopped.
 3 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
3 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” A woman with a rare scalp lymphoma had unusual hair loss after treatment.
 January 2003 in “Postgraduate medicine”
January 2003 in “Postgraduate medicine” The article concludes that hair loss has many causes and treatments, with medication options like finasteride and minoxidil for men, and minoxidil, hormones, or iron for women, while warning against unproven remedies.
[object Object]  391 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
391 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Half of people with Alopecia Areata may see hair regrowth within a year without treatment, but recovery is unpredictable.
 24 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
24 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of hair loss in children is crucial due to limited treatment options and the condition's psychological impact.
 3 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology”
3 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology” Frequent use of hair straighteners can cause hair loss similar to scarring alopecia in young Turkish women.
 2 citations,
November 1990 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
November 1990 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Albendazole can cause hair loss, and piroxicam can cause fixed drug eruption.
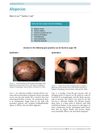 February 2013 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice”
February 2013 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice” Different types of alopecia in children require specific diagnoses and treatments.
 April 1955 in “Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine”
April 1955 in “Archives of pediatrics & adolescent medicine” Children's skin diseases need special care and treatment.
 32 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology Research and Practice”
32 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology Research and Practice” Trichoscopy can effectively tell apart tinea capitis and alopecia areata in children by looking for specific hair shapes.
 February 2024 in “The Open dermatology journal”
February 2024 in “The Open dermatology journal” Alopecia Areata affects people of all ages worldwide, is likely caused by genetic and environmental factors, and can lead to stress and depression, highlighting the need for treatments that address both physical and mental health.
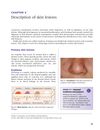
The document explains different types of skin lesions and their characteristics, causes, and related conditions.
 January 2021 in “Acta Scientiae Veterinariae”
January 2021 in “Acta Scientiae Veterinariae” Levothyroxine effectively treated a dog's skin and hair problems caused by hypothyroidism.
 13 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in oncology”
13 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in oncology” Melanoma development can be linked to the breakdown of skin's melanin-producing units.
56 citations,
October 2010 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” Epidermal nevi are skin cell clusters linked to various syndromes.
January 2022 in “Clinical Cases in Dermatology” A 12-year-old boy has a rare, harmless hair loss on his chin with no need for treatment.
32 citations,
August 2016 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Temporal triangular alopecia is a non-scarring hair loss in children, often linked to other health conditions.
 July 2023 in “Deleted Journal”
July 2023 in “Deleted Journal” Alopecia areata is the most common type of baldness treated with corticosteroids and minoxidil.
 1 citations,
August 2023 in “Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews”
1 citations,
August 2023 in “Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews” Microneedles are promising for long-acting drug delivery and can improve patient compliance, but more data is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
 85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition often starting before age 20, with varied treatment success and a need for personalized treatment plans.
 14 citations,
January 1985 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
14 citations,
January 1985 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The cause of alopecia areata was unknown, and while various treatments existed, no best treatment was agreed upon.

Some vaccines, like the hepatitis B vaccine, might be linked to the hair loss condition Alopecia Areata, but more research is needed.
 109 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
109 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Alopecia areata is a type of hair loss that can lead to complete baldness, often associated with other autoimmune conditions, and half of the cases may see hair return within a year.



























