 32 citations,
January 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
32 citations,
January 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Hormone therapy affects hair growth in transgender individuals, with testosterone potentially causing hair loss in trans men and estrogen reducing facial/body hair in trans women; treatment options vary.
 3 citations,
February 2016 in “Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America”
3 citations,
February 2016 in “Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America” Manage women's cholesterol with diet, exercise, and careful treatment choices, especially during pregnancy, PCOS, and menopause.
[object Object]  20 citations,
January 2003 in “Treatments in Endocrinology”
20 citations,
January 2003 in “Treatments in Endocrinology” Testosterone therapy can help improve mood, sexual function, and bone health in women with low androgen levels, but more research is needed to establish safe and effective guidelines.
 24 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
24 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Women's ovarian hormones and adrenal androgens change throughout life, affecting hair loss and health.
 34 citations,
December 2015 in “Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews”
34 citations,
December 2015 in “Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews” Some hormone-related drugs may protect brain cells in Parkinson's disease differently in men and women.
 37 citations,
February 2013 in “Maturitas”
37 citations,
February 2013 in “Maturitas” Testosterone therapy is beneficial for women's health and does not cause masculinization or liver damage, and it protects the heart and breasts.
[object Object]  28 citations,
October 2018 in “Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology”
28 citations,
October 2018 in “Clinical Obstetrics and Gynecology” Testosterone therapy seems safe and effective for transgender men with proper care, but more long-term research is needed.
 21 citations,
December 2012 in “Maturitas”
21 citations,
December 2012 in “Maturitas” Testosterone implants in women require pharmacological dosing to be effective and are generally safe and well-tolerated.
83 citations,
August 2018 in “BJOG” Uterine transplants for transgender women are feasible but need more research.
 8 citations,
May 2021 in “Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology”
8 citations,
May 2021 in “Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology” Different levels of anti-Müllerian hormone can help diagnose polycystic ovary syndrome in women of different ages.
 9 citations,
May 2015 in “Cardiology Clinics”
9 citations,
May 2015 in “Cardiology Clinics” The conclusion is that managing cholesterol is important for women, especially during pregnancy, breastfeeding, and with PCOS, and involves regular screening and careful treatment choices.
 11 citations,
September 2012 in “Journal of obstetrics and gynaecology Canada”
11 citations,
September 2012 in “Journal of obstetrics and gynaecology Canada” Testosterone therapy seems safe for short-term use in postmenopausal women with low sexual desire, but more research on long-term effects is needed.
 7 citations,
April 2012 in “Clinical investigation”
7 citations,
April 2012 in “Clinical investigation” Transdermal testosterone can improve sexual desire in postmenopausal women but lacks long-term safety data and is not FDA-approved for this use.
 35 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes”
35 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes” The conclusion is that accurately identifying the cause of high androgen levels in women with PCOS is crucial and requires specific tests.
 13 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of Womens Health”
13 citations,
June 2018 in “Journal of Womens Health” Combination therapy with oral contraceptives and spironolactone improves hair growth, menstrual issues, and acne in women with PCOS.
 98 citations,
July 2011 in “Fertility and Sterility”
98 citations,
July 2011 in “Fertility and Sterility” An mFG score of 5 or more indicates above-normal hair growth in Southern Chinese women.
 55 citations,
January 2007 in “Climacteric”
55 citations,
January 2007 in “Climacteric” Menopause and aging can affect women's quality of life and sexuality, but hormone therapies may help alleviate these issues.
 215 citations,
January 2011 in “Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology”
215 citations,
January 2011 in “Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology” About 7% to 15% of Iranian women have polycystic ovary syndrome, depending on the criteria used to diagnose it.
 53 citations,
September 2014 in “Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology”
53 citations,
September 2014 in “Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology” Different types of PCOS have different levels of metabolic problems, with the most severe type showing the highest disturbances.
 18 citations,
May 2014 in “Menopause”
18 citations,
May 2014 in “Menopause” A 5 mg dose of transdermal testosterone cream effectively restores testosterone levels in postmenopausal women.
 28 citations,
May 2013 in “The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology”
28 citations,
May 2013 in “The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology” Testosterone therapy can improve sexual desire and function in postmenopausal women but should be used cautiously and not based solely on testosterone levels.
 46 citations,
May 2009 in “Maturitas”
46 citations,
May 2009 in “Maturitas” Taking DHEA for a year is generally safe for postmenopausal women but may cause acne and more facial hair without improving metabolism or aging.
 48 citations,
July 2009 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine”
48 citations,
July 2009 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine” DHEA did not improve sexual function, well-being, or menopausal symptoms in postmenopausal women with low libido but caused side effects like acne and increased facial hair.
 36 citations,
January 2014 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine”
36 citations,
January 2014 in “The Journal of Sexual Medicine” Testosterone may help increase sexual events for women with low libido due to antidepressants.
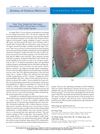 35 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology”
35 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology” A cancer patient died from a severe skin reaction after taking the drug cetuximab.
 5 citations,
June 2004 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society”
5 citations,
June 2004 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society” Testosterone therapy can improve sexual satisfaction and mood in surgically menopausal women when used with estrogen, but its long-term safety and effects on naturally menopausal and premenopausal women are unclear.
 February 1960 in “Journal of the American Medical Association”
February 1960 in “Journal of the American Medical Association” Treatments for hair loss include estrogen therapy and special shampoos.
 59 citations,
August 2004 in “Human Reproduction Update”
59 citations,
August 2004 in “Human Reproduction Update” Testosterone replacement can help women with low libido and mood, but they need to have enough estrogen first to avoid side effects.
 June 2003 in “Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey”
June 2003 in “Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey” After chemotherapy for a gestational trophoblastic tumor, normal pregnancy rates are possible, but there's a slightly higher risk of the tumor reoccurring in future pregnancies.
 90 citations,
December 2007 in “Current Oncology”
90 citations,
December 2007 in “Current Oncology” Non-hormonal treatments should be used first for sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal breast cancer patients on aromatase inhibitors, with hormones as a second option.




























