 19 citations,
March 2011 in “Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology”
19 citations,
March 2011 in “Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology” Some chemicals absorbed through the skin can cause serious health problems.
 14 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of Natural Medicines”
14 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of Natural Medicines” Chaga mushrooms contain compounds that may promote hair growth better than common treatments.
[object Object] 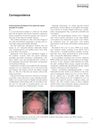 12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
November 2011 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A woman developed a scalp condition from using minoxidil, which improved with a different treatment but left scarring.
 40 citations,
August 2006 in “Current Drug Safety”
40 citations,
August 2006 in “Current Drug Safety” Some drugs can cause hair loss, excessive growth, or color changes, often reversible but sometimes permanent.
 April 1999 in “Therapeutische Umschau”
April 1999 in “Therapeutische Umschau” Hair loss and excessive growth treated with various options, including new laser technology.
 12 citations,
May 1989 in “Postgraduate Medicine”
12 citations,
May 1989 in “Postgraduate Medicine” The document concludes that hair loss is common and can be treated with medications like minoxidil or surgical options, and it significantly affects people's psychological well-being.
 111 citations,
March 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery”
111 citations,
March 2012 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery” Liposomes could improve how skin care products work but are costly and not very stable.
 4 citations,
April 2020 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
4 citations,
April 2020 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Hair loss in women is complex to diagnose and treat, and hair restoration should be done by experts. Using minoxidil before surgery can help manage post-surgery hair shock loss. The Follicular Unit Transplantation method is recommended for women due to its speed, no need for shaving, and better graft quality. Strategies like L, T, and reverse L patterns can help restore central hair density, and regenerative methods can improve graft survival in hair transplants.
 60 citations,
January 2014 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia”
60 citations,
January 2014 in “Anais Brasileiros De Dermatologia” Nanotechnology in dermatology shows promise for better drug delivery and treatment effectiveness but requires more safety research.
 162 citations,
August 2002 in “Survey of Ophthalmology”
162 citations,
August 2002 in “Survey of Ophthalmology” Latanoprost can make eyelashes longer, thicker, and darker.
 October 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that various hair disorders have different treatments, including medication, surgery, and addressing underlying causes.
 33 citations,
June 2007 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics”
33 citations,
June 2007 in “International Journal of Pharmaceutics” The conclusion is that measuring how drugs partition into artificial sebum is important for predicting their delivery into hair and sebaceous follicles, and it provides better information than traditional methods.
1 citations,
February 2024 in “Pharmaceutics” Nanovesicles improve drug delivery through the skin, offering better treatment outcomes and fewer side effects.
 42 citations,
February 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
42 citations,
February 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Minoxidil boosts hair growth by triggering growth factor release from specific stem cells.
 24 citations,
May 2013 in “Drug Design Development and Therapy”
24 citations,
May 2013 in “Drug Design Development and Therapy” Multimodal minoxidil microemulsion is more effective in treating hair loss than minoxidil alone.
 15 citations,
July 1991 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
15 citations,
July 1991 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Laser Doppler velocimetry is a valuable noninvasive tool for skin blood flow research in dermatology.
 34 citations,
December 1991 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences”
34 citations,
December 1991 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” The conclusion is that small hair follicles cause baldness in macaques, and treatments like antiandrogens and minoxidil can prevent hair loss and promote regrowth.
 July 2011 in “Springer eBooks”
July 2011 in “Springer eBooks” The document concluded that FDA-approved treatments like minoxidil and finasteride are effective for hair loss, while the effectiveness of natural remedies and other non-approved treatments is not well-supported by evidence.
 September 1999 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society”
September 1999 in “The Journal of The British Menopause Society” The document concludes that skin aging in women can be caused by UV exposure and hormonal changes, and treatments like hormone replacement therapy and various skin therapies can help.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” 36 citations,
May 2005 in “BMC dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” 36 citations,
May 2005 in “BMC dermatology” DPCP is effective for treating severe alopecia areata, but relapse is common.
 3 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
April 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Mesotherapy lacks strong evidence for effectiveness and safety, and its ingredients are not FDA-approved for subcutaneous use.
 4 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
4 citations,
August 2018 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), a protein-rich extract from a patient's blood, shows promise in improving hair density, thickness, and quality, but the best method of use and number of treatments needed for noticeable results are still unclear.
 January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Taking finasteride daily can effectively and safely increase hair density and thickness for women with hair loss.
[object Object]  22 citations,
July 2019 in “PLOS ONE”
22 citations,
July 2019 in “PLOS ONE” Skin lymphatic vessels are essential for hair growth.
 76 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
76 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Dermal Papilla cells are a promising tool for evaluating hair growth treatments.
20 citations,
March 2021 in “Drug design, development and therapy” Topical immunotherapy can treat alopecia areata, but its effectiveness varies and the exact mechanism is unclear.
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” Alopecia areata in children is usually mild and effectively treated with strong topical steroids.
 9 citations,
January 2014 in “Annals of Dermatology”
9 citations,
January 2014 in “Annals of Dermatology” Some breast cancer patients on hormonal therapy may develop male or female pattern hair loss, which can sometimes be improved with topical treatments.

Genetic testing can help diagnose skin conditions but needs more research for full effectiveness.


























