 July 2011 in “Springer eBooks”
July 2011 in “Springer eBooks” The document concluded that FDA-approved treatments like minoxidil and finasteride are effective for hair loss, while the effectiveness of natural remedies and other non-approved treatments is not well-supported by evidence.
November 2014 in “PharmaTutor” Finasteride may help postmenopausal women with hair loss but is not effective for all and should be used cautiously in premenopausal women.
 20 citations,
October 2006 in “Skin Research and Technology”
20 citations,
October 2006 in “Skin Research and Technology” Women with AGA have less hair on midscalp, more thin and non-growing hair.
 15 citations,
February 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
15 citations,
February 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The study suggests computer-assisted analysis of scalp biopsies could improve hair loss diagnosis but needs more validation.
 2 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of Pakistan Association of Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of Pakistan Association of Dermatology” Finasteride 1mg daily effectively increases hair growth and slows hair loss in men with male pattern baldness over two years.
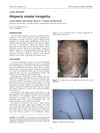 December 2007 in “CRC Press eBooks”
December 2007 in “CRC Press eBooks” Alopecia areata incognita causes widespread hair loss without patches and needs a scalp biopsy for diagnosis.
 November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
November 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” The workshop aimed to improve hair loss disorder diagnosis and understanding.

AGA causes permanent hair loss; women use 2% minoxidil, men use 1 mg finasteride daily.
 April 2008 in “Blackwell Publishing Ltd eBooks”
April 2008 in “Blackwell Publishing Ltd eBooks” AGA causes permanent hair loss; minoxidil helps men, finasteride helps men, minoxidil somewhat helps women, estrogens/antiandrogens lack evidence for women.
 170 citations,
December 2009 in “Histopathology”
170 citations,
December 2009 in “Histopathology” The conclusion is that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires good teamwork between skin doctors and lab experts.
 47 citations,
August 2000 in “Endocrine Reviews”
47 citations,
August 2000 in “Endocrine Reviews” The document concludes that more research is needed to understand excessive hair growth in women with normal hormone levels and regular ovulation.
 37 citations,
September 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
37 citations,
September 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Treat genetic hair loss early with FDA-approved medications and consider hair transplantation.
 32 citations,
August 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
32 citations,
August 1999 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Early onset hair loss linked to genetics and androgen levels.
 29 citations,
September 2014 in “Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Obesity”
29 citations,
September 2014 in “Current Opinion in Endocrinology, Diabetes and Obesity” Finasteride and dutasteride effectively treat hair loss in men and women, but may cause side effects like low libido and depression.
 22 citations,
May 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
22 citations,
May 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Treatments for common hair loss include minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplantation.
 22 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss from genetics and hormones can be treated with drugs or surgery.
 18 citations,
February 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
18 citations,
February 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” PGD2 increases androgen receptor activity in hair cells, which could be targeted to treat hair loss.
 11 citations,
January 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology”
11 citations,
January 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology” Polarized microscopy is a quick and free method to correctly identify types of hair loss.
 9 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
9 citations,
September 2019 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” PRP injections improve hair density in male hair loss.
 6 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation”
6 citations,
August 2020 in “Journal of Pharmaceutical Innovation” Nanoemulgel improves hair growth and quality using finasteride without irritation.
 6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Different hair loss types need accurate diagnosis for proper treatment.
 6 citations,
March 2014 in “Herba Polonica”
6 citations,
March 2014 in “Herba Polonica” Plant extracts may help treat hormone-related hair loss.
 5 citations,
February 2013 in “Dermatology and therapy”
5 citations,
February 2013 in “Dermatology and therapy” Crescina® lotion helps reduce hair loss and increase hair growth in males with androgenetic alopecia.
 2 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Trichoscopy is a helpful and quick method to diagnose hair loss without shaving.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Heredity and hormones cause common hair loss, and topical minoxidil is the first recommended treatment.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition, with various treatments showing mixed effectiveness and no guaranteed cure.
 1 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
1 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” Finasteride treats hair loss but may cause side effects like low libido and dizziness.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” The document says a skin condition called alopecia areata causes hair loss and stress, and is treated with strong skin creams, injections, or other therapies, but treatment success varies.
 1 citations,
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks” Finasteride increases hair count and improves hair growth with low risk of side effects.
 March 2021 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
March 2021 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” The microbiome may be linked to hair loss and could be a target for new treatments.




























