 October 2024 in “JEADV Clinical Practice”
October 2024 in “JEADV Clinical Practice” UK dermatologists commonly use corticosteroids and minoxidil to treat hair loss conditions.
 July 2022 in “Singapore Medical Journal”
July 2022 in “Singapore Medical Journal” Most children with alopecia areata improved with treatment, but those with more hair loss had worse outcomes.
8 citations,
January 2020 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” PRP works faster and is a safe alternative to steroids for treating alopecia areata.
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” Alopecia areata in children is usually mild and effectively treated with strong topical steroids.
 1 citations,
March 2020 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
March 2020 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” The paper concludes that recognizing bitemporal alopecia areata is important for early treatment and preventing its progression.
 25 citations,
August 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science”
25 citations,
August 2017 in “Lasers in Medical Science” Fractional lasers seem effective and safe for treating hair loss, but more research is needed to find the best treatment methods.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “International journal of research in dermatology”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “International journal of research in dermatology” Intralesional corticosteroids are the best for limited alopecia areata, oral steroids are less effective, and PRP is safe and promising, especially for children and severe cases.
 48 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
48 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition, treated based on severity, with half of patients regrowing hair within a year without treatment.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
 October 2024 in “International Journal of Medical Arts”
October 2024 in “International Journal of Medical Arts” Corticosteroids regrow hair better and faster than pentoxifylline for alopecia areata.
 September 2003 in “Clinics in Family Practice”
September 2003 in “Clinics in Family Practice” Different hair diseases affect people during childbearing years, with treatments ranging from medication to psychological support.
 September 2024 in “PubMed”
September 2024 in “PubMed” Hair loss can be treated based on its type and cause, improving quality of life.
 November 2023 in “Dermatologica sinica/Zhōnghuá pífūkē yīxué zázhì”
November 2023 in “Dermatologica sinica/Zhōnghuá pífūkē yīxué zázhì” Upadacitinib helped regrow hair in a severe alopecia areata patient but stopping treatment caused hair loss to return.
 74 citations,
March 2001 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
74 citations,
March 2001 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” The document concludes that skin biopsies, genetic and environmental factors, and specific treatments are important in managing cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
48 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical corticosteroids are the best initial treatment for children's alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
October 2023 in “BMC oral health”
1 citations,
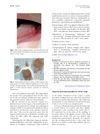
October 2023 in “BMC oral health” Two patients treated with TAC for mouth fibrosis improved but developed Cushing's Syndrome symptoms.
 23 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
23 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Permanent hair loss from cicatricial alopecia is treated by reducing inflammation and managing symptoms, but regrowth in scarred areas is unlikely.
 December 2024 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
December 2024 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Early treatment can help reverse hair loss caused by cosmetic fillers.

A patient with patchy hair loss was successfully treated for Tumid Lupus Erythematosus after other treatments failed.
 23 citations,
October 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
23 citations,
October 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Two transplant patients on cyclosporine unexpectedly developed hair loss.
 13 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
13 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” A rare scalp condition causing hair loss and cysts in young men can be treated effectively with a specific steroid injection.
 2 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology”
2 citations,
March 2019 in “Journal of Dermatology” Trichoscopy helped diagnose and treat a woman with two different types of hair loss.
 26 citations,
June 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
26 citations,
June 2019 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Regenerative therapies show promise for treating vitiligo and alopecia areata.
 December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” A 45-year-old woman with autoimmune diseases experienced patchy hair loss due to alopecia areata, which has no cure but can be treated, with varying success.
28 citations,
May 1998 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Scalp inflammation can cause multiple hairs to grow from one follicle.
 November 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
November 2024 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Early treatment can reverse hair loss from dermal fillers.
37 citations,
November 2011 in “Photodermatology Photoimmunology & Photomedicine” Narrowband UVB phototherapy alone is not very effective for treating alopecia areata.
10 citations,
October 2018 in “Neurology Neuroimmunology & Neuroinflammation” Systemic corticosteroids might help treat hair loss caused by alemtuzumab in MS patients.
November 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine” PRP shows promise for treating mild alopecia areata but needs more research for cicatricial alopecias.
278 citations,
May 2013 in “Ca” Targeted anticancer therapies can cause severe side effects similar to traditional chemotherapy, but with different types.






















