 September 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks”
September 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” CCCA is a common hair loss condition in African American women, often inherited and influenced by hairstyling, with unique scalp features detectable by special tools.
 23 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology”
23 citations,
February 2004 in “Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology” A boy with chromosome 13q deletion syndrome developed eye cancer, a woman with breast cancer lost vision due to a rare side-effect of her treatment, a man's vision worsened after using a hair loss drug, and two rare disorders were discussed. Optical Coherence Tomography is useful for diagnosing and monitoring these conditions.

The document concludes that Syndromes of Severe Insulin Resistance are rare disorders with limited treatment options.
[object Object]  8 citations,
September 2016 in “Pediatric dermatology”
8 citations,
September 2016 in “Pediatric dermatology” People with Mucopolysaccharidoses often have skin problems like thick skin and extra hair, and recognizing these can help diagnose and treat the condition early.
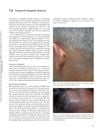 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Temporal triangular alopecia is a lifelong condition with hairless patches on the side of the head that may be present from birth.
 81 citations,
June 2012 in “European journal of human genetics”
81 citations,
June 2012 in “European journal of human genetics” Inherited ichthyoses cause widespread skin scaling and thickening due to gene mutations.
 6 citations,
February 1974 in “The BMJ”
6 citations,
February 1974 in “The BMJ” The document concludes that scalp disorders can be treated with hair washing, specific shampoos, medications, and sometimes surgery or hair transplants, but hereditary baldness is untreatable.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Evolutionary studies”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Evolutionary studies” Different human traits like skin color and hair type vary between populations due to genetic adaptations to the environment.

The document concludes that the girl's hairlessness is likely inherited from her parents.
 6 citations,
May 1993 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood”
6 citations,
May 1993 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood” Children's hair loss can be caused by many factors, including autoimmune diseases, emotional stress, genetics, and infections, with treatment and prognosis varying.
[object Object]  65 citations,
March 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
65 citations,
March 2018 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Skin problems can be caused or worsened by physical forces and pressure on the skin.
 39 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Clinical Investigation”
39 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Clinical Investigation” Hirsutism can be caused by various conditions besides PCOS, and it's important to treat the underlying issue and manage symptoms with medication and cosmetic approaches.
 7 citations,
February 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
7 citations,
February 2021 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Sebaceous glands are involved in various skin disorders, some treatable with medications like finasteride and minoxidil.
 25 citations,
May 2003 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents”
25 citations,
May 2003 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents” Steroid Sulfatase inhibitors show promise in treating hormone-dependent disorders like cancers, hair loss, and acne, with 667COUMATE being a potential candidate for breast cancer treatment trials.
 32 citations,
April 2013 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
32 citations,
April 2013 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” The document concludes that inherited epidermolysis bullosa is a challenging genetic condition requiring multidisciplinary care and new treatments.

Iron supplements may reverse premature graying in iron-deficient individuals; ingrown nails are common in diabetics with certain risk factors; topical finasteride may reduce scalp DHT as effectively as oral finasteride; monilethrix treatment is challenging but some medications can help.
 12 citations,
October 2004 in “Experimental Gerontology”
12 citations,
October 2004 in “Experimental Gerontology” Changes in testosterone and estrogen receptor genes can affect how men age, influencing body fat, hair patterns, and possibly leading to skin disorders.

The chapter explains that there are many genetic skin disorders affecting skin cell formation, including both common and rare types.
 March 2012 in “Pathy's Principles and Practice of Geriatric Medicine”
March 2012 in “Pathy's Principles and Practice of Geriatric Medicine” Older adults often have skin problems due to aging, and treating these conditions requires attention to both physical and mental health.
 1 citations,
January 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2014 in “Elsevier eBooks” Melanocytes produce melanin; their defects cause vitiligo and hair graying, with treatments available for vitiligo.
 100 citations,
September 2017 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology”
100 citations,
September 2017 in “Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology” Male hormones and their receptors play a key role in hair loss and skin health, with potential new treatments being explored.
 30 citations,
June 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
30 citations,
June 2021 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Mutations in the WNT10A gene can cause skin, hair, teeth, and other disorders, and may also affect other areas like kidney and cancer, with potential for targeted treatments.
1 citations,
November 2003 in “Humana Press eBooks” AFM helps study hair surfaces for dermatology, cosmetics, and forensics.
 75 citations,
June 1999 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
75 citations,
June 1999 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” The document concludes that early recognition and treatment of PCOS in adolescents is crucial for managing symptoms and long-term health risks.
 9 citations,
March 2015 in “International reviews of immunology”
9 citations,
March 2015 in “International reviews of immunology” Skin abnormalities can indicate immunodeficiency due to shared origins with the immune system.
151 citations,
June 2010 in “Endocrinology and metabolism clinics of North America” Two rare genetic diseases cause severe rickets in children due to defects in vitamin D metabolism.
 12 citations,
May 2005 in “Current obstetrics and gynaecology/Current obstetrics & gynaecology”
12 citations,
May 2005 in “Current obstetrics and gynaecology/Current obstetrics & gynaecology” Hirsutism is too much hair growth in women like the pattern in men, often caused by high male hormones, and can be treated with hormone control and hair removal methods.
 1 citations,
May 2018 in “Clinical chemistry”
1 citations,
May 2018 in “Clinical chemistry” The girl's unexpected pubic hair growth led to a diagnosis different from complete androgen insensitivity syndrome.
 57 citations,
March 2011 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
57 citations,
March 2011 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Nearly half of children with primary immunodeficiency disorders showed skin problems, often as the first sign of their condition.
 124 citations,
July 2012 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
124 citations,
July 2012 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Targeting androgen receptors could be a promising way to treat skin disorders with fewer side effects.




























