 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that there are various causes and treatments for hair loss, with hair transplantation being a notable option.
 138 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
138 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Hair loss can significantly affect a person's self-esteem and body image, especially in young people, those who value their looks highly, and women.
 64 citations,
November 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
64 citations,
November 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A new type of rapid hair loss called ADTA usually gets better on its own within 6 months.
[object Object] July 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dentistry” A 46-year-old man showed symptoms of a rare condition usually seen in postmenopausal women, highlighting the need for dentist-dermatologist collaboration.
 5 citations,
November 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
5 citations,
November 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan are crucial for managing hair loss in children, with a focus on both medical and psychological support.
 July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” The conclusion is that emotional support and a variety of treatments are important for alopecia areata, but more research is needed.
 42 citations,
July 2015 in “Cosmetics”
42 citations,
July 2015 in “Cosmetics” Nanotechnology improves hair care products by enhancing ingredient stability, targeting treatment, and reducing side effects, but more research on its toxicity is needed.
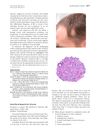
The man has Temporal Triangular Alopecia, a stable, non-scarring hair loss condition best treated with hair transplantation.
 2 citations,
September 2021 in “International Journal of STD & AIDS”
2 citations,
September 2021 in “International Journal of STD & AIDS” People living with HIV in Turkey often have skin conditions, which are more common in advanced HIV stages and may help in diagnosing the infection.
 5 citations,
March 2011 in “Journal of pediatric health care”
5 citations,
March 2011 in “Journal of pediatric health care” The girl with autoimmune hair loss might regrow hair within a year, and treatments can help but not prevent recurrence; dermatologist referral and corticosteroids are recommended.
 May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” The first Japanese family with Marie Unna hereditary hypotrichosis showed hair condition improvement in a child and highlighted the risk of misdiagnosis.
[object Object]  May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Adjusting the medication tacrolimus resolved a boy's red nail beds after a stem cell transplant.
 1 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatology online journal”
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Dermatology online journal” A unique case showed a rare combination of two types of lichen planus on the face.
 December 2023 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
December 2023 in “Clinical Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” An 8-year-old Saudi boy was diagnosed with a rare genetic disorder causing hair loss, skin issues, and light sensitivity.
 2 citations,
January 2022 in “Eduvest”
2 citations,
January 2022 in “Eduvest” A teenage girl with a fungal scalp infection got better with antifungal and allergy medication, and special shampoo.
 July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition caused by immune factors and can be treated with JAK inhibitors.
2 citations,
December 2019 in “The Open Dermatology Journal” Linear Discoid Lupus Erythematosus of the scalp can cause hair loss and should be considered in similar cases.
 December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” A 45-year-old woman with autoimmune diseases experienced patchy hair loss due to alopecia areata, which has no cure but can be treated, with varying success.

COVID-19 may trigger or worsen rapid hair loss in alopecia areata.
 February 2020 in “Scholars international journal of traditional and complementary medicine”
February 2020 in “Scholars international journal of traditional and complementary medicine” Ayurveda treats hair problems like hair loss and dandruff by balancing body elements and using natural remedies like Indian Gooseberry and false Daisy.
 36 citations,
January 2010 in “Human & experimental toxicology”
36 citations,
January 2010 in “Human & experimental toxicology” Eating paradise nuts led to selenium poisoning, causing nausea, hair loss, and other symptoms in two women.
 3 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Nepal Medical Association”
3 citations,
September 2021 in “Journal of Nepal Medical Association” A woman with complete hair loss and severe hyperthyroidism was successfully treated with azathioprine and hydroxychloroquine.
 16 citations,
November 2015 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
16 citations,
November 2015 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia greatly lowers the quality of life for South African Black women, especially affecting their self-image and social interactions.
 December 2015 in “Journal of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis”
December 2015 in “Journal of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis” A patient experienced long-lasting hair loss after using acitretin for psoriasis.
 4 citations,
November 2018 in “JAAD case reports”
4 citations,
November 2018 in “JAAD case reports” Alopecia areata can sometimes appear as a straight line of hair loss instead of round patches.
 4 citations,
April 2020 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
4 citations,
April 2020 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Hair loss in women is complex to diagnose and treat, and hair restoration should be done by experts. Using minoxidil before surgery can help manage post-surgery hair shock loss. The Follicular Unit Transplantation method is recommended for women due to its speed, no need for shaving, and better graft quality. Strategies like L, T, and reverse L patterns can help restore central hair density, and regenerative methods can improve graft survival in hair transplants.
New treatments for alopecia areata, like JAK inhibitors and immunomodulators, are promising.
 April 2023 in “Authorea (Authorea)”
April 2023 in “Authorea (Authorea)” Hair transplantation can improve scars after removing a rare skin cancer.
 April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal”
April 2021 in “Sohag Medical Journal” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss, linked to genetic factors and immune system issues, with no cure yet.
 1 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
1 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Cosmetic foam product reduces hair loss and increases hair density in men.



























