 9 citations,
January 1981 in “Australian journal of biological sciences”
9 citations,
January 1981 in “Australian journal of biological sciences” Lambs fed a liquid diet showed abnormal wool and skin, which improved with more B-vitamins, suggesting a link to B-vitamin deficiency.
[object Object] 37 citations,
February 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Overexpression of SSAT causes hair loss and skin issues, but reducing putrescine can help.
 32 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
32 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Mice without certain skin proteins had abnormal skin and hair development.
January 2021 in “Dermatology online journal” One twin girl has Loose anagen syndrome with poorly anchored hair, diagnosed with a simple hair pull test, while her identical twin does not have the condition.
 24 citations,
September 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
24 citations,
September 1985 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The report suggests a possible link between hair loss and hidden scalp tumors but states more evidence is needed to confirm this.
 1 citations,
August 2019 in “Pediatric dermatology”
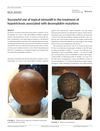
1 citations,
August 2019 in “Pediatric dermatology” Topical minoxidil helped an 8-year-old boy with a genetic hair disorder grow hair.
 13 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
13 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Certain factors like allergies, nail problems, and hair loss patterns can predict how well someone with patchy hair loss will respond to skin cream treatments.
 26 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
26 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” New gene identification techniques have improved the understanding and classification of inherited hair disorders.
54 citations,
September 2012 in “Acta ophthalmologica” Cancer treatments can cause various eye problems, so eye doctors should know how to diagnose and treat these early.
 1 citations,
June 2023 in “Curēus”
1 citations,
June 2023 in “Curēus” PCOS affects nearly 25% of female medical and dental students, impacting their academic and social lives.
163 citations,
October 2001 in “EMBO journal” Overexpressing follistatin in mice delays wound healing and reduces scar size.
16 citations,
September 1990 in “Fertility and sterility” Ketoconazole can treat ovarian hyperandrogenism but should be used cautiously with monitoring and birth control.
 July 2024 in “Medical alphabet”
July 2024 in “Medical alphabet” JAK inhibitors like tofacitinib may effectively treat alopecia in children without major side effects.
 June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
June 2023 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” A girl with Becker naevus syndrome has a genetic variant in the ACTB gene related to her symptoms.
 December 2005 in “Endocrine-related cancer”
December 2005 in “Endocrine-related cancer” A woman's adrenal tumor disappeared after treatment with cyproterone acetate.
 December 2023 in “American journal of medical genetics. Part A”
December 2023 in “American journal of medical genetics. Part A” A new syndrome was linked to two new genetic changes in the MBTPS1 gene in a 14-year-old girl.
April 2019 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” A woman's severe insulin resistance improved with treatment, but she still had high testosterone levels due to ovarian issues.

Eating healthy, exercising, and certain nutrients like myoinositol and omega-3s can help manage PCOS symptoms.
188 citations,
June 1998 in “Molecular cell” Researchers created a mouse with the same mutation as humans with trichothiodystrophy, showing similar symptoms and confirming the condition is due to defects in DNA repair and gene activity.
January 2024 in “Veterinary Science and Medicine Journal” The Pomeranian recovered well after treatment for pneumonia and demodecosis.
 August 2024 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
August 2024 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Androgenetic alopecia may be linked to metabolic syndrome.
[object Object]  January 2014 in “European Geriatric Medicine”
January 2014 in “European Geriatric Medicine” A postmenopausal woman's virilization was caused by a rare ovarian tumor that was hard to detect but was successfully treated with surgery.
 32 citations,
June 2003 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
32 citations,
June 2003 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Lipedematous scalp is mainly caused by an increase in fat tissue under the skin and is different from lipedematous alopecia.
 32 citations,
April 1994 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
32 citations,
April 1994 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” High androgen levels and genetic factors likely cause Becker's nevus and related symptoms.
 1540 citations,
October 2008 in “Fertility and Sterility”
1540 citations,
October 2008 in “Fertility and Sterility” The report concludes that PCOS is mainly a condition of excess male hormones and its definition may change as new information is discovered.
 21 citations,
September 2018 in “International journal of women’s dermatology”
21 citations,
September 2018 in “International journal of women’s dermatology” People with Lichen planopilaris are more likely to have certain autoimmune and endocrine disorders but less likely to have conditions like allergies and diabetes.
 2 citations,
May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine”
2 citations,
May 2006 in “Women's Health Medicine” Ovulation disorders are a major cause of infertility and menstrual problems in women.
 81 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
81 citations,
December 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Fat tissue stem cells may help increase hair growth.
 57 citations,
November 1987 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
57 citations,
November 1987 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Children's hair grows in different types from before birth through puberty, with growth rates and characteristics varying by age, sex, and race.
 209 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
209 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Androgens can both increase and decrease hair growth in different parts of the body.






















