 211 citations,
April 2018 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology”
211 citations,
April 2018 in “Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology” Keratins are crucial for cell structure, growth, and disease risk.
 31 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms”
31 citations,
May 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today: Disease Mechanisms” Different hair growth problems are caused by genetic issues or changes in hair growth cycles, and new treatments are being developed.
 2 citations,
March 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
2 citations,
March 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Hairless mammals have genetic changes in both their protein-coding and regulatory sequences related to hair.
 41 citations,
November 2011 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
41 citations,
November 2011 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Some hair loss disorders are caused by genetic mutations affecting hair growth.
26 citations,
September 2005 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair shape is determined by genetic, molecular, and cellular factors.
5 citations,
September 2018 in “International journal of genomics” Genetic mutations that disrupt homocysteine breakdown lead to increased damage in mouse hair keratin.
44 citations,
February 2023 in “Cell” Fingerprints form uniquely before birth due to specific genetic pathways and local signals.
 28 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of structural biology”
28 citations,
November 2018 in “Journal of structural biology” Different populations have distinct hair structures related to their ancestry.
 21 citations,
January 2005 in “Skinmed”
21 citations,
January 2005 in “Skinmed” Hair and nails are similar keratin structures with different shapes and growth, affected by the same diseases and environmental factors.
17 citations,
May 2012 in “Journal of biological chemistry/The Journal of biological chemistry” Hairless protein affects hair follicle structure by regulating the Dlx3 gene.
 1 citations,
June 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
June 2021 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Activating β-catenin in mammary cells leads to changes that cause early-stage abnormal growths similar to skin structures.
1 citations,
June 2016 in “Medicina” Monilethrix is a genetic disorder causing brittle hair, diagnosed using tricoscopy.
23 citations,
February 2015 in “The American journal of pathology” Keratosis pilaris is often linked to genetic mutations and causes skin and hair abnormalities, regardless of those mutations.
 September 2022 in “Annals of medicine and surgery”
September 2022 in “Annals of medicine and surgery” Three siblings with a rare genetic condition had abnormal sexual development and chose different gender identities, needing surgery and therapy.
4 citations,
June 2023 in “Journal of developmental biology” The skin systems of jawed vertebrates evolved diverse appendages like hair and scales from a common structure over 420 million years ago.
 10 citations,
October 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
10 citations,
October 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” Nail stem cells and Wnt signaling are important for fingertip regeneration but not sufficient for regenerating more complex limb structures.
 5 citations,
January 2015 in “Current Topics in Developmental Biology”
5 citations,
January 2015 in “Current Topics in Developmental Biology” Fish teeth and taste bud densities are linked and can change between types due to shared genetic and molecular factors.
 January 2014 in “Pathology”
January 2014 in “Pathology” The document concludes that understanding nail anatomy is key for diagnosing nail diseases, early signs of nail melanoma may allow for less aggressive treatment, and specific genetic mutations are important in thyroid cancer prognosis and treatment.
854 citations,
February 2002 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Understanding hair follicle development can help treat hair loss, skin regeneration, and certain skin cancers.
166 citations,
November 2008 in “Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism” Biotin and biotinidase are essential to prevent health issues, and deficiencies require lifelong supplementation.
116 citations,
January 1957 in “Australian Journal of Agricultural Research” Certain hair follicle traits in Merino sheep may be inherited.
30 citations,
October 2010 in “Biochemical and biophysical research communications” The Gsdma3 gene is essential for normal hair development in mice.
 9 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
9 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Scientists have found specific genes linked to different hair loss conditions, which could lead to new treatments.
 7 citations,
November 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
7 citations,
November 2000 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Most hair loss in children is caused by a few common conditions and is easy to diagnose, but rare types require careful evaluation.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Evolutionary studies”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Evolutionary studies” Different human traits like skin color and hair type vary between populations due to genetic adaptations to the environment.
 March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Hair disease research is a growing and evolving field in dermatology, with recent significant advances.
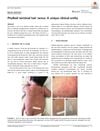 August 2018 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A baby had a unique skin condition with a pale patch and surrounding dark hairs, not linked to other health issues.
 February 2024 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
February 2024 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Tandem repeats significantly influence hair color, especially darker shades, across different ancestries.
December 2022 in “Aesthetic Cosmetology and Medicine” Proper treatments can greatly improve hair and scalp health in men with androgenetic alopecia.
 277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association”
277 citations,
July 2011 in “Journal of the Dermatology Nurses’ Association” The skin's layers protect, sense, and regulate the body's internal balance, but can be prone to cancer.


















