 January 2025 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
January 2025 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a challenging hair loss condition with no known cause or definitive treatment.
 May 2022 in “European medical journal”
May 2022 in “European medical journal” An 11-year-old girl with a hair-pulling disorder had a hairball in her stomach and was treated with medication, therapy, and a team of doctors.
 12 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology”
12 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Infrared thermography, especially with dermoscopy, improves accuracy in diagnosing active hair loss due to inflammation.
 3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” AGA is a genetic, hormonal hair loss treated with finasteride, minoxidil, and supplements, but new compounds are being developed.
 1 citations,
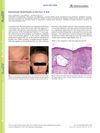
January 2019 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
1 citations,
January 2019 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” The woman's skin and hair symptoms were confirmed as frontal fibrosing alopecia, and while facial papules are common in such cases, there's no effective local treatment, but systemic treatments can help.
 January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” A woman's hair loss was linked to a rare hormone-secreting ovarian tumor, treated with surgery and hair loss medication.
 234 citations,
December 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
234 citations,
December 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Middle-aged women with chronic telogen effluvium experience increased hair shedding but usually don't get significantly thinner hair.
 12 citations,
October 2016 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
12 citations,
October 2016 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia may be linked to autoimmune diseases like Sjögren's syndrome.

Low-dose oral isotretinoin improved hair loss and facial bumps in patients with a specific type of hair loss.
 103 citations,
June 2007 in “Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America”
103 citations,
June 2007 in “Endocrinology and Metabolism Clinics of North America” Male pattern hair loss is genetic and influenced by hormones, with treatments like minoxidil and surgery available.
 75 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
75 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Chronic Telogen Effluvium is a hair loss condition in middle-aged women that usually doesn't lead to complete baldness.
 54 citations,
January 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
54 citations,
January 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Most patients with chronic hair shedding did not progress to permanent hair loss, and one showed improvement with treatment.
 43 citations,
November 1992 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
43 citations,
November 1992 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil 2% effectively treats female hair loss, promoting growth and density.
 40 citations,
June 2009 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
40 citations,
June 2009 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” AGA patients have fewer hairs and smaller follicles; T:V ratio above 4:1 may indicate AGA.
 16 citations,
January 2007 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas”
16 citations,
January 2007 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” The document concludes that there are no reliable treatments for frontal fibrosing alopecia, with only temporary benefits from current options.
 11 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
11 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” The conclusion is that treatments like finasteride and minoxidil can prevent baldness progression and improve hair density, but more research is needed on other therapies.
 9 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
9 citations,
October 1988 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Hair loss is caused by genetics and hormones, diagnosed through examination and biopsy, and treated with medications or surgery.
 6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
6 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Different hair loss types need accurate diagnosis for proper treatment.
 3 citations,
December 2020 in “Journal of the turkish academy of dermatology”
3 citations,
December 2020 in “Journal of the turkish academy of dermatology” Stromal Vascular Fraction treatment increases hair density and thickness, making it a safe and effective treatment for Androgenetic Alopecia.
 1 citations,
May 2014 in “European Journal of Inflammation”
1 citations,
May 2014 in “European Journal of Inflammation” A lotion with minoxidil, hydrocortisone butyrate, and 17a-estradiol can improve or stabilize Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia in some cases, but there's no universally-accepted treatment yet.
 1 citations,
January 2008 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
1 citations,
January 2008 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Treat hair loss in postmenopausal women with diet, avoiding certain drugs, and using medications like minoxidil or finasteride.
 125 citations,
May 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
125 citations,
May 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The BASP classification is a detailed and accurate way to categorize hair loss in both men and women.
 74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Minoxidil and finasteride are effective for male hair loss, minoxidil for female hair loss, and various treatments like corticosteroids work for alopecia areata; treatment should be tailored to the individual.
 66 citations,
April 2002 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
66 citations,
April 2002 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Finasteride increases hair weight and count in men with hair loss.
 57 citations,
October 2013 in “international journal of endocrinology and metabolism”
57 citations,
October 2013 in “international journal of endocrinology and metabolism” Female pattern hair loss is common, linked to polycystic ovarian syndrome, and treated with topical Minoxidil.
 49 citations,
August 2003 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
49 citations,
August 2003 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Higher IGF-1 levels in hair follicles link to better finasteride results for hair loss.
 33 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
33 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Familial frontal fibrosing alopecia affects premenopausal women too, and early diagnosis is important, but no proven medication exists yet.
 22 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss from genetics and hormones can be treated with drugs or surgery.
 14 citations,
August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
14 citations,
August 2019 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” 10% minoxidil solution better promotes hair growth and reduces hair loss without significant side effects.
 9 citations,
January 2001 in “Dermatology”
9 citations,
January 2001 in “Dermatology” Pili anulati may cause hair loss, proper diagnosis and treatment needed.






























