
Researchers found a genetic link for hereditary hair loss but need more analysis to identify the exact gene.
86 citations,
November 2020 in “Annals of Oncology” Early intervention and tailored management can reduce skin side effects from cancer treatments.
 April 2016 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Dermoscopy helped correctly diagnose a skin condition that was previously misidentified as a different hair loss disease.
 January 1982 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 1982 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Experts discussed treatments for skin conditions in children, emphasizing hydration, cautious medication use, and early intervention for infections.
 108 citations,
November 1980 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
108 citations,
November 1980 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Oral retinoids are effective for various skin conditions but have side effects and should not be used during pregnancy.
 68 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
68 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The conclusion is that Fgf18 and Tgf-ß signaling could be targeted for hair loss treatments.
 59 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
59 citations,
June 2008 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The article explains the genetic causes and symptoms of various hair disorders and highlights the need for more research to find treatments.
 31 citations,
January 1981 in “Pharmacology & Therapeutics”
31 citations,
January 1981 in “Pharmacology & Therapeutics” Oral retinoids are effective for treating severe skin disorders but have reversible side effects and risks for pregnant women.
 2 citations,
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Segmental Vitiligo is a stable, early-onset form of vitiligo that responds well to early treatment and is ideal for repigmentation studies.

Tailored nonsurgical cosmetic procedures are crucial for safely treating diverse skin types, especially skin of color.
 5 citations,
July 2022 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases”
5 citations,
July 2022 in “Orphanet journal of rare diseases” RSPO1 mutations in certain patients lead to skin cells that don't develop properly and are more likely to become invasive, increasing the risk of skin cancer.
1 citations,
November 2013 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” Experts met to improve care for ichthyosis patients in Spain.
 3 citations,
June 2022 in “European journal of human genetics”
3 citations,
June 2022 in “European journal of human genetics” A new type of pachyonychia congenita linked to a specific keratin gene mutation was found in two Pakistani families.
 52 citations,
June 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
52 citations,
June 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Oral retinoids are effective for severe skin conditions but require careful use due to side effects.
 23 citations,
November 2001 in “Archives of Dermatology”
23 citations,
November 2001 in “Archives of Dermatology” Genetic discoveries are key for understanding, diagnosing, and treating inherited hair and nail disorders.
 11 citations,
March 2020 in “American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A”
11 citations,
March 2020 in “American Journal of Medical Genetics Part A” A mutation in the EDNRA gene causes Oro-Oto-Cardiac syndrome, affecting face and heart development.
 1 citations,
June 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
1 citations,
June 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Covers common skin issues in kids, their diagnosis, treatment, and need for specialist care.

The chapter explains that there are many genetic skin disorders affecting skin cell formation, including both common and rare types.
53 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of toxicologic pathology” The project created a standardized system for classifying skin lesions in lab rats and mice.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Current Dermatology Reports”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Current Dermatology Reports” Early baldness in men may indicate risks for obesity, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and heart disease, similar to women with PCOS. Alopecia areata is often linked with autoimmune diseases and mental health issues. Certain hair disorders are due to genetic issues, and chemotherapy can cause hair loss through specific biological pathways. Iron deficiency's link to hair loss is still disputed.
 2 citations,
March 2015 in “Hepatitis Monthly”
2 citations,
March 2015 in “Hepatitis Monthly” A woman's hair loss during Hepatitis C treatment with PEG-INF-a-2a and Ribavirin was reversible after stopping the medication.
 1 citations,
January 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
1 citations,
January 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” The combination therapy of PEG-IFN α-2a and Ribavirin can cause widespread hair loss and skin reactions.
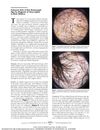 108 citations,
March 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
108 citations,
March 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Corkscrew hair may be a new sign for quickly diagnosing scalp fungus in black children.
 106 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
106 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document concludes that assessing hair follicle damage due to cyclophosphamide in mice involves analyzing structural changes and suggests a scoring system for standardized evaluation.
 80 citations,
March 2004 in “Neuropediatrics”
80 citations,
March 2004 in “Neuropediatrics” Coats' Plus is a genetic disorder with eye abnormalities, brain calcification, poor growth, bone and skin issues, and movement disorders.
71 citations,
January 1998 in “Pathobiology” The document concludes that certain rats and mice are useful for studying hair loss in humans and testing treatments.
48 citations,
February 1998 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Thallium poisoning can cause severe neurological symptoms and hair loss.
45 citations,
July 2006 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Chemotherapy affects blood vessels in hair follicles, not stem cells, allowing hair regrowth.
 36 citations,
April 1994 in “PubMed”
36 citations,
April 1994 in “PubMed” Cyclosporine A slows down hair loss from chemotherapy in mice, while dexamethasone increases hair loss but speeds up regrowth.
31 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Trichoscopy effectively diagnoses eyebrow loss, distinguishing between alopecia areata and frontal fibrosing alopecia.























