 2 citations,
September 2020
2 citations,
September 2020 Long-term high testosterone levels can improve bone density and reduce body fat but may increase the risk of prostate cancer and high blood pressure.
2 citations,
October 2018 in “Skin appendage disorders” A boy's hair that was frizzy and hard to comb returned to normal after 9 months, possibly due to genetic factors.
 September 2021 in “Physiology News”
September 2021 in “Physiology News” Increasing research diversity is key for better understanding and treating Parkinson's Disease.

Increased free testosterone can lead to stronger bones and less body fat but also higher risks of prostate cancer, hair loss, spine issues, and high blood pressure.
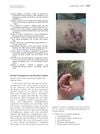
A 72-year-old man was diagnosed with a rare skin form of Rosai-Dorfman disease after years of misdiagnosis.
 87 citations,
May 2012 in “PLOS Genetics”
87 citations,
May 2012 in “PLOS Genetics” Six new genetic regions linked to early hair loss also connect to Parkinson's disease and prostate cancer, possibly leading to new treatments.
 6 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of pediatric endocrinology & metabolism/Journal of pediatric endocrinology and metabolism”
6 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of pediatric endocrinology & metabolism/Journal of pediatric endocrinology and metabolism” Three siblings with a genetic form of rickets showed different symptoms of the disease.
 June 2022 in “Indian journal of clinical and experimental opthalmology”
June 2022 in “Indian journal of clinical and experimental opthalmology” The report shows a young man with Hutchinson-Gilford Progeria Syndrome had typical and additional eye problems related to the disease.
 36 citations,
July 2014 in “Neuromuscular Disorders”
36 citations,
July 2014 in “Neuromuscular Disorders” A patient with a larger than usual genetic mutation had a broader range of symptoms for a muscle disease.
 2 citations,
September 2004 in “Fertility and sterility”
2 citations,
September 2004 in “Fertility and sterility” High androgen levels can cause excessive hair growth and may indicate serious health issues, including heart disease and fertility problems.
June 2020 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The symposium highlighted the importance of genetics in understanding and treating complex skin diseases.
 November 2018 in “International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Research”
November 2018 in “International Journal of Current Pharmaceutical Research” PCOS is a hormonal disorder causing symptoms like irregular periods and acne, and increases the risk of diabetes and heart disease.
 June 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
June 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Japanese researchers created new hair follicles from human cells that grew hair when put into mice, and other findings showed a link between eye disease severity and corneal thickness, gene mutations affecting hearing and touch, and the safety of the shingles vaccine for adults over 50.
 13 citations,
December 2006 in “Journal of experimental animal science”
13 citations,
December 2006 in “Journal of experimental animal science” Interferon gamma alone can't cause alopecia areata in C3H/HeJ mice.
 8 citations,
September 2017 in “The Journal for Nurse Practitioners”
8 citations,
September 2017 in “The Journal for Nurse Practitioners” Most women with PCOS use positive coping strategies, but some with more psychological stress use negative ones.
 1 citations,
March 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
1 citations,
March 2022 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” Low-coverage sequencing is a cost-effective way to identify genes related to wool traits in rabbits.
 January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that managing PCOS involves lifestyle changes, medication, and monitoring for associated health risks.
 January 1982 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
January 1982 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Experts discussed treatments for skin conditions in children, emphasizing hydration, cautious medication use, and early intervention for infections.
 421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss with no cure and treatments that often don't work well.
 391 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
391 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Half of people with Alopecia Areata may see hair regrowth within a year without treatment, but recovery is unpredictable.
 86 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
86 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” FPHL is a common, age-related, genetic hair loss with unclear causes and limited treatment options.
 82 citations,
March 2016 in “Autoimmunity reviews”
82 citations,
March 2016 in “Autoimmunity reviews” Animal models have helped understand hair loss from alopecia areata and find new treatments.
 74 citations,
March 1963 in “Archives of Dermatology”
74 citations,
March 1963 in “Archives of Dermatology” Triparanol therapy can cause hair loss and skin dryness without inflammation or damage to hair follicles or skin structures.
 67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy”
67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy” Hirsutism is excessive hair growth in women often caused by polycystic ovarian syndrome, and identifying the cause is important for managing associated health risks.
 47 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
47 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Premature graying of hair may suggest health issues and currently lacks effective treatments.
 30 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
30 citations,
May 2004 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for children with hair loss to prevent permanent damage, although not all conditions can be effectively treated.
 24 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
24 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that eyelash trichomegaly, which is the abnormal growth of eyelashes, can be present from birth, caused by diseases, or result from certain medications.
 7 citations,
February 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
February 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Gray hair is caused by reduced melanin production or transfer issues, linked to aging and possibly health conditions, with treatments focusing on color camouflage.
 6 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of International Medical Research”
6 citations,
March 2020 in “Journal of International Medical Research” Early hair loss common in Chinese males, linked to family history and smoking; early treatment advised.
 2 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
2 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Almost 40% of Greek women with acne show signs of androgen-related disorders, with adult women more likely affected.



























