Decades of Progressive Red and Yellow Nodules
November 2011
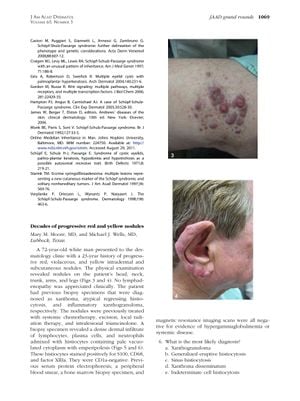
TLDR A 72-year-old man was diagnosed with a rare skin form of Rosai-Dorfman disease after years of misdiagnosis.
A 72-year-old white man with a 23-year history of progressive red, violaceous, and yellow intradermal and subcutaneous nodules was diagnosed with Sinus histiocytosis or Rosai-Dorfman (RD) disease, a benign, non-Langerhans cell histiocytosis. The nodules, located on various parts of his body, were previously misdiagnosed and treated with chemotherapy, excision, radiation therapy, and intralesional triamcinolone. Biopsy revealed a dense dermal infiltrate of lymphocytes, plasma cells, and neutrophils, with histiocytes staining positive for S100, CD68, and factor XIIIa, but negative for CD1a. Systemic disease was ruled out through various tests. RD typically presents with massive cervical lymphadenopathy and extranodal manifestations, often affecting younger males, but purely cutaneous RD is rarer and presents differently. Diagnosis relies on clinical presentation and ruling out systemic disease. Histologically, RD cells exhibit emperipolesis and stain positive for S100. Treatment can include surgical excision, radiotherapy, intralesional corticosteroids, cryotherapy, and thalidomide for extensive disease. However, observation may be appropriate as cutaneous RD can spontaneously resolve. The recommended answers for the case questions are: 6, c; 7, a; 8, e; 9, e.





