 666 citations,
September 1977 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
666 citations,
September 1977 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Common baldness, also known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is caused by a combination of genetic factors and hormones called androgens.
 9 citations,
December 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
December 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that early diagnosis is key for treating common baldness in women, but reassurance is often the best approach as hair thinning can be a normal part of aging.
 6 citations,
March 1991 in “PubMed”
6 citations,
March 1991 in “PubMed” The document talks about common baldness, its features, and potential treatments.
 2 citations,
July 1999 in “International Journal of Clinical Practice”
2 citations,
July 1999 in “International Journal of Clinical Practice” Common baldness treatments include cosmetic methods, medication like minoxidil, and surgery, but no cure exists.
 1 citations,
February 2004 in “Medical Hypotheses”
1 citations,
February 2004 in “Medical Hypotheses” Certain cultural hair practices might cause baldness by affecting natural hair oils and stem cell delivery to hair follicles.
Topical minoxidil can help regrow hair in people with common baldness.
 43 citations,
July 1984 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
43 citations,
July 1984 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Antiandrogen therapy helped increase hair growth in women with hormonal imbalances related to baldness.
 January 1998 in “KAGAKU TO SEIBUTSU”
January 1998 in “KAGAKU TO SEIBUTSU” The document suggests that male hormones likely affect hair growth and baldness, and future treatments might involve stem cells and androgen-independent cells.
 November 1983 in “American Biology Teacher”
November 1983 in “American Biology Teacher” Pattern baldness is likely caused by a dominant gene influenced by testosterone levels, making it more common in men.
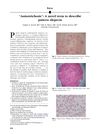 25 citations,
April 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
25 citations,
April 2007 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document suggests "anisotrichosis" as a new term for hair thickness variation in common baldness.
 June 2023 in “Brazilian Journal of Health Review”
June 2023 in “Brazilian Journal of Health Review” Common baldness is a hereditary condition that can be treated with medications or surgery to prevent progression and improve self-esteem.

The herbal mixture Xiantene may help treat common baldness, and men who grey early tend to be less bald but more grey.
 January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks”
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks” Androgenetic alopecia, or common baldness, is the main cause of hair loss in men due to shrinking hair follicles from hormones, and it's normal but can be a problem if it's too much or too early.
 126 citations,
January 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
126 citations,
January 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Baldness is more common in Chinese men than women, increasing with age, and is influenced by genetics.
 34 citations,
April 2009 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
34 citations,
April 2009 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” Some treatments work for common baldness, but there's less evidence for other hair loss types, and more research is needed.
 1 citations,
September 2016 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
1 citations,
September 2016 in “Dermatologic Surgery” New hair loss subtype found, mimics common baldness.
 40 citations,
July 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today”
40 citations,
July 2008 in “Drug Discovery Today” Current treatments for male pattern baldness include minoxidil and finasteride, with new options being developed.
 4 citations,
May 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
4 citations,
May 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Cicatricial pattern hair loss is likely advanced common baldness, not a type of lichen planopilaris.
 1 citations,
February 1988 in “The BMJ”
1 citations,
February 1988 in “The BMJ” The document explains different hair and scalp conditions, including common hair loss after pregnancy or illness, drug-induced hair loss, hereditary excessive hair growth, patterned baldness, autoimmune hair loss, and permanent loss due to skin disease, with generally limited treatment options.
 31 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
31 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some breast cancer patients developed permanent hair loss after chemotherapy and hormonal therapy, showing patterns similar to common baldness and alopecia areata.
 8 citations,
June 2019 in “Scientific Reports”
8 citations,
June 2019 in “Scientific Reports” Increased PPARGC1α relates to hair thinning in common baldness.
 June 2023 in “Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)”
June 2023 in “Zenodo (CERN European Organization for Nuclear Research)” Inflammation in hair follicles is a key risk factor for developing common baldness.
 38 citations,
February 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
38 citations,
February 2012 in “British Journal of Dermatology” AR/EDA2R gene linked to early-onset female hair loss, but 20p11 gene not involved.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “ARC journal of dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “ARC journal of dermatology” Ahmad's NPRT system accurately documents and predicts male pattern baldness.
 June 2012 in “Nature digest”
June 2012 in “Nature digest” A substance called prostaglandin D2 is linked to stopping hair growth in men with common baldness.

Nepenthes kampotiana extract can potentially prevent hair loss and could be an effective treatment for common baldness.
 November 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks”
November 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” Fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution is a new type of scarring hair loss that resembles common baldness and an autoimmune skin disease.
 May 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
May 2015 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Melanoma risk tools need improvement, a gene mutation causes a hair disorder that might be treated by managing cell stress, a potential therapy for a skin-ear disorder involves blocking cell channels, skin wrinkling may indicate lung aging regardless of smoking, and oxidative stress might contribute to common baldness.
 13 citations,
January 1988 in “Contact Dermatitis”
13 citations,
January 1988 in “Contact Dermatitis” Some patients using Minoxidil for baldness developed allergic skin reactions.
 7 citations,
June 1967 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
7 citations,
June 1967 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Plucking hairs in a certain way can result in intact hair roots, not related to baldness.





























