 81 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of the National Cancer Institute”
81 citations,
November 2012 in “Journal of the National Cancer Institute” The tumor suppressor gene FLCN affects mitochondrial function and energy use in cells.
[object Object]  77 citations,
December 2010 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
77 citations,
December 2010 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Human skin cells produce proenkephalin, which changes with environmental factors and skin diseases.
 September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Some aggressive scalp cancers are hard to treat and can be deadly, even when removed with specialized surgery.
 18 citations,
September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
18 citations,
September 2006 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Aggressive scalp squamous cell carcinomas have a high death rate and need early, strong treatment.

Inhibiting AP-1 changes skin tumor types and affects tumor cell identity.
Ribonucleotide excision repair is crucial to prevent skin cancer.
 4 citations,
January 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
4 citations,
January 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Scalp basal cell carcinoma may be more aggressive and harder to treat than other types, requiring special attention and further research.
 1540 citations,
October 2008 in “Fertility and Sterility”
1540 citations,
October 2008 in “Fertility and Sterility” The report concludes that PCOS is mainly a condition of excess male hormones and its definition may change as new information is discovered.
 54 citations,
September 2005 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
54 citations,
September 2005 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Dermatologists are more accurate than general practitioners in diagnosing skin conditions, especially skin cancer.
 42 citations,
October 2004 in “Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes”
42 citations,
October 2004 in “Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes” The main cause of excessive hair growth in Turkish women is Polycystic ovary syndrome, but in about one fifth of cases, the reason for high male hormone levels is unknown.
 25 citations,
July 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
25 citations,
July 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Imiquimod cream activates hair follicle stem cells and causes early hair growth by changing immune cells and certain protein expressions.
12 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of clinical biochemistry and nutrition” Deferasirox combined with sorafenib reduces liver cancer risk and lessens treatment side effects.
 March 1965 in “Hospital Topics”
March 1965 in “Hospital Topics” Chemotherapy provides symptom relief and extends life in 30-50% of gynecological cancer cases, but has only cured choriocarcinoma.
 60 citations,
February 2013 in “Cell reports”
60 citations,
February 2013 in “Cell reports” The balance between androgen receptor and p53 is crucial for sebaceous gland differentiation.
1 citations,
January 2022 in “Clinical dermatology review” A young man's cheek papule was identified as a benign hair follicle tumor using a skin surface microscope.
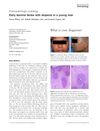 3 citations,
April 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
April 2016 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A young man was diagnosed with trichoepitheliomas, causing thick skin and hair loss.
 3 citations,
July 1996 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
3 citations,
July 1996 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Cytokines are important for immune responses and treating diseases, but they can cause side effects like fever and skin issues.
 25 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of drugs in dermatology”
25 citations,
January 2021 in “Journal of drugs in dermatology” Sonidegib and vismodegib are similarly effective for advanced basal cell carcinoma, but sonidegib might have a slightly better safety profile.
 October 2020 in “Veterinary Dermatology”
October 2020 in “Veterinary Dermatology” New treatments and diagnostic methods for various animal skin conditions showed promising results.
 July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” The document concludes that careful history and physical exams are crucial for accurately diagnosing polycystic ovary syndrome and distinguishing it from other similar conditions.
 15 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of clinical medicine”
15 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of clinical medicine” Biologic treatments for Crohn's disease and ulcerative colitis can cause skin problems, and doctors should adjust treatment if these occur.
 6 citations,
July 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
6 citations,
July 2011 in “British Journal of Dermatology” A man with KID syndrome developed a rare cancer in a long-term skin infection.
 April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Male pattern baldness is linked to a higher risk of certain skin cancers, especially on the scalp.
[object Object]  1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” UV photography can help identify people at higher risk for skin cancer, and male pattern baldness at age 45 is linked to a higher risk of certain skin cancers.
 20 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of skin cancer”
20 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of skin cancer” Most people with basal cell carcinoma on their head or neck were 60-70 years old, and it often came back even after being fully removed, especially in certain areas and types.
 7 citations,
December 2011 in “Elsevier eBooks”
7 citations,
December 2011 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing skin diseases in ferrets.
 22 citations,
April 1998 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
22 citations,
April 1998 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Interferons are effective for some skin conditions and cancers, but can have side effects and need more research for optimal use.
 2 citations,
May 2012 in “Annals of Oncology”
2 citations,
May 2012 in “Annals of Oncology” Patients with advanced breast cancer and high hormone receptor levels who had surgery for ovarian/pelvic metastases lived longer, especially if they had high estrogen receptor levels.
 35 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes”
35 citations,
March 2012 in “Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes” The conclusion is that accurately identifying the cause of high androgen levels in women with PCOS is crucial and requires specific tests.
224 citations,
February 2013 in “The Journal of clinical investigation/The journal of clinical investigation” ERG increases SOX9, promoting prostate cancer growth and invasion.


























