 2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2014 in “Springer eBooks” The book details skin conditions in older adults, their link to mental health, cancer treatment importance, hair loss remedies, and managing autoimmune and itchy skin.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Pigmentary Disorders”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Pigmentary Disorders” Melasma is a skin condition linked to female hormones, genetics, UV exposure, and certain medications, but not to pituitary, adrenal, or thyroid diseases.
 March 2016 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
March 2016 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” The April 2016 JEADV issue covered various dermatology topics, including psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, mTOR inhibitors, autoimmune diseases, photodynamic therapy, viral DNA in skin diseases, chronic hand eczema, and female hair loss.
 June 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
June 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Herpes gestationis is linked to certain antigens, atopic eczema affects T cell populations and may be eased by breastfeeding, higher doses of anti-androgen treatment can improve androgenic alopecia, topical minoxidil increases hair thickness, long-term methotrexate therapy can cause liver fibrosis in psoriasis patients, and Lichen Sclerosus et Atrophicus patients aren't at higher risk for autoimmune disorders.
8 citations,
January 2013 in “International journal of trichology” Two people had unusual ring-shaped hair loss due to an autoimmune disorder.
 May 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Graves' disease can cause hair loss in children and should be considered when treating pediatric alopecia areata.
 144 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
144 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Telogen effluvium is a common type of hair loss that can resolve on its own or become chronic, with treatment depending on early diagnosis.
143 citations,
January 2004 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease causing hair loss, treatable with immune-modulating drugs, and linked to genetics.
 35 citations,
January 2002 in “Dermatology”
35 citations,
January 2002 in “Dermatology” A woman's hair loss during treatment with specific hepatitis C drugs grew back after stopping the medication.
 34 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
34 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” People with pemphigus are more likely to have conditions like hypothyroidism, inflammatory bowel disease, and diabetes.
 23 citations,
July 2021 in “Advances in Therapy”
23 citations,
July 2021 in “Advances in Therapy” Most people with Alopecia Areata don't get treatment within a year; it's costly and often comes with other health issues.
 15 citations,
August 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
15 citations,
August 2019 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) may help treat hair loss in patients with frontal fibrosing alopecia who don't respond to other treatments.
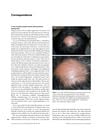 11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
11 citations,
July 2008 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Greying hairs may be protected from alopecia areata.
 3 citations,
March 2021 in “JAAD case reports”
3 citations,
March 2021 in “JAAD case reports” Switching from adalimumab to ixekizumab improved a patient's psoriasis and reversed hair whitening.
 3 citations,
November 2020 in “Curēus”
3 citations,
November 2020 in “Curēus” A child's hair loss from alopecia areata was fully reversed in five months using diet and supplements.
 3 citations,
October 1982 in “Postgraduate Medicine”
3 citations,
October 1982 in “Postgraduate Medicine” Most types of hair loss can regrow naturally, but there are no effective cures for male pattern or age-related hair loss, and only limited options for females.
 1 citations,
August 2021 in “Movement disorders clinical practice”
1 citations,
August 2021 in “Movement disorders clinical practice” A man with Isaac's syndrome affecting only one side of his body improved after immune system-targeted treatment.
 March 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
March 2024 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Tofacitinib successfully treated vitiligo in a patient with lupus without side effects.
 June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy”
June 2023 in “Dermatology and therapy” Doctors in the Middle East need better treatments and more knowledge about new therapies for hair loss condition Alopecia Areata.

Screening for iron levels in patients with hair loss may help find a genetic iron overload condition early.
 February 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences”
February 2021 in “Journal of pharmaceutical and biological sciences” No cure exists for alopecia areata, and treatments are personalized.
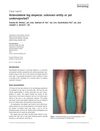 September 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
September 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Anterolateral leg alopecia is a benign, nonprogressive hair loss condition on the lower legs that is not well understood and may resolve on its own.

Some vaccines, like the hepatitis B vaccine, might be linked to the hair loss condition Alopecia Areata, but more research is needed.
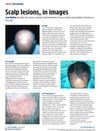 January 2015 in “Independent Nurse”
January 2015 in “Independent Nurse” Different scalp conditions can lead to hair loss or tumors, with treatments varying from creams to surgery; early detection is crucial.
 January 2013 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
January 2013 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hair disorders need a holistic approach, including medical, cosmetic, and psychological support.
 January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks” Hair transplantation is a treatment for hair loss mainly caused by genetics, with various techniques and potential complications, and results visible after 8-12 months.
 January 2003 in “Steinkopff eBooks”
January 2003 in “Steinkopff eBooks” Alopecia Areata is a hair loss condition affecting all genders, often linked to other diseases, with treatments available but varying success rates.
 391 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
391 citations,
January 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Half of people with Alopecia Areata may see hair regrowth within a year without treatment, but recovery is unpredictable.
 166 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
166 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Mostly postmenopausal Caucasian women get Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, which often includes eyebrow loss and has limited treatment success.
 151 citations,
February 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
151 citations,
February 2007 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia areata causes hair loss, has no cure, and various treatments exist.




























