 December 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
December 2016 in “Springer eBooks” A 45-year-old woman with autoimmune diseases experienced patchy hair loss due to alopecia areata, which has no cure but can be treated, with varying success.
[object Object] 6 citations,
May 2013 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Autoimmune reactions may cause both alopecia areata and HAM.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hydroxychloroquine may cause false results in tuberculosis tests for patients with autoimmune skin diseases.

People with psoriasis have more health problems, including autoimmune diseases, than those without it.
15 citations,
January 2022 in “Immune Network/Immune network” New targeted immunotherapies are improving treatment for inflammatory skin diseases.

The paper concludes that the patchiness of alopecia areata is likely due to when the immune attack happens in the hair growth cycle.
 January 2022 in “Medical research archives”
January 2022 in “Medical research archives” Taking vitamin D might improve life for MS patients and reduce skin side effects from alemtuzumab treatment.
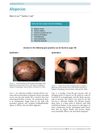 February 2013 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice”
February 2013 in “Archives of Disease in Childhood: Education & Practice” Different types of alopecia in children require specific diagnoses and treatments.
April 2017 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Topical Vorinostat shows promise for treating alopecia areata by promoting hair regrowth.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Current Dermatology Reports”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Current Dermatology Reports” Early baldness in men may indicate risks for obesity, metabolic syndrome, insulin resistance, and heart disease, similar to women with PCOS. Alopecia areata is often linked with autoimmune diseases and mental health issues. Certain hair disorders are due to genetic issues, and chemotherapy can cause hair loss through specific biological pathways. Iron deficiency's link to hair loss is still disputed.
[object Object]  January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition that often starts before age 30 and can affect various body parts, with unpredictable hair regrowth chances.
 3 citations,
August 2022 in “Curēus”
3 citations,
August 2022 in “Curēus” The SARS-CoV-2 vaccine may be linked to triggering autoimmune conditions like Alopecia Areata.
 February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A woman with thymoma developed a rare chronic condition similar to graft versus host disease after surgery.
 January 2023 in “International Journal of Homoeopathic Sciences”
January 2023 in “International Journal of Homoeopathic Sciences” Homoeopathic treatment may help restore hair in Alopecia Areata by balancing the immune system.
 June 2022 in “Journal of pharmaceutical research international”
June 2022 in “Journal of pharmaceutical research international” Alopecia causes patchy hair loss and can be diagnosed with new techniques; treatments like strong creams and contact immunotherapy can help.
 January 2015 in “Turkiye Klinikleri Journal of Endocrinology”
January 2015 in “Turkiye Klinikleri Journal of Endocrinology” PCOS patients with autoimmune thyroid disease have lower DHEAS levels.
 January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal”
January 2023 in “Indian dermatology online journal” A child with trichothiodystrophy also had autoimmune thyroiditis and anemia, which is a new finding.
 January 2023 in “Karger Kompass. Dermatologie”
January 2023 in “Karger Kompass. Dermatologie” Scientists are still unsure what triggers the immune system to attack hair follicles in Alopecia areata.

COVID-19 may trigger or worsen rapid hair loss in alopecia areata.
 4 citations,
September 2021 in “Frontiers in allergy”
4 citations,
September 2021 in “Frontiers in allergy” The conclusion is that understanding the complex relationship between allergies, autoimmunity, and psychological factors is key to treating skin disorders with itching.
 February 2014 in “Medicine - Programa De Formación Médica Continuada Acreditado”
February 2014 in “Medicine - Programa De Formación Médica Continuada Acreditado” The document concludes that non-scarring alopecias can be reversed, but scarring alopecias cause permanent hair loss.
 July 2022 in “International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics”
July 2022 in “International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics” Machine learning and deep learning can effectively diagnose alopecia areata.
5 citations,
September 2021 in “Clinical case reports” GLPLS is a rare skin condition with specific hair loss and skin symptoms.
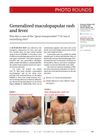 July 2023 in “The Journal of Family Practice”
July 2023 in “The Journal of Family Practice” The man was diagnosed with lupus and improved with treatment.
 11 citations,
September 2013 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
11 citations,
September 2013 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” People with alopecia areata may be more likely to have a certain type of hearing loss.
 2 citations,
September 2011 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
2 citations,
September 2011 in “Pediatric Dermatology” The document suggests there might be a link between Kawasaki Disease and Alopecia Areata that needs more research.
 July 2021 in “PARIPEX INDIAN JOURNAL OF RESEARCH”
July 2021 in “PARIPEX INDIAN JOURNAL OF RESEARCH” PRP injections significantly improve hair regrowth in alopecia areata.
31 citations,
July 2021 in “ImmunoTargets and therapy” Alopecia areata is an incurable autoimmune condition causing hair loss, with research aiming for better treatments.
 6 citations,
June 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology”
6 citations,
June 2016 in “Experimental Dermatology” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is a poorly understood condition that is hard to treat and causes distressing hair loss.
 7 citations,
December 2011 in “Elsevier eBooks”
7 citations,
December 2011 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing skin diseases in ferrets.

























