 5 citations,
October 2013 in “Endocrine”
5 citations,
October 2013 in “Endocrine” Blood tests can detect ovarian Leydig cell tumors when scans don't, and surgery can confirm and treat these tumors.

Androgen suppression therapy (AST) doesn't significantly lower bladder cancer risk, but using finasteride, a type of AST, might reduce it. AST decreases recurrence-free survival but doesn't affect overall survival or progression-free survival. More research is needed to understand AST's benefits.

Androgen suppression therapy (AST) doesn't significantly lower bladder cancer risk, but using finasteride, a type of AST, might decrease the risk. AST also lessens the chance of cancer coming back but doesn't really affect survival rates. More research is needed to understand AST's benefits for different bladder cancers.

Women with androgenetic alopecia (hair loss) have normal prostate specific antigen levels but higher testosterone levels.
 March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements”
March 2011 in “European Urology Supplements” CEC levels may be a useful marker for predicting prostate cancer progression.
 50 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
50 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Genes and hormones cause hair loss, with four genes contributing equally.
 45 citations,
November 2015 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
45 citations,
November 2015 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hormones might affect the skin condition hidradenitis suppurativa, but their exact role is unclear.
 13 citations,
June 2007 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
13 citations,
June 2007 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Researchers created a cell line to study hair growth and found specific genes affected by dihydrotestosterone.
 12 citations,
August 2000 in “Fertility and Sterility”
12 citations,
August 2000 in “Fertility and Sterility” Topical finasteride doesn't reduce DHT levels, hinting at an endocrine role in hair loss.
 4 citations,
August 2019 in “General and Comparative Endocrinology”
4 citations,
August 2019 in “General and Comparative Endocrinology” Male yak hair growth is influenced by DHT synthesis, which is promoted by 5α-red1 and AR during growth phases, while E2 may inhibit growth through ERα.
 117 citations,
May 2017 in “Human Reproduction Update”
117 citations,
May 2017 in “Human Reproduction Update” The update highlights that non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia is common in women with excess male hormones, requires specific hormone tests for diagnosis, and has various treatment options depending on age and symptoms.
 55 citations,
August 2008 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders”
55 citations,
August 2008 in “Reviews in endocrine and metabolic disorders” Nonclassic adrenal hyperplasia is a genetic condition that can cause early puberty and fertility problems, treated with specific steroids.
 32 citations,
February 2024 in “Growth Hormone & IGF Research”
32 citations,
February 2024 in “Growth Hormone & IGF Research” Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) stops hair growth in mice by lowering a growth factor important for hair.
 25 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of exposure science & environmental epidemiology/Journal of exposure science and environmental epidemiology”
25 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of exposure science & environmental epidemiology/Journal of exposure science and environmental epidemiology” Common Black hair care products may affect hormone levels and potentially impact health, especially in reproductive and metabolic areas.
 17 citations,
December 2015 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science”
17 citations,
December 2015 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Science” Visible light can improve skin disorders and hair loss, but more research is needed to understand long-term effects.
 16 citations,
February 2018 in “European Journal of Endocrinology”
16 citations,
February 2018 in “European Journal of Endocrinology” Diagnosing hyperandrogenism in women is complex and requires accurate testing methods and consideration of SHBG levels.
 11 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology”
11 citations,
May 2021 in “Journal of Medical Virology” Men are more likely to have severe respiratory viral infections like COVID-19 due to hormonal and genetic differences, while women generally have stronger immune responses.
 8 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
October 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The review suggests there's no agreed treatment for Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia, but hydroxychloroquine and 5a-reductase inhibitors are most effective. New treatments like platelet-rich plasma and LED light could help if standard treatments fail.
 7 citations,
September 2014 in “Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences”
7 citations,
September 2014 in “Beni-Suef University Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences” Cuscuta reflexa extracts and an isolate promoted hair growth and could be natural treatments for hair loss.
 7 citations,
July 2005 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
7 citations,
July 2005 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” The gene URB is more active in human hair growth cells and responds to a hair-related hormone.
 24 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
24 citations,
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Age, smoking, and lower BMI increase facial wrinkles; men wrinkle more than women, except in old age; pale skin and certain hormonal factors can protect against wrinkles.
 9 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology”
9 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology” A woman's ovarian tumor causing high testosterone was successfully removed, and her symptoms improved.
 6 citations,
July 2016 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
6 citations,
July 2016 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” PSA levels are higher in women with PCOS, but FAI is a more accurate marker for diagnosis.
 4 citations,
May 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
4 citations,
May 2013 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Most Spanish Caucasian women have a widow's peak, and their hormone levels suggest they process certain hormones faster.
 3 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of Molecular Graphics & Modelling”
3 citations,
July 2017 in “Journal of Molecular Graphics & Modelling” The study found that baicalin has different stable shapes in gas and water, with two shapes better for interacting with positive charges in water.
 November 2023 in “ACS Omega”
November 2023 in “ACS Omega” New liposome treatment successfully delivers CRISPR to deactivate a key enzyme in androgen-related disorders.
 1 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
1 citations,
August 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” A woman's hyperandrogenism was caused by a genetic mutation leading to non-classic adrenogenital syndrome.
 14 citations,
June 2015 in “Toxicology and Industrial Health”
14 citations,
June 2015 in “Toxicology and Industrial Health” Low doses of BPA can increase prostate growth and change hormone levels in adult rats.
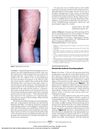 10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
10 citations,
June 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Finasteride caused blisters on hands and feet.
 8 citations,
March 2010 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
8 citations,
March 2010 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” Free Testosterone Index, bioavailable testosterone, and androstenedione are the most accurate for diagnosing excess male hormones in PCOS.






























