 4 citations,
March 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology”
4 citations,
March 2006 in “Archives of Dermatology” The conclusion is that dermatologists can improve women's skin health but must overcome cultural and economic barriers to do so.
10 citations,
February 2022 in “Epidemiologia” One-third of COVID-19 patients had long-term symptoms like hair loss and fatigue, with women, older individuals, blood group B, smokers, and those with more virus exposure at higher risk.
 21 citations,
May 2021 in “Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases”
21 citations,
May 2021 in “Prostate Cancer and Prostatic Diseases” COVID-19 might worsen symptoms and progression of benign prostatic hyperplasia, possibly due to inflammation and metabolic disturbances in the prostate gland. More research is needed to confirm this.
 October 2020 in “Проблемы эндокринологии”
October 2020 in “Проблемы эндокринологии” Men with higher androgen levels may have severe COVID-19 symptoms, but those on antiandrogen therapy are less likely to contract the virus and have milder symptoms. Anti-androgen drugs could potentially treat COVID-19, but more research is needed.
 8 citations,
May 2010 in “Dermatologic clinics”
8 citations,
May 2010 in “Dermatologic clinics” New treatments for skin conditions in children include a preferred drug for birthmark reduction, proactive creams for eczema and vitiligo, a safe psoriasis medication, and special tissues and socks for eczema and fungal infections.
 6 citations,
May 2021 in “Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine”
6 citations,
May 2021 in “Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine” Different ACE2 gene versions may affect COVID-19 impact based on age and suggest some hair loss drugs could be potential treatments.
3 citations,
November 2022 in “The Egyptian Rheumatologist” Macrophage activation syndrome can be a deadly first sign of systemic lupus erythematosus.
 121 citations,
November 2020 in “Endocrine”
121 citations,
November 2020 in “Endocrine” Male hormones like testosterone may make COVID-19 worse, and testing for sensitivity to these hormones could help predict how severe a patient's symptoms might be. Treatments that reduce these hormones are being explored.
 December 2018 in “DergiPark (Istanbul University)”
December 2018 in “DergiPark (Istanbul University)” The cat's skin condition improved with treatment, but underlying health issues must be addressed.
40 citations,
August 2021 in “JAAD international” Teledermatology became a valuable and convenient tool for skin care during the COVID-19 pandemic.

COVID-19 may trigger or worsen rapid hair loss in alopecia areata.
 November 2020 in “Holistic Nursing Practice”
November 2020 in “Holistic Nursing Practice” COVID-19 can cause hair loss, loss of taste and smell, skin changes, and eye problems.
 8 citations,
July 2011 in “Critical reviews in analytical chemistry”
8 citations,
July 2011 in “Critical reviews in analytical chemistry” The document concludes that validated methods are needed to ensure the quality of fluconazole drugs and that new antifungal medications are necessary due to safety and resistance concerns.
 4 citations,
April 2014 in “Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics”
4 citations,
April 2014 in “Journal of Pharmacology and Pharmacotherapeutics” The boy's hair loss was caused by the tuberculosis drug isoniazid but grew back after stopping the medication.
 35 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology”
35 citations,
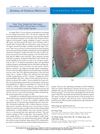
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology” A cancer patient died from a severe skin reaction after taking the drug cetuximab.
 23 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Endocrinological Investigation”
23 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Endocrinological Investigation” Betacoronaviruses, like COVID-19, may cause hormone system dysfunction and affect disease susceptibility and severity.
 165 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology Research and Practice”
165 citations,
January 2014 in “Dermatology Research and Practice” Zinc is effective for treating various skin conditions, including warts and acne.
 100 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
100 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” People with alopecia areata often have other health issues like skin diseases, metabolic syndrome, stomach infections, lupus, anemia, thyroid problems, mental health issues, vitamin D deficiency, and hearing and eye problems.
 43 citations,
November 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
43 citations,
November 2007 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” The document concludes that proper diagnosis and treatment of common scalp disorders are important for both physical and psychological health.
 February 2023 in “Vaccines”
February 2023 in “Vaccines” COVID-19 may harm male reproductive health and lower testosterone levels, potentially affecting fertility and causing erectile dysfunction. More research is needed.
 9 citations,
March 2011 in “Oxidative stress and disease”
9 citations,
March 2011 in “Oxidative stress and disease” Some herbal treatments are effective for skin disorders, but more research and regulation are needed.
 16 citations,
July 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
16 citations,
July 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” The patient was diagnosed with anorexia nervosa and severe malnutrition, requiring urgent refeeding and monitoring.

Social media data can help track and predict COVID-19 symptoms and trends.
 3 citations,
January 2020 in “Acta Dermato Venereologica”
3 citations,
January 2020 in “Acta Dermato Venereologica” Netherton Syndrome can cause severe skin lesions in rare cases.
5 citations,
January 2016 in “Open Journal of Regenerative Medicine” Myoblast transplantation shows promise for treating various muscle and heart conditions.
 39 citations,
June 1982 in “The BMJ”
39 citations,
June 1982 in “The BMJ” Blood tests confirmed a baby in the womb had a CMV infection.
 8 citations,
August 2009 in “Pediatric transplantation”
8 citations,
August 2009 in “Pediatric transplantation” A five-month-old boy with Omenn syndrome successfully recovered after a stem cell transplant with reduced intensity conditioning.
83 citations,
June 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical JAK inhibitors may help children with alopecia areata regrow hair.
3 citations,
January 2016 in “Dermatology online journal” Some people with lichen planus pigmentosus might later develop frontal fibrosing alopecia.
 2 citations,
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” The conclusion is that different blood diseases cause specific oral symptoms and require varied treatments to manage these symptoms and improve patient health.
























