 1 citations,
October 2006 in “Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care”
1 citations,
October 2006 in “Journal of Family Planning and Reproductive Health Care” The contraceptive implant Implanon may be linked to hair loss, but the reported case of alopecia could be unrelated to the implant.
[object Object]  January 2022 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2022 in “Journal of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Trichoscopy is useful for quickly diagnosing different types of hair loss without needing biopsies.
 6 citations,
August 2006 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
6 citations,
August 2006 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Two teenage brothers had a rare, treatment-resistant form of female-pattern hair loss with unusual scalp changes.
 May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Adjusting the medication tacrolimus resolved a boy's red nail beds after a stem cell transplant.
 10 citations,
November 1997 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
November 1997 in “British Journal of Dermatology” A 10-year-old boy had the earliest reported case of hair that became progressively kinkier but eventually returned to normal on its own.
 July 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
July 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The research found that male pattern hair loss is mostly genetic and involves hair thinning due to hormonal effects and changes in gene expression.
1 citations,
May 2022 in “Journal of Drugs in Dermatology” Low-dose naltrexone and platelet-rich plasma can regrow hair in lichen planopilaris.
 16 citations,
August 1967 in “JAMA”
16 citations,
August 1967 in “JAMA” Oral contraceptives may cause hair loss in women.
 April 2024 in “Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology”
April 2024 in “Oral Surgery Oral Medicine Oral Pathology and Oral Radiology” The patient was diagnosed with oral lichen sclerosus and needs long-term monitoring.
[object Object]  September 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
September 2023 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” A new surgical method using special sutures significantly reduced wound size and prevented disease return in patients with a scarring scalp condition.
 1 citations,
May 1965 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
1 citations,
May 1965 in “Medical Clinics of North America” Hair growth dysfunction involves various conditions with limited treatment options.
 3 citations,
December 2021 in “Dermatology reports”
3 citations,
December 2021 in “Dermatology reports” Dupilumab can improve both atopic dermatitis and alopecia universalis.
November 2014 in “PharmaTutor” Finasteride may help postmenopausal women with hair loss but is not effective for all and should be used cautiously in premenopausal women.
 August 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
August 2010 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document explains the diagnosis and characteristics of woolly hair nevus and alopecia neoplastica.
 2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology”
2 citations,
June 2005 in “Clinical Oncology” A man's bald spot grew hair after starting cancer treatment with gefitinib.
 January 2020 in “Open Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology”
January 2020 in “Open Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology” All women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) in a study had at least one skin disorder, with the most common being excessive hair growth, acne, dark skin patches, hair loss, and oily skin.
 125 citations,
January 1999 in “Drugs”
125 citations,
January 1999 in “Drugs” Finasteride effectively treats baldness but may cause sexual side effects.
 10 citations,
December 2002 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
December 2002 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Cyproterone acetate can cause rare shortness of breath in women.

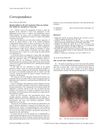
A rare case of a woman having both lichen planus pigmentosus and classic lichen planopilaris at the same time.
 31 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
31 citations,
March 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some breast cancer patients developed permanent hair loss after chemotherapy and hormonal therapy, showing patterns similar to common baldness and alopecia areata.
 July 2023 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online”
July 2023 in “Nasza Dermatologia Online” More research is needed on CCCA in children, especially Black and Asian adolescents.
 1 citations,
July 2021 in “Curēus”
1 citations,
July 2021 in “Curēus” A child had a rare case of scarring hair loss with skin disease, which is hard to treat and stressful.
 40 citations,
March 1982 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
40 citations,
March 1982 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Young women with diffuse hair loss may have low SHBG levels, which could lead to more active testosterone and contribute to their hair loss.
 19 citations,
May 2020 in “Cells”
19 citations,
May 2020 in “Cells” Substance from human umbilical cord blood cells promotes hair growth.
 25 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
25 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” PRP injections increase hair density and diameter in female androgenetic alopecia patients.
 26 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
26 citations,
December 2015 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” New method measures female hair loss: Female Pattern Hair Loss Severity Index (FPHL-SI).
 February 2024 in “Curēus”
February 2024 in “Curēus” Regional nerve blocks are better than ring blocks for pain relief during PRP hair treatment.
 2 citations,
December 2003
2 citations,
December 2003 Saw palmetto is an effective natural treatment for hair loss with minimal side effects.
 3 citations,
May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
3 citations,
May 2018 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Photodynamic therapy may not work for erythroplasia of Queyrat and could lead to invasive squamous cell carcinoma.
 January 2025 in “Skin Health and Disease”
January 2025 in “Skin Health and Disease” Baricitinib may effectively treat both alopecia areata and immune thrombocytopenia.




























