 21 citations,
June 2009 in “Current Medical Research and Opinion”
21 citations,
June 2009 in “Current Medical Research and Opinion” Most men with hair loss worry, try self-treatments, and delay doctor visits due to cost, uncertainty, and embarrassment.
 19 citations,
February 2008 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
19 citations,
February 2008 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Mast cells might contribute to hair loss by causing skin thickening.
[object Object]  15 citations,
September 2006 in “Journal of International Medical Research”
15 citations,
September 2006 in “Journal of International Medical Research” Nourkrin® significantly increased hair growth and was well-tolerated by people with hair loss.
 6 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
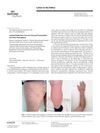
6 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” A man with rare Lichen Planopilaris lost body hair, not scalp hair, and treatment stopped itching but didn't regrow hair.
 5 citations,
February 2016 in “Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers”
5 citations,
February 2016 in “Genetic Testing and Molecular Biomarkers” Hair loss is significantly linked to lower levels of certain genes in hair follicles.
 3 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology”
3 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology” Frequent use of hair straighteners can cause hair loss similar to scarring alopecia in young Turkish women.
 2 citations,
January 1980 in “Acupuncture & electro-therapeutics research”
2 citations,
January 1980 in “Acupuncture & electro-therapeutics research” Hair loss might be due to nerve issues, treatable with electric stimulation or acupuncture.
 1 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
1 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Vertex baldness has higher DHT levels than frontal baldness, but testosterone and PSA levels are similar.
 1 citations,
February 2013 in “Clinical pediatrics”
1 citations,
February 2013 in “Clinical pediatrics” The baby’s hair loss was due to a rare genetic condition, not treatable by usual methods.
[object Object]  January 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine”
January 2023 in “Frontiers in medicine” Early diagnosis and personalized treatments are crucial for better hair loss management.
Low-level light therapy, possibly combined with other treatments, may become a leading hair loss treatment, while hirsutism often worsens with age and lacks preventive options.
 January 2017 in “Journal of traditional medicine & clinical naturopathy”
January 2017 in “Journal of traditional medicine & clinical naturopathy” Combining trichology and homeopathy is effective for diagnosing and treating hair loss.
 January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” Some alternative treatments may help with hair loss, but more evidence is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
 January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks” Hair loss can cause emotional and social issues, and various treatments, including medication, surgery, and psychological support, are needed.
 June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
June 2021 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” New scale reliably assesses male hair loss with female pattern.
 October 2020 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
October 2020 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Hair loss improved after removing pituitary tumor.
 236 citations,
July 2001 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine”
236 citations,
July 2001 in “Trends in Molecular Medicine” Future hair loss treatments should aim to extend hair growth, reactivate resting follicles, reverse shrinkage, and possibly create new follicles, with gene therapy showing promise.
 226 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
226 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Hair loss in women is genetic, diagnosed by examination and biopsy, and treated with minoxidil, finasteride, or transplantation.
 207 citations,
April 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
207 citations,
April 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Iron deficiency may be related to hair loss, but there's not enough evidence to recommend iron screening or supplements for all hair loss patients.
 183 citations,
January 2014 in “BioMed Research International”
183 citations,
January 2014 in “BioMed Research International” AA-PRP injections effectively increase hair count and thickness for male pattern hair loss.
 165 citations,
August 2013 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
165 citations,
August 2013 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Low-Level Laser Therapy is effective and safe for hair growth with minimal side effects.
 137 citations,
July 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
137 citations,
July 2004 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Horizontally sectioned scalp biopsies are more reliable for diagnosing hair loss in women when three samples are taken instead of one.
 129 citations,
October 2007 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
129 citations,
October 2007 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Over one-third of women experience hair loss, with female-pattern hair loss being most common, and treatments include minoxidil and possibly hair transplantation.
 86 citations,
June 2017 in “Stem cell investigation”
86 citations,
June 2017 in “Stem cell investigation” Stem cells from hair follicles can safely treat hair loss.
 83 citations,
November 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
83 citations,
November 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Low iron levels are not directly linked to chronic hair loss and iron supplements may not help.
 83 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
83 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss that spreads out can often fix itself or be treated by finding and handling the cause.
 81 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
81 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Effective hair loss treatment in women requires correct diagnosis and can include medications like minoxidil, antiandrogens, and treatments for underlying conditions like PCOS.
 76 citations,
December 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
76 citations,
December 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Japanese women typically start experiencing hair loss after 40, with reduced hair density and thickness being the main factors.
 72 citations,
January 2004 in “Dermatology”
72 citations,
January 2004 in “Dermatology” Finasteride can slow hair loss and promote growth in postmenopausal women.
 63 citations,
March 2000 in “Annals of clinical psychiatry”
63 citations,
March 2000 in “Annals of clinical psychiatry” Some psychiatric medications can cause hair loss, but it usually grows back after adjusting the medication.




























