September 2018 in “CRC Press eBooks” Hair and nail disorders can cause changes in scalp pigmentation, especially with sun exposure and alopecia.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-cost videomicroscopes might not be reliable for examining scalp disorders compared to standard methods.
 18 citations,
March 2015 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports”
18 citations,
March 2015 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports” Rectangular black granules, solitary yellow dots, and mostly single-hair follicles suggest Loose Anagen Hair Syndrome.
[object Object]  4 citations,
January 2012 in “Springer eBooks”
4 citations,
January 2012 in “Springer eBooks” The document concludes that signs of male and female pattern baldness include uneven hair thickness, yellow spots, skin discoloration around hair follicles, more thin and soft hairs, and many hair follicles with just one hair.
 July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia is a type of hair loss affecting mostly older women, with no agreed best treatment.
 18 citations,
July 2018 in “Skin appendage disorders”
18 citations,
July 2018 in “Skin appendage disorders” Trichoscopy helps diagnose hair and scalp disorders in dark-skinned people by identifying unique patterns.
 9 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
July 2020 in “Journal of Dermatology” Asian patients with Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia often lose eyebrow hair and respond well to combined antiandrogen or antimalarial and topical treatments.
October 2023 in “Asian journal of pharmaceutical and clinical research” Standardized data is essential for diagnosing scalp and hair conditions in males.
 March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks”
March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” The document concludes that different patterns of hair thickness and scalp changes can help diagnose types of non-scarring hair loss.
 January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” The report concludes that atypical Brauer nevus is more common in males, present at birth, and often misdiagnosed due to its unusual scalp locations.
October 2021 in “QJM: An International Journal of Medicine” N-acetyl-cysteine improves hair growth and is safe for treating early male hair loss.
 23 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
23 citations,
July 2018 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Chemotherapy caused hair loss with specific patterns, but most patients had hair regrowth after treatment, while some had lasting hair loss.
 15 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
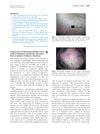
15 citations,
November 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Exclamation mark hairs suggest early scalp disease, while white dots indicate it's chronic.
 89 citations,
December 2010 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
89 citations,
December 2010 in “The Journal of Dermatology” The conclusion is that an algorithm using trichoscopy helps diagnose different types of hair loss but may need updates and a biopsy if results are unclear.
 45 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology”
45 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopy is better than trichogram for diagnosing female hair loss.
 8 citations,
June 2021 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
8 citations,
June 2021 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Trichoscopy is a reliable method for diagnosing hair-pulling disorder.
 7 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
7 citations,
August 2021 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Early treatment of fibrosing alopecia in a pattern distribution may improve outcomes.
 2 citations,
June 2023 in “Skin Research and Technology”
2 citations,
June 2023 in “Skin Research and Technology” Yellow dots and short vellus hairs are the most common signs of Alopecia Areata (AA), and trichoscopy can help diagnose AA and track treatment progress.
 December 2024 in “Archiv Euromedica”
December 2024 in “Archiv Euromedica” Trichoscopy is essential for diagnosing and treating autoimmune cicatricial alopecia early.
 March 2024 in “Journal of clinical medicine”
March 2024 in “Journal of clinical medicine” Trichoscopy shows hair diameter variability, vellus hairs, and the peripilar sign are key indicators for diagnosing Androgenetic Alopecia.
 December 2023 in “Portuguese journal of dermatology and venereology”
December 2023 in “Portuguese journal of dermatology and venereology” Trichoscopy can reliably distinguish between alopecia areata and trichotillomania.
November 2021 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopy is effective for diagnosing and monitoring female pattern hair loss.
 38 citations,
January 2016 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
38 citations,
January 2016 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Trichoscopy is useful for diagnosing different types of hair loss.
 5 citations,
October 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
5 citations,
October 2012 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing hair and scalp diseases without needing skin biopsies.
 2 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
2 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing and managing hair and scalp conditions, often better than traditional methods.
 March 2023 in “Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy”
March 2023 in “Photodiagnosis and Photodynamic Therapy” Low vitamin D levels are linked to severe and active alopecia areata.
[object Object]  69 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology”
69 citations,
January 2015 in “Current problems in dermatology” Trichoscopy is a quick, noninvasive method to diagnose hair and scalp disorders, often reducing the need for biopsies.
 43 citations,
August 2013 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
43 citations,
August 2013 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Trichoscopy is good for diagnosing and monitoring hair and scalp problems in children but needs more research for certain conditions.
 42 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
42 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing different hair and scalp diseases without surgery.
 36 citations,
August 2018 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
36 citations,
August 2018 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing hair disorders without pulling out hair.

























