 2 citations,
January 2012 in “InTech eBooks”
2 citations,
January 2012 in “InTech eBooks” Chemotherapy often causes hair loss, which usually grows back within 3 to 6 months, but there's no effective treatment to prevent it.
 421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
421 citations,
April 2012 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition causing hair loss with no cure and treatments that often don't work well.
 159 citations,
December 2007 in “American Journal of Pathology”
159 citations,
December 2007 in “American Journal of Pathology” Stress-related substance P may lead to hair loss and negatively affect hair growth.
 39 citations,
August 2021 in “JAAD International”
39 citations,
August 2021 in “JAAD International” COVID-19 patients often experience hair loss and scalp pain, which may be related to the severity of their infection and treatment drugs.
35 citations,
August 2009 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Melanocytes might be targeted by the immune system in people with alopecia areata, but more research is needed.
 28 citations,
February 2016 in “F1000Research”
28 citations,
February 2016 in “F1000Research” Understanding glycans and enzymes that alter them is key to controlling hair growth.
 15 citations,
May 2016 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
15 citations,
May 2016 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” ULBP3 could be a marker for diagnosing alopecia areata incognita and may be linked to its cause and development.
 3 citations,
October 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Scalp melanoma, a deadly skin cancer, is often found late due to its hard-to-see location, especially in older men. Early detection, possible treatments, and the role of hairdressers in spotting it early are discussed. More research is needed to improve detection and treatment.
 1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
October 2018 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that treatments for cicatricial alopecia are not well-supported by evidence, but hair transplantation shows more predictable and satisfactory results.
 1 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of Pathology of Nepal”
1 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of Pathology of Nepal” Testing hair roots with a special dye is a simple, non-invasive way to check disease progress in pemphigus vulgaris patients.
 1 citations,
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that the skin is a complex organ providing protection, sensation, and healing, with challenges in treating conditions like itchiness.
 January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” The conference highlighted new diagnostic tools, the role of genetics in hair loss, and emerging treatments.
 June 2001 in “Proceedings of SPIE”
June 2001 in “Proceedings of SPIE” Low energy laser therapy effectively treats certain skin conditions and improves recovery time without side effects.
162 citations,
October 2014 in “Autoimmunity reviews” Alopecia areata is caused by the immune system attacking hair follicles.
 47 citations,
December 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology”
47 citations,
December 2019 in “Frontiers in immunology” A new mutation in the STING protein causes a range of symptoms and its severity may be affected by other genetic variations; treatment with a specific inhibitor showed improvement in one patient.
 7 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine”
7 citations,
December 2004 in “Medicine” Knowing how skin works and its diseases helps doctors diagnose and treat skin conditions better.
286 citations,
August 2007 in “Journal of Clinical Investigation” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disease where T cells attack hair follicles.
 November 2023 in “npj regenerative medicine”
November 2023 in “npj regenerative medicine” Skin spheroids with both outer and inner layers are key for regrowing skin patterns and hair.

Dupilumab helped improve skin and prevent new lesions in a child with a rare immune disorder and severe eczema.
 September 2017 in “Majallah-i taḥqīqāt-i ̒ulūm-i pizishkī-i Zāhidān”
September 2017 in “Majallah-i taḥqīqāt-i ̒ulūm-i pizishkī-i Zāhidān” Androgenetic alopecia is a long-term, immune-related disorder that starts during puberty due to androgen secretion, and it might be improved with iron tablets, platelet transfusion, and anti-inflammation therapy.
 72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Anti-TNF therapy can cause a unique type of hair loss that may get better with topical treatments without stopping the therapy.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” Hair loss in Androgenetic alopecia (AGA) is due to altered cell sensitivity to hormones, not increased hormone levels. Hair growth periods shorten over time, causing hair to become thinner and shorter. This is linked to miscommunication between cell pathways in hair follicles. There's also a change in gene expression related to blood vessels and cell growth in balding hair follicles. The exact molecular causes of AGA are still unclear.
 1 citations,
October 1990 in “The Lancet”
1 citations,
October 1990 in “The Lancet” Using minoxidil for hair growth may cause skin lesions in some people, and taking breaks from nitrate patches for angina might worsen symptoms.
 209 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
209 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Androgens can both increase and decrease hair growth in different parts of the body.
 97 citations,
September 2006 in “Pharmaceutical Research”
97 citations,
September 2006 in “Pharmaceutical Research” No treatment fully prevents hair loss from chemotherapy yet.
 12 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
12 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hair loss in autoimmune blistering skin diseases varies and may regrow with disease control.
 10 citations,
May 2020 in “Dermatology Research and Practice”
10 citations,
May 2020 in “Dermatology Research and Practice” Proteoglycans are important for hair growth, and a specific treatment can help reduce hair loss.
 3 citations,
June 2004 in “Alternative and Complementary Therapies”
3 citations,
June 2004 in “Alternative and Complementary Therapies” The document concludes that hair loss is influenced by genetics and other factors, and while treatments like finasteride can help, they have limitations and side effects.
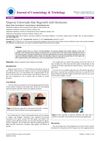 January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology”
January 2017 in “Journal of cosmetology & trichology” A man with severe hair loss regrew hair after hormone treatment.
 28 citations,
October 2013 in “Cornea”
28 citations,
October 2013 in “Cornea” Scientists have made progress in creating replacement teeth, hair, and glands that work, which could lead to new treatments for missing teeth, baldness, and dryness conditions.



























