 41 citations,
January 2014 in “Annals of Dermatology”
41 citations,
January 2014 in “Annals of Dermatology” Dermoscopic examination helps diagnose different types of hair loss conditions by showing specific patterns.
 6 citations,
March 2018 in “Hair transplant forum international”
6 citations,
March 2018 in “Hair transplant forum international” The Graft Quality Index grades hair transplant grafts to predict placement difficulty and surgery results.
 4 citations,
May 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
4 citations,
May 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Congenital triangular alopecia can occur outside the typical fronto-temporal region.
[object Object]  April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-cost videomicroscopes might not be reliable for examining scalp disorders compared to standard methods.
 9 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
9 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Transplanting body hair helped repigment and treat a man's vitiligo.
 42 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
42 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for diagnosing different hair and scalp diseases without surgery.
 January 2019 in “SAGE Open Medical Case Reports”
January 2019 in “SAGE Open Medical Case Reports” A scalp biopsy revealed systemic amyloidosis in a woman who initially seemed to have a common hair loss condition.
 January 2019 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine”
January 2019 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine” Trichoscopy helps effectively tell apart different types of patchy hair loss in Egyptian patients.
 8 citations,
November 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
8 citations,
November 2018 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia in families shows similar signs to individual cases and may have a genetic link.
 10 citations,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders”
10 citations,
January 2015 in “Skin appendage disorders” Low-cost videomicroscopes are not as reliable as standard videodermatoscopes for scalp examination due to lower image quality.
 207 citations,
January 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
207 citations,
January 2011 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Laser hair removal is the most requested cosmetic procedure and has become a scientifically-based treatment suitable for all skin types.
 1 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of dermatology”
1 citations,
July 2009 in “Journal of dermatology” A 29-year-old man had a jaw plaque diagnosed as follicular mucinosis, linked to nestin-positive hair follicle stem cells.
 5 citations,
June 2019 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
5 citations,
June 2019 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Tofacitinib was more effective than apremilast in treating hair loss in a mouse model of alopecia areata.
January 2023 in “Indian journal of pharmacy practice” Over-the-counter cosmetic creams can cause skin damage on the face that is visible under dermoscopy and confirmed by tissue analysis.
 19 citations,
July 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
19 citations,
July 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” The study found that long-term sun exposure does not significantly affect follicular plugs on the scalp, and the scalp's appearance is unique compared to other body parts.
 46 citations,
April 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports”
46 citations,
April 2009 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports” Researchers established normal hair and scalp characteristics for healthy women using trichoscopy.
 March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks”
March 2021 in “CRC Press eBooks” Trichoscopy helps tell apart Lichen planopilaris and Frontal fibrosing alopecia from other hair loss conditions.
 129 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology”
129 citations,
January 2009 in “International Journal of Trichology” Trichoscopy can diagnose female hair loss with high accuracy by looking for specific patterns in hair and scalp appearance.
 25 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports”
25 citations,
December 2008 in “Journal of Dermatological Case Reports” In vivo reflectance confocal microscopy is useful for evaluating hair shaft diseases but needs improvement for deeper hair follicle issues.
March 2021 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Fat tissue around hair follicles releases a growth factor that helps hair grow and develop color.
 September 2022 in “Intisasi sains media”
September 2022 in “Intisasi sains media” A young child with complete hair loss improved significantly with a combination of hair growth treatments and laser therapy.
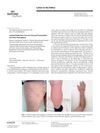 6 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders”
6 citations,
January 2016 in “Skin appendage disorders” A man with rare Lichen Planopilaris lost body hair, not scalp hair, and treatment stopped itching but didn't regrow hair.
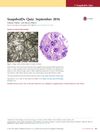 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Scalp psoriasis features reversible hair loss and specific immune activation, with no significant hair follicle damage.
[object Object] December 2020 in “Forum Dermatologicum” Intralesional triamcinolone acetonide can effectively limit the progression of GLPLS.
 6 citations,
January 2012 in “Springer eBooks”
6 citations,
January 2012 in “Springer eBooks” Trichoscopy is not specific for diagnosing telogen effluvium and both telogen effluvium and androgenetic alopecia often occur together.
 June 2003 in “Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey”
June 2003 in “Obstetrical & Gynecological Survey” Postmenopausal ovary stromal cells have a unique makeup and limited steroid production, suggesting androgens come from the adrenal gland.
 7 citations,
December 2002 in “PubMed”
7 citations,
December 2002 in “PubMed” The scalp has a natural speckled pattern of increased pigment around hair follicles, possibly linked to local hormone production.
 January 2025 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
January 2025 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia is a challenging hair loss condition with no known cause or definitive treatment.
 12 citations,
February 1999 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
12 citations,
February 1999 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil increased small openings in blood vessel walls near growing hair in rats.
 17 citations,
May 1998 in “Contact Dermatitis”
17 citations,
May 1998 in “Contact Dermatitis” Minoxidil can cause pustular allergic reactions on skin.



























