 January 2024 in “Skin Research and Technology”
January 2024 in “Skin Research and Technology” Oral tofacitinib may be an effective future treatment for children with severe alopecia areata, but more research is needed.
 May 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
May 2017 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Graves' disease can cause hair loss in children and should be considered when treating pediatric alopecia areata.
 15 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the Formosan Medical Association”
15 citations,
January 2019 in “Journal of the Formosan Medical Association” Adalimumab helped control a child's severe eye disease when other treatments failed.
 8 citations,
September 2016 in “Pediatric dermatology”
8 citations,
September 2016 in “Pediatric dermatology” People with Mucopolysaccharidoses often have skin problems like thick skin and extra hair, and recognizing these can help diagnose and treat the condition early.
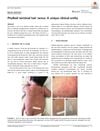 August 2018 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
August 2018 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A baby had a unique skin condition with a pale patch and surrounding dark hairs, not linked to other health issues.

research Acne
2 citations,
May 2011 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” Acne is a common skin condition linked to diet, hormones, and genetics, and early treatment can prevent scarring.
 April 2020 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology”
April 2020 in “IP Indian journal of clinical and experimental dermatology” Many children with alopecia areata also have other autoimmune diseases.
16 citations,
January 2013 in “Pediatric Gastroenterology Hepatology & Nutrition” Azathioprine caused side effects in over half of the Korean pediatric inflammatory bowel disease patients, requiring close monitoring.

Calcipotriene ointment improved a child's skin condition known as En coup de sabre.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Many patients with autoimmune blistering skin disorders change their diets, avoiding foods like alcohol, citrus, and spices, and some find vegetables and dairy helpful.
 75 citations,
May 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
75 citations,
May 2013 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Zinc deficiency in children can cause skin issues and can be serious if not diagnosed and treated properly.
 12 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
12 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Minoxidil, applied on the skin or taken orally, can improve hair growth in kids, but more research is needed due to possible side effects.
 7 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
7 citations,
July 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” During the COVID-19 pandemic in Turkey, the most common skin problem for both kids and adults was acne.
 May 2023 in “Sučasna pedìatrìâ. Ukraïna”
May 2023 in “Sučasna pedìatrìâ. Ukraïna” An 11-year-old child with total hair loss may have a genetic autoimmune disease, and the outlook for hair regrowth is not good.
 13 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
13 citations,
July 2016 in “Pediatric Dermatology” Loose Anagen Syndrome is more common in females and may be inherited, often confused with other hair disorders, and lacks evidence for biotin treatment effectiveness.
 40 citations,
January 2009 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology”
40 citations,
January 2009 in “Skin Pharmacology and Physiology” Fetal cells could improve skin repair with minimal scarring and are a potential ready-to-use solution for tissue engineering.
 11 citations,
September 2015 in “Medical Principles and Practice”
11 citations,
September 2015 in “Medical Principles and Practice” In a Tuscan pediatric clinic, 7.19% of children had hair or scalp disorders, with nonscarring alopecia being the most common.
 2 citations,
July 2008 in “Paediatrics & child health”
2 citations,
July 2008 in “Paediatrics & child health” Severe acne in a young girl may indicate underlying hormonal issues.
 13 citations,
July 2019 in “Pediatric dermatology”
13 citations,
July 2019 in “Pediatric dermatology” Pediatric dermatologists need to understand the unique skin health needs of LGBTQIA youth to provide better care.
 1 citations,
August 2020 in “Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences”
1 citations,
August 2020 in “Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences” Skin problems like rashes and hair loss can help diagnose and predict COVID-19.
 7 citations,
March 2012 in “European Journal of Pediatrics”
7 citations,
March 2012 in “European Journal of Pediatrics” A boy with a rare skin condition and kidney disease improved with cyclosporine after steroids failed, suggesting a new treatment approach.
60 citations,
September 2004 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A girl developed vitiligo and psoriasis after hepatitis B treatment, and stopping the treatment didn't help.
 January 2024 in “Pediatric rheumatology online journal”
January 2024 in “Pediatric rheumatology online journal” Early genetic testing and JAK inhibitors can help treat systemic inflammation in SAVI patients.
 September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Pediatric Dermatology” The document concludes that an experimental drug may help wound healing in Epidermolysis Bullosa, links Hydroa vacciniforme to EBV, discusses diagnosing hair loss disorders, finds many children with eczema have allergies, reviews the safety of a skin medication in children, notes side effects of a Duchenne's treatment, and identifies a marker for pediatric mastocytosis.
 80 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatopathology”
80 citations,
June 2020 in “Dermatopathology” COVID-19 can cause various skin lesions, which may result from the virus and immune response, and are not directly linked to illness severity.
 10 citations,
April 2020 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
10 citations,
April 2020 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Biotin supplements improved skin and hair problems in a girl with biotinidase deficiency.
 1 citations,
May 2021 in “Annals of the rheumatic diseases”
1 citations,
May 2021 in “Annals of the rheumatic diseases” Tofacitinib is a promising treatment for children with rheumatic diseases.

A girl with Crohn's disease developed hair loss due to her increased medication, a rare side effect seen in some children.
 June 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
June 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Finasteride improved hidradenitis suppurativa in kids without side effects.
 2 citations,
December 2007 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
2 citations,
December 2007 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are key for pediatric hair loss disorders, and addressing the emotional effects on children is important.




























