 January 2021 in “Journal of Allergy and Therapy”
January 2021 in “Journal of Allergy and Therapy” Electric Follicle Stimulation may promote hair growth and density with no known side effects.
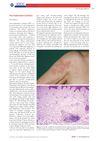 October 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
October 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Post-implantation erythema is a red skin condition after medical device implantation that sometimes goes away on its own.
 220 citations,
August 1988 in “Clinical endocrinology”
220 citations,
August 1988 in “Clinical endocrinology” Melatonin may help with sleep issues, depression, and cancer, but more research is needed.
 166 citations,
August 2010 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
166 citations,
August 2010 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” Scientists found a new, less invasive way to study body clocks using hair cells, which shows shift workers' body clocks don't match their lifestyles.
 113 citations,
March 2018 in “Biological reviews/Biological reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society”
113 citations,
March 2018 in “Biological reviews/Biological reviews of the Cambridge Philosophical Society” Animals that change color with the seasons mainly do so in response to daylight changes, but climate change is causing camouflage problems that may require evolutionary changes.
 67 citations,
January 2007 in “Climacteric”
67 citations,
January 2007 in “Climacteric” Estrogens and SERMs can help with skin aging, but their safety and effectiveness need more research.
 62 citations,
August 2014 in “BMC Endocrine Disorders”
62 citations,
August 2014 in “BMC Endocrine Disorders” New findings explain how genetic changes, body clocks, and certain molecules affect tissue response to stress hormones.
 59 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in medicine”
59 citations,
June 2022 in “Frontiers in medicine” There are still challenges in diagnosing and treating chronic skin diseases, but there is hope for future improvements.
 51 citations,
September 2015 in “Medical Clinics of North America”
51 citations,
September 2015 in “Medical Clinics of North America” The conclusion is that acne, alopecia, and hyperhidrosis are common skin issues with various treatments available, and accurate diagnosis is key for effective management.
 47 citations,
July 2013 in “Pharmacological Reviews”
47 citations,
July 2013 in “Pharmacological Reviews” Regenerative pharmacology, which combines drugs with regenerative medicine, shows promise for repairing damaged body parts and needs more interdisciplinary research.
 38 citations,
November 2000 in “Hastings Center Report”
38 citations,
November 2000 in “Hastings Center Report” The document suggests medicine should integrate biological and cultural factors and focus on holistic, equitable care.
 35 citations,
May 2012 in “Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews”
35 citations,
May 2012 in “Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews” Minoxidil effectively treats female pattern hair loss.
 21 citations,
May 2016 in “The Cochrane library”
21 citations,
May 2016 in “The Cochrane library” Topical minoxidil helps treat female pattern hair loss, but more research needed for other treatments.
 18 citations,
April 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
18 citations,
April 2004 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Skin patterns are formed by simple reaction-diffusion mechanisms.
 14 citations,
June 2016 in “Hypertension research”
14 citations,
June 2016 in “Hypertension research” New method uses hair follicle cells to estimate human body clock phase, potentially improving sleep disorder diagnosis.
 12 citations,
July 2017 in “Scientific reports”
12 citations,
July 2017 in “Scientific reports” Researchers developed a way to study human body clocks using hair tissue, which works similarly in both healthy and dementia patients.
 10 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine”
10 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine” The article explains how to identify and treat excessive hair growth in women, which can be distressing and may signal other health problems.
 2 citations,
October 2015 in “Human Gene Therapy”
2 citations,
October 2015 in “Human Gene Therapy” The congress highlighted new gene therapy techniques and cell transplantation methods for treating diseases.
 1 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
1 citations,
February 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Artificial hair implants can quickly improve looks and life quality, but they have risks like infection and early fiber loss, so more research is needed to confirm their safety and effectiveness.

The trial aims to understand how obesity and lifestyle affect circadian rhythms in people with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
 March 2024 in “GSC Advanced Research and Reviews”
March 2024 in “GSC Advanced Research and Reviews” Different light affects cell functions and can help treat skin conditions.
 January 2024 in “Diabetes & metabolism journal”
January 2024 in “Diabetes & metabolism journal” Disrupting natural body clocks increases the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The document provides detailed care instructions for elderly patients.
101 citations,
August 2008 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings” PAD is common but often missed, needing lifestyle changes and medication for better outcomes.
92 citations,
September 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” BMAL1 and Period1 genes can influence human hair growth.
66 citations,
June 2020 in “Advanced Intelligent Systems” Surgical robots have improved but still can't perform tasks or make decisions on their own.
37 citations,
August 2019 in “Frontiers in Microbiology” Staphylococcus epidermidis A/C strains are more antibiotic-resistant and infection-adapted, while B strains thrive in hair follicles.
28 citations,
June 2015 in “Journal of circadian rhythms” An individual's morning or evening preference can predict changes in their body clock gene expression.
27 citations,
August 2008 in “Mayo Clinic proceedings” Early recognition and treatment of Peripheral Arterial Disease is crucial to improve survival and health outcomes.
 8 citations,
May 2022 in “Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases”
8 citations,
May 2022 in “Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases” The UD-PrOZA program successfully diagnosed 18% of adult patients with rare diseases, often using genetic testing.























