 122 citations,
April 1995 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
122 citations,
April 1995 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” The document describes how to tell different types of non-scarring hair loss apart by looking at hair and scalp tissue under a microscope.
 January 2023 in “Frontiers in bioscience”
January 2023 in “Frontiers in bioscience” Artemis protein may help control hair growth and health by influencing cell processes.
 January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” Understanding hair structure and growth is key for diagnosing hair diseases accurately.
 May 2014 in “JAMA Dermatology”
May 2014 in “JAMA Dermatology” Mother and son diagnosed with a rare genetic hair loss condition with no effective treatment.
January 2012 in “Chinese Journal of Aesthetic Medicine” Increased androgen receptor expression in certain hair follicle areas may cause male pattern baldness.
 144 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
144 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Telogen effluvium is a common type of hair loss that can resolve on its own or become chronic, with treatment depending on early diagnosis.
 83 citations,
November 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
83 citations,
November 2002 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Low iron levels are not directly linked to chronic hair loss and iron supplements may not help.
 44 citations,
September 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology”
44 citations,
September 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology” Hair breakage may be an early sign of a hair loss condition called CCCA in African American women.
 41 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
41 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Effective hair loss assessment requires a mix of precise measurement methods.
 37 citations,
December 2010 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
37 citations,
December 2010 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Aging alone rarely causes significant hair loss; hormones are a bigger factor.
 3 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology”
3 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin Research and Technology” Frequent use of hair straighteners can cause hair loss similar to scarring alopecia in young Turkish women.
 3 citations,
July 1997 in “Current problems in dermatology”
3 citations,
July 1997 in “Current problems in dermatology” Hair restoration surgery has evolved over time, with a focus on natural-looking results and managing patient expectations, while also considering potential complications and the lifelong progression of male pattern baldness.
 April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
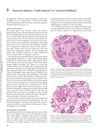
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” Senescent alopecia is a type of hair loss that occurs after age 50, not caused by genetics, and involves a gradual thinning of hair without significant inflammation.
34 citations,
March 2007 in “Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications” Thioredoxin reductase 1 does not affect glucocorticoid receptor activity in hair follicle cells.
 30 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
30 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” The most common causes of hair loss in Jordanian children are fungal infections, autoimmune hair loss, and hair shedding after fever, with zinc deficiency also being a notable cause.
 24 citations,
July 1987 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
24 citations,
July 1987 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Systemic diseases can cause hair loss, which is often reversible with treatment.
 July 2021 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal”
July 2021 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” Using lasers and fat grafting before hair transplant improves hair growth on scarred skin.
 30 citations,
August 1983 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America”
30 citations,
August 1983 in “Pediatric Clinics of North America” Most hair loss in children is caused by a few common conditions, and it's important to diagnose these properly and support the child's mental health.
 1 citations,
October 2012 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
October 2012 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A Korean girl developed kinky hair without known cause or effective treatment.
 January 2023 in “Open Life Sciences”
January 2023 in “Open Life Sciences” VEGFR-2 activation is likely involved in hair follicle growth, survival, and development.
 November 2017 in “Pediatrics in Review”
November 2017 in “Pediatrics in Review” A 4-year-old girl with hair loss was diagnosed with early-onset trichotillomania and improved with behavioral interventions.
September 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” The girl likely has Loose anagen hair syndrome, which may improve on its own or with minoxidil.
 27 citations,
September 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
27 citations,
September 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Traction may not be the only cause of cicatricial marginal alopecia.
 24 citations,
September 2018 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
24 citations,
September 2018 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Multiphoton microscopy can non-invasively tell apart scarring from non-scarring hair loss and could aid in treatment.
 3 citations,
February 2022 in “Frontiers in Genetics”
3 citations,
February 2022 in “Frontiers in Genetics” The LncRNA AC010789.1 slows down hair loss by promoting hair follicle growth and interacting with miR-21 and the Wnt/β-catenin pathway.
14 citations,
June 1989 in “Journal of dermatology” Three siblings had both Vohwinkel's disease and congenital alopecia, with no effective treatment.
 10 citations,
April 1976 in “Archives of Dermatology”
10 citations,
April 1976 in “Archives of Dermatology” A woman's significant hair loss was linked to rapid weight loss and hormone injections.
 1 citations,
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks”
1 citations,
April 2012 in “Informa Healthcare eBooks” The conclusion is that detailed clinical descriptions help pathologists diagnose hair loss conditions more accurately.
 January 2024 in “Pan African Medical Journal”
January 2024 in “Pan African Medical Journal” Non-scarring hair loss is common in lupus patients and can be diagnosed with specific hair and tissue tests.
 January 1991 in “Journal of Pediatric Health Care”
January 1991 in “Journal of Pediatric Health Care” Hair loss in children can be caused by fungal infections, trauma, autoimmune disorders, or stress, and treatments vary depending on the cause.


























