 6 citations,
October 1997 in “CNS Drugs”
6 citations,
October 1997 in “CNS Drugs” Psychotropic drugs can cause hair loss or excessive hair growth.
 3 citations,
June 2023 in “Medicines”
3 citations,
June 2023 in “Medicines” Some antiseizure medications can cause reversible hair loss, with valproate, lamotrigine, and carbamazepine being the most common.
 2 citations,
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Cancer treatments can cause skin-related side effects that may affect patient quality of life and require changes in treatment.
 November 2017 in “Pediatrics in Review”
November 2017 in “Pediatrics in Review” A 4-year-old girl with hair loss was diagnosed with early-onset trichotillomania and improved with behavioral interventions.
 March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The document lists various dermatology topics, treatments, and diagnostic methods.
 5 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications”
5 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Cosmetics, Dermatological Sciences and Applications” New treatments for hair loss are promising.
 8 citations,
May 2017 in “Singapore Medical Journal”
8 citations,
May 2017 in “Singapore Medical Journal” A Korean woman with complete hair loss regrew her hair after taking tofacitinib, with no side effects.

No treatment alters the natural progression of alopecia areata, and effectiveness varies, with some possibly working better in children.
 September 2023 in “JEADV Clinical Practice”
September 2023 in “JEADV Clinical Practice” People with common hair loss conditions may have a higher risk of heart disease and related health issues.
 83 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
83 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss that spreads out can often fix itself or be treated by finding and handling the cause.
 November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology”
November 2019 in “Harper's Textbook of Pediatric Dermatology” The document is a detailed medical reference on skin and genetic disorders.

Topical minoxidil helps treat hair loss in teens, but more research needed for safe options.
 20 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
20 citations,
March 2006 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Minoxidil and finasteride can help with hair loss, but more research is needed to improve treatments for certain types of hair loss.
 23 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings”
23 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disease affecting hair follicles, influenced by genetic and environmental factors, with rodent models being essential for research.
 52 citations,
March 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
52 citations,
March 2010 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Alopecia areata shows a unique type 1 interferon signature, suggesting potential treatment by targeting this pathway.

Baricitinib quickly improved severe alopecia areata, with almost total hair regrowth in three months.
 September 2024 in “Archiv Euromedica”
September 2024 in “Archiv Euromedica” Trichoscopy is a quick, accurate, and non-invasive method to diagnose and treat non-scarring hair loss.

The document concludes that hair loss in women is complex, often linked to aging, health conditions, and nutritional deficiencies, and emotional impacts should not be underestimated.
 8 citations,
January 2020 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Nursing”
8 citations,
January 2020 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Nursing” The article concludes that different types of hair loss require specific treatments and psychological support is important.
 53 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
53 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Cancer treatments often cause hair disorders, significantly affecting patients' quality of life, and better management methods are needed.
14 citations,
April 2021 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Mesenchymal stem cells may help treat hair loss by improving hair cell growth and reducing inflammation.
 18 citations,
May 2016 in “Annals of Medicine”
18 citations,
May 2016 in “Annals of Medicine” The article concludes that correctly diagnosing systemic causes of hair loss requires a detailed clinical evaluation and a systematic diagnostic approach.
 January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery”
January 2012 in “Yearbook of Dermatology and Dermatologic Surgery” Alopecia areata is a hair loss condition that often starts before age 30 and can affect various body parts, with unpredictable hair regrowth chances.
 9 citations,
October 2021 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
October 2021 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Tofacitinib is effective and safe for treating severe hair loss in a Saudi population.
 May 2023 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
May 2023 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Alopecia areata has a high chance of persisting and relapsing, with a significant risk of total hair loss, especially if it starts in childhood.
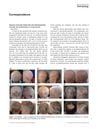 1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” A 6-year-old girl with alopecia universalis regrew most of her hair after treatment with simvastatin/ezetimibe, minoxidil, and prednisolone.
 41 citations,
August 2007 in “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology”
41 citations,
August 2007 in “European Journal of Gastroenterology & Hepatology” A woman's total hair loss from hepatitis C treatment grew back after stopping the medication.
 39 citations,
April 2016 in “Case Reports in Dermatology”
39 citations,
April 2016 in “Case Reports in Dermatology” Tofacitinib temporarily regrew hair in a man with alopecia, but its effects didn't last.
 16 citations,
July 2017 in “Rheumatology and Therapy”
16 citations,
July 2017 in “Rheumatology and Therapy” Tofacitinib, a medication for arthritis, showed potential for treating severe hair loss in a small Brazilian case series, but more research is needed.
 9 citations,
August 2018 in “JAAD Case Reports”
9 citations,
August 2018 in “JAAD Case Reports” Tofacitinib can temporarily improve hair growth in alopecia universalis, but its effectiveness may decrease over time.





























