 37 citations,
March 1990 in “The Journal of Pediatrics”
37 citations,
March 1990 in “The Journal of Pediatrics” Toxic shock syndrome is caused by a complex interaction of bacterial toxins and the immune system, and understanding this can help improve diagnosis and treatment.
[object Object]  33 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of clinical immunology”
33 citations,
September 2017 in “Journal of clinical immunology” New treatments for immune disorders caused by FOXN1 deficiency are promising.
 32 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
32 citations,
January 2012 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Skin side effects from EGFR inhibitor cancer treatment can be managed effectively, often without stopping the medication.
 26 citations,
June 2018 in “The journal of immunology/The Journal of immunology”
26 citations,
June 2018 in “The journal of immunology/The Journal of immunology” AIRE-deficient rats developed severe autoimmune disease similar to APECED, useful for testing treatments.
 26 citations,
September 1969 in “The American journal of medicine”
26 citations,
September 1969 in “The American journal of medicine” Cronkhite-Canada Syndrome often leads to death within 6-18 months.
 22 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
22 citations,
March 2021 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Ultrasound is a useful, non-invasive tool in dermatology for diagnosing skin conditions and guiding treatments, but it has some limitations.
 21 citations,
January 2013 in “Clinical Endoscopy”
21 citations,
January 2013 in “Clinical Endoscopy” First Korean case of Cronkhite-Canada syndrome with colon cancer and serrated adenoma.
 19 citations,
August 2020 in “Gastroenterology report”
19 citations,
August 2020 in “Gastroenterology report” There is no standard treatment for the rare Cronkhite–Canada syndrome, which can be fatal and lead to cancer.
 13 citations,
August 1982 in “Archives of dermatology”
13 citations,
August 1982 in “Archives of dermatology” A new side effect of aromatic retinoid treatment is soft nails.
 10 citations,
October 2017 in “Archivos Argentinos De Pediatria”
10 citations,
October 2017 in “Archivos Argentinos De Pediatria” Most hospitalized children with skin issues were boys, with allergic skin diseases like atopic dermatitis being most common, and treatments were usually topical.
 7 citations,
December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
December 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The report suggests that hair loss in Cronkhite-Canada syndrome may be caused by alopecia areata incognita, as shown by a patient's improvement with treatment.
 7 citations,
October 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
October 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” HIV can cause skin disorders, which are often the first sign of infection, especially in people with darker skin.
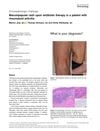 1 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Methotrexate caused a rare skin rash in a rheumatoid arthritis patient, which resolved after stopping the drug.
 1 citations,
May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
May 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Lichen planus pigmentosus and fibrosing frontal alopecia in Colombia are likely different stages of the same disease.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” Chemotherapy can cause skin side effects that affect patients' lives, but they can be managed to avoid interrupting cancer treatment.
 June 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
June 2020 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” The HoxC gene cluster and its enhancers are essential for developing hair and nails in mammals.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” PDE inhibitors, especially PDE4 inhibitors like apremilast, are effective for certain inflammatory skin conditions but have side effects and can be costly.
 September 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
September 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” People with advanced chronic kidney disease often have skin problems, which can be treated with various medications and procedures to improve their quality of life.
 January 1993 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
January 1993 in “Side effects of drugs annual” Natural products like propolis are causing more skin allergies, and certain skin treatments and medications have various side effects and risks.
 109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics”
109 citations,
September 2011 in “Human molecular genetics online/Human molecular genetics” New treatments targeting specific genes show promise for treating keratin disorders.
 13 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic therapy”
13 citations,
December 2001 in “Dermatologic therapy” Alopecia areata causes varying hair loss patterns, affecting hair, nails, and possibly glands, with treatment outcomes depending on disease duration and extent.
[object Object]  60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology”
60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology” Lymphocytes, especially CD8+ T cells, play a key role in causing alopecia areata, and targeting them may lead to new treatments.
 13 citations,
September 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders”
13 citations,
September 2017 in “Skin appendage disorders” Some women with Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia also have Lichen Planopilaris, which can lead to more symptoms and affect hair outside the scalp.
 4 citations,
July 2019 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
4 citations,
July 2019 in “Clinics in Dermatology” The document concludes that while white skin, nail, and mucosa diseases increase skin cancer risk, they are generally harmless, especially compared to darker pigmentation conditions.
 February 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
February 2006 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Most patients with anal Pemphigus Vulgaris had repeated episodes but fully recovered with treatment, without long-term problems.
 78 citations,
April 1994 in “Archives of dermatology”
78 citations,
April 1994 in “Archives of dermatology” The study found that Keratosis Pilaris Atrophicans is a genetic skin condition that starts in childhood, involves inflammation and scarring, and current treatments are only somewhat effective.
 35 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
35 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Intralesional triamcinolone acetonide is effective for treating patchy hair loss, and dermoscopy helps detect treatment response and side effects early.
 December 2024 in “Nutrients”
December 2024 in “Nutrients” Skin, hair, and nail changes can help detect eating disorders early.
 March 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
March 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Alopecia areata is relatively common in children, has a variable course, and shows different responses to treatment; thyroid testing is recommended for those affected.
 January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology”
January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology” Many treatments for alopecia areata have inconsistent results; for under 10s, use minoxidil with a corticosteroid, and for over 10s, add ILC and consider diphenylcyclopropenone for widespread cases.






























