
Alopecia areata, a type of hair loss, may be passed through T cells and has genetic links, while treatments vary in effectiveness. Male pattern baldness can be treated with finasteride and is influenced by androgens in hair follicles.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Springer eBooks” The document explains how hair loss patterns in men and women, known as Androgenetic alopecia, are classified using the Hamilton-Norwood system for men and the Ludwig grade system for women.
 January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” The document explains how hair loss in men and women, known as Androgenetic alopecia, is categorized using the Hamilton-Norwood system for men and the Ludwig grade system for women.
[object Object]  666 citations,
September 1977 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
666 citations,
September 1977 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Common baldness, also known as Androgenetic Alopecia, is caused by a combination of genetic factors and hormones called androgens.
 47 citations,
September 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
47 citations,
September 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Ludwig pattern hair loss in women results from varying sensitivity in hair follicles, causing fewer visible hairs.
 30 citations,
June 2019 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
30 citations,
June 2019 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” The document concludes that managing non-classical congenital adrenal hyperplasia in females requires personalized treatment, genetic counseling, and a team of specialists.
 1 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatology” Baldness is common in Korean men (60.5%), and those with a family history are 3.1 times more likely to have hairline recession.
 31 citations,
March 2011 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
31 citations,
March 2011 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The new hairline classification and correction methods can improve the appearance of Asian women with wide or M-shaped foreheads.
 8 citations,
October 2016 in “Experimental dermatology”
8 citations,
October 2016 in “Experimental dermatology” Hair follicles may help teach the immune system to tolerate new self-antigens, but this can sometimes cause hair loss.
 4 citations,
May 2002 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal”
4 citations,
May 2002 in “Aesthetic Surgery Journal” A new hair loss classification for women improves treatment, but careful patient selection is crucial for successful hair transplantation.
 5 citations,
June 2020 in “Journal of Endocrinological Investigation”
5 citations,
June 2020 in “Journal of Endocrinological Investigation” Women with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) have more sexual function issues than those with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), but physical activity can improve sexual functioning in all women.
 February 2020 in “Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences”
February 2020 in “Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences” The patient with severe hirsutism improved after being diagnosed with non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia and treated with corticosteroids.
1 citations,
January 2024 in “Pharmaceuticals” A new carrier improves skin delivery of tofacitinib for treating inflammatory skin diseases.
 73 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
73 citations,
March 2009 in “Seminars in Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” The document concludes that accurate diagnosis of hair disorders is crucial and requires a range of diagnostic methods.
 42 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
42 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The conclusion is that oral contraceptives and antiandrogens can treat hirsutism and acne in women with cutaneous hyperandrogenism, but more research is needed for effective treatments, especially for hair loss.
[object Object]  1 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
August 2018 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Combination of minoxidil and finasteride is more effective in increasing hair diameter than minoxidil alone for female-pattern hair loss.
 4 citations,
October 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology”
4 citations,
October 2012 in “Archives of Dermatology” Hair diameter diversity is a key sign for diagnosing and managing male pattern baldness.
 January 2020 in “Medpulse International Journal of General Medicine”
January 2020 in “Medpulse International Journal of General Medicine” Trichoscopy helps diagnose and monitor hair loss, showing different signs at various stages of hair thinning.
 27 citations,
December 2005 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
27 citations,
December 2005 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” Niacin derivatives may increase hair fullness in women with hair loss.
 15 citations,
October 2003 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
15 citations,
October 2003 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplantation combined give best results for hair loss.
 1 citations,
October 2012 in “Gynäkologische Endokrinologie”
1 citations,
October 2012 in “Gynäkologische Endokrinologie” The document concludes that proper diagnosis and individualized treatment are crucial for managing androgenization in women effectively.
 November 2003 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
November 2003 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplantation combined give best results for hair loss.
 56 citations,
December 2011 in “Steroids”
56 citations,
December 2011 in “Steroids” The document suggests treating individuals with nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia who show symptoms, especially those related to excess male hormones.
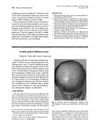 9 citations,
November 1993 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
9 citations,
November 1993 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some men can have female pattern baldness without hormonal abnormalities or signs of feminization.
 November 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
November 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Finasteride and minoxidil are effective, low-risk treatments for male hair loss, and patient education on these therapies is important.
 277 citations,
July 2002 in “Molecular Endocrinology”
277 citations,
July 2002 in “Molecular Endocrinology” Removing part of the vitamin D receptor stops vitamin D from working properly.
 145 citations,
March 2010 in “Fertility and Sterility”
145 citations,
March 2010 in “Fertility and Sterility” Different types of polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have varying severity, with Type I being the most severe and common.
 22 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
22 citations,
May 1999 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair loss from genetics and hormones can be treated with drugs or surgery.
 21 citations,
May 1996 in “Current problems in dermatology”
21 citations,
May 1996 in “Current problems in dermatology” Detailed patient history and physical exams are crucial for diagnosing hair loss.



























