 30 citations,
November 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery”
30 citations,
November 2008 in “Facial Plastic Surgery” The conclusion is that the best approach for treating Female Pattern Hair Loss is a combination of different treatments.
22 citations,
September 2014 in “JAMA dermatology” Ichthyosis with confetti is a genetic skin disorder with consistent ectodermal malformations and various KRT10 gene mutations.
 January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders”
January 2023 in “Skin appendage disorders” Low-dose oral minoxidil may help treat hair loss but is not FDA-approved and can cause side effects like unwanted hair growth and heart issues.
 July 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
July 2008 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Cyclosporin doesn't stop hair loss.
 131 citations,
March 2004 in “The American journal of pathology”
131 citations,
March 2004 in “The American journal of pathology” Modulating BMP activity changes the number, size, shape, and type of ectodermal organs.
1 citations,
January 2021 in “Skin appendage disorders” Alopecia areata in children is usually mild and effectively treated with strong topical steroids.
 January 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2019 in “Elsevier eBooks” Early detection and skin biopsies are crucial for treating skin cancer and diagnosing various skin conditions.
 3 citations,
April 2012 in “Bioinformation”
3 citations,
April 2012 in “Bioinformation” Two specific SNPs in the TRPS1 gene cause excessive hair growth by altering the protein's structure.
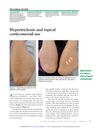 February 2022 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine”
February 2022 in “Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine” Prolonged use of topical corticosteroids can cause excessive hair growth.
 May 2003 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
May 2003 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Hair loss can be treated with medications like minoxidil and finasteride or surgery, but treatment effectiveness varies by alopecia type and accurate diagnosis is important.
 November 2024 in “Skin Health and Disease”
November 2024 in “Skin Health and Disease” Minoxidil is effective for promoting hair growth and has various dermatological uses.
 1 citations,
October 1984 in “Clinics in dermatology”
1 citations,
October 1984 in “Clinics in dermatology” People distressed by minor skin changes should consult dermatologists with cosmetic expertise, and a public Cosmetic Dermatology Service with mental health support is recommended.
 4 citations,
January 2012 in “Chemical Immunology”
4 citations,
January 2012 in “Chemical Immunology” Some drugs, especially biologics, can cause skin reactions that look like other skin diseases, and stopping the drug usually helps clear up these reactions.
 11 citations,
March 2008 in “Experimental Dermatology”
11 citations,
March 2008 in “Experimental Dermatology” A substance called compound-1 could help increase hair growth by maintaining prostaglandin levels in hair follicles.
 195 citations,
May 2003 in “Obstetrics and gynecology (New York. 1953. Online)/Obstetrics and gynecology”
195 citations,
May 2003 in “Obstetrics and gynecology (New York. 1953. Online)/Obstetrics and gynecology” Most women with excess hair growth have an underlying hormonal issue, often treated with medication and hair removal methods.
 January 1989 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
January 1989 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” The symposium concluded that hair growth involves complex processes, including the hair follicle life cycle, the role of the dermal papilla, hair strength, pigmentation, and the impact of diseases and treatments like minoxidil on hair and skin.
 November 2023 in “International Journal of Medical Sciences”
November 2023 in “International Journal of Medical Sciences” New regenerative medicine-based therapies for hair loss look promising but need more clinical validation.
 19 citations,
January 1997 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
19 citations,
January 1997 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Most treatments for hair loss in 1997 were not effective for most people, and maintaining hair growth was difficult.
 January 2021 in “Erciyes medical journal”
January 2021 in “Erciyes medical journal” The COVID-19 pandemic changed the types of skin conditions seen at a clinic, with fewer patients and varying numbers of specific conditions.
 61 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
61 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Hair usually grows back 1-3 months after treatment for anagen effluvium, and children with Loose Anagen Hair Syndrome often improve by adolescence.
 16 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
16 citations,
January 2005 in “Pediatric Dermatology” A 10-year-old girl with Fox Fordyce disease improved with treatment, suggesting the disease can occur before puberty and might be underdiagnosed in young girls.
 21 citations,
March 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
21 citations,
March 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” Immune cells around hair follicles help control hair growth and could be targets for treating hair disorders.
 May 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
May 2003 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The meeting covered advances in understanding hair growth, causes of hair loss, and potential treatments.
 26 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
26 citations,
April 1999 in “Dermatologic Clinics” The long-pulsed alexandrite laser is effective for hair reduction, particularly for light-skinned individuals with dark hair, but caution is needed for darker skin.
 15 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
15 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Two plywood factory workers developed contact dermatitis from phenol-formaldehyde resin, a known allergen.
 12 citations,
November 1996 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
12 citations,
November 1996 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” A kidney transplant patient on cyclosporin experienced unexpected severe hair loss, which improved with treatment adjustments.
 10 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
July 2002 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Careful management of blood thinners is crucial for lupus patients with APS.
 1 citations,
January 2005 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
1 citations,
January 2005 in “Side effects of drugs annual” The document concluded that various dermatological treatments have different effectiveness and side effects, with some causing irritation, allergic reactions, or systemic effects.
 December 2017 in “Springer eBooks”
December 2017 in “Springer eBooks” Transplant patients often get skin problems, with treatments varying by condition.
 July 2011 in “Springer eBooks”
July 2011 in “Springer eBooks” The document concluded that FDA-approved treatments like minoxidil and finasteride are effective for hair loss, while the effectiveness of natural remedies and other non-approved treatments is not well-supported by evidence.




























