15 citations,
February 2014 in “PloS one” LIPH mutations in Japan cause varying degrees of hair loss and woolly hair.
September 2016 in “Journal of dermatological science” The conclusion is that the variation in hair thinness in patients is mostly due to the amount of underdeveloped hairs, and treatments that thicken fine hairs might work for those with mild to severe conditions.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Researchers found a new genetic mutation linked to a hair condition in a Japanese boy.
March 2022 in “Journal of cosmetic dermatology” Botanical extracts can help treat hair loss in people with certain genetic conditions.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Certain gene mutations in Japanese people are linked to different types of hair loss, with some causing mild hair thinning and others leading to complete baldness.
 9 citations,
February 2018 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
February 2018 in “The Journal of Dermatology” A new mutation in the LIPH gene was found to cause a rare hair disorder in a Japanese boy.
7 citations,
February 2011 in “Journal of dermatology” The 736T>A mutation in the LIPH gene is common in Japanese people with autosomal recessive woolly hair.
 7 citations,
March 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
7 citations,
March 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Applying minoxidil can help improve hair growth in people with hair loss caused by LIPH gene mutations.
 February 2023 in “Journal of dermatology”
February 2023 in “Journal of dermatology” The first Japanese case of a genetic hair disorder caused by specific mutations in the LIPH gene was identified.
1 citations,
September 2020 in “Journal of dermatology” Researchers found a new mutation in the LIPH gene of a woman with a rare hair condition.
 May 2024 in “Frontiers in medicine”
May 2024 in “Frontiers in medicine” A genetic mutation in the LIPH gene causes tightly curled hair that stops growing in some Japanese individuals.
 12 citations,
July 2016 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
12 citations,
July 2016 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Different hair fiber development might explain why hair loss severity varies in patients with a specific genetic mutation, and treatments that thicken hair could help.
 1 citations,
February 2013 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
February 2013 in “InTech eBooks” Genetic mutations cause various hair diseases, and whole genome sequencing may reveal more about these conditions.
 41 citations,
November 2011 in “The Journal of Dermatology”
41 citations,
November 2011 in “The Journal of Dermatology” Some hair loss disorders are caused by genetic mutations affecting hair growth.
 1 citations,
February 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
February 2009 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Lipase H is important for hair follicle function and shaping hair fibers.
June 2022 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Oral minoxidil and growth factors improved hair density and thickness in a girl with hereditary hair loss.
9 citations,
May 2021 in “JEADV. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology/Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Topical minoxidil may help treat a rare genetic hair condition with no fully effective treatments yet.
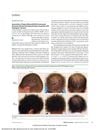 5 citations,
July 2020 in “JAMA Dermatology”
5 citations,
July 2020 in “JAMA Dermatology” Minoxidil solution applied twice daily improved hair growth in patients with Woolly Hair/Hypotrichosis due to LIPH gene issues, with mild side effects.
11 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A specific mutation in PA-PLA1α causes abnormal hair growth.
 26 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
26 citations,
December 2011 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” New gene identification techniques have improved the understanding and classification of inherited hair disorders.
 8 citations,
April 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
8 citations,
April 2015 in “British Journal of Dermatology” White piedra, a rare fungal infection, was diagnosed in two women in a northern climate.
 2 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
2 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Squarticles, tiny particles made from sebum-derived lipids, can effectively deliver minoxidil, a hair growth drug, directly to hair follicles and skin cells, with less skin penetration and more tolerability.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Certain factors can start hair growth in adult skin by making cells communicate and form new hair follicles.
 1 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
1 citations,
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” FGF18 treatment during hair's resting phase can protect against hair loss from radiation.
 September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
September 2016 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” Wnt-10b is important for keeping mouse skin cells healthy for hair growth.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” DHT reduces a cell's ability to promote hair growth, while 3D culture without DHT improves it.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The endocannabinoid system affects oil production and inflammation in skin cells.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Zinc deficiency disrupts hair growth and cycle, but zinc supplements can fix this.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The research found that certain microRNAs are important for human hair growth and health.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”





















