 1 citations,
November 2001 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2001 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Oral cyclosporin doesn't stop hair loss.
 16 citations,
April 1984 in “Archives of Dermatology”
16 citations,
April 1984 in “Archives of Dermatology” Topical minoxidil can help hair regrowth in alopecia areata patients, but maintaining the growth after stopping treatment is inconsistent.
 1 citations,
December 2017
1 citations,
December 2017 The study suggests that treating early hair loss with Nourkrin® with Marilex® can help prevent further hair loss and may be linked to reducing the risk of lifestyle diseases.
 January 2018 in “Sohag Medical Journal”
January 2018 in “Sohag Medical Journal” Combining topical dutasteride with microneedling is more effective for hair growth than microneedling alone.
 4 citations,
September 2020 in “Frontiers in Microbiology”
4 citations,
September 2020 in “Frontiers in Microbiology” Algal oligosaccharides help prevent hair loss and promote hair growth.
 2 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
2 citations,
July 2023 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” The topical treatment reduced hair loss and improved hair growth in patients with certain types of hair loss.
 4 citations,
October 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
4 citations,
October 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” Dermoscopy shows that diffuse alopecia areata progresses through specific hair growth stages.
 51 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
51 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil keeps most hair growth from first year and twice-daily use is better with few side effects.
 15 citations,
May 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
15 citations,
May 2017 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Latanoprost works better for hair growth, and combining it with betamethasone valerate is most effective.
 10 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
10 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Cold caps and certain drugs may help prevent or reduce hair loss from chemotherapy, but more research is needed.
 61 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
61 citations,
January 2013 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Hair usually grows back 1-3 months after treatment for anagen effluvium, and children with Loose Anagen Hair Syndrome often improve by adolescence.
 23 citations,
January 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
23 citations,
January 2019 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Finasteride improves hair growth and reduces hirsutism in women, but side effects and optimal dosages need further research.
 4 citations,
July 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment”
4 citations,
July 2021 in “Journal of Dermatological Treatment” Finasteride helps hair growth but may cause sexual side effects and depression.
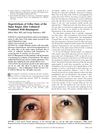 15 citations,
March 2004 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology”
15 citations,
March 2004 in “American Journal of Ophthalmology” Using bimatoprost on one side of the face caused increased cheek hair growth in a patient.
 3 citations,
July 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
July 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Effective treatments for excessive hair growth in women include creams, laser therapy, and medications, with the choice depending on individual needs and potential side effects.
 August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
August 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Some men don't respond to common hair loss treatments, but a new inhibitor, FOL-005, shows promise for targeting unwanted hair growth.
 14 citations,
January 2006 in “Skinmed”
14 citations,
January 2006 in “Skinmed” A woman developed white patches on her skin and curly hair after hepatitis C treatment, likely due to the medication interferon alpha.
 58 citations,
October 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
58 citations,
October 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Activating Nrf2 protects human hair follicles from oxidative stress and helps prevent hair growth inhibition.

The new treatment regimen was effective in promoting significant hair growth in all 15 male patients with androgenic alopecia.
 15 citations,
January 1988 in “Drugs”
15 citations,
January 1988 in “Drugs” The document concludes that treatments for female hair loss and excessive hair growth are temporary and not well-studied.
 17 citations,
October 2015 in “Medicine and Pharmacy Reports”
17 citations,
October 2015 in “Medicine and Pharmacy Reports” Animal models are crucial for learning about hair loss and finding treatments.
 4 citations,
January 2023 in “Skin health and disease”
4 citations,
January 2023 in “Skin health and disease” Blocking Janus kinase 1 helps stop inflammation and regrow hair, making it a good treatment for hair loss from alopecia areata.
 1 citations,
January 1967 in “The BMJ”
1 citations,
January 1967 in “The BMJ” The document concludes that while some hair and scalp disorders can be treated, hair loss from destroyed follicles is permanent, and damaged hair can only regrow naturally.
 December 2021 in “Biomedical journal of scientific & technical research”
December 2021 in “Biomedical journal of scientific & technical research” Oral processed egg yolk improves hair regrowth and quality in alopecia patients.
 36 citations,
November 1995 in “Clinical endocrinology”
36 citations,
November 1995 in “Clinical endocrinology” Low-dose flutamide helps reduce excessive hair growth and is even more effective with birth control, without bad effects on blood fats.
 September 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
September 2014 in “Springer eBooks” Aging causes hair to gray and thin, with the timing of graying varying by race, and factors like oxidative stress and genetics can lead to hair loss.
 36 citations,
May 2015 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
36 citations,
May 2015 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” Low dose oral minoxidil helps regrow hair in permanent chemotherapy-induced alopecia.
 1 citations,
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2009 in “CRC Press eBooks” Finasteride increases hair count and improves hair growth with low risk of side effects.
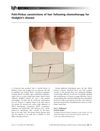 8 citations,
February 2005 in “British Journal of Haematology”
8 citations,
February 2005 in “British Journal of Haematology” Chemotherapy caused the patient's hair to have alternating thick and thin segments.
 87 citations,
July 2018 in “Nursing Clinics of North America”
87 citations,
July 2018 in “Nursing Clinics of North America” PCOS is a common hormonal disorder in women, marked by symptoms like hair growth and menstrual issues, and requires personalized treatment.






























