 19 citations,
August 1993 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology”
19 citations,
August 1993 in “Journal of Cutaneous Pathology” Alopecia causes smaller hair follicles and affects growth-related structures.
 1 citations,
January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2017 in “Elsevier eBooks” The document concludes that new treatments for hair loss may involve a combination of cosmetics, clinical methods, and genetic approaches.
28 citations,
July 1993 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Dermal papilla cells are crucial for hair growth and can induce new hair follicles.
January 2010 in “Actas dermo-sifiliográficas/Actas dermo-sifiliográficas” Chemical relaxers may cause scarring alopecia in black women.
 25 citations,
December 1992 in “Seminars in cell biology”
25 citations,
December 1992 in “Seminars in cell biology” Skin stem cells are maintained by signals from nearby cells and vary in their ability to renew and mature.
 22 citations,
July 2003 in “Military medicine”
22 citations,
July 2003 in “Military medicine” New treatments are available for managing ingrown hair inflammation.
January 2008 in “한국미용학회지” Sandalwood and rose absolute oils can help hair regrow faster.
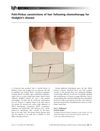 8 citations,
February 2005 in “British Journal of Haematology”
8 citations,
February 2005 in “British Journal of Haematology” Chemotherapy caused the patient's hair to have alternating thick and thin segments.
 68 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
68 citations,
April 2012 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The conclusion is that Fgf18 and Tgf-ß signaling could be targeted for hair loss treatments.
 18 citations,
March 2003 in “PubMed”
18 citations,
March 2003 in “PubMed” Hair loss in women can be due to abnormal hair growth cycles or damaged hair follicles, with the most common type being androgenetic alopecia; treatment varies by cause, and the psychological impact is significant.
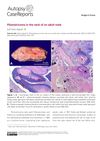 January 2022 in “Autopsy and Case Reports”
January 2022 in “Autopsy and Case Reports” A man had a non-cancerous neck tumor related to hair follicles removed with no return of the tumor.
78 citations,
June 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Curly hair shape is determined by the hair bulb.
8 citations,
July 2020 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” Excessive sun protection might cause frontal fibrosing alopecia by disrupting skin immune balance.
34 citations,
June 2020 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Frontal fibrosing alopecia is linked to increased immune system activity and reduced stem cells, suggesting early treatment targeting this pathway might prevent hair follicle damage.
 33 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Science”
33 citations,
January 2006 in “Journal of Dermatological Science” A long-acting Vitamin C derivative helps hair grow by stimulating cells and increasing growth factors.
 33 citations,
October 2004 in “Archives of Dermatological Research”
33 citations,
October 2004 in “Archives of Dermatological Research” Large prostate links to more hair loss, but age of onset doesn't affect it.
2 citations,
February 2023 in “International journal of molecular sciences” Body hairs can be used in forensic science and toxicology like scalp hair.
 December 2021 in “Medicina estética”
December 2021 in “Medicina estética” Serenoa repens may help treat hair loss but is less effective than common medications and needs more research to confirm its effectiveness.
3 citations,
January 2003 in “Facial plastic surgery” Laser hair removal is a noninvasive way to reduce unwanted hair long-term.
 September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
September 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The research concluded that hyaluronic acid affects the formation and growth of hair follicle-like structures in a lab setting.
 26 citations,
March 2014 in “International journal of pharmaceutics”
26 citations,
March 2014 in “International journal of pharmaceutics” Researchers created a skin treatment that could effectively deliver medication into hair follicles.
96 citations,
February 2002 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Pseudofolliculitis barbae is a chronic skin condition affecting mainly African American and Hispanic individuals, caused by shaving tightly curled hair, and managed by prevention and treatment but not curable.

Black hair's diversity in patterns and textures is influenced by follicle shape and keratin, and it holds cultural, artistic, and mathematical significance.
 September 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
September 2024 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Estetrol (E4) may help treat female pattern hair loss by prolonging hair growth.
19 citations,
January 2012 in “Dermatology” Topical human epidermal growth factor may effectively treat acne caused by cancer medication.
 December 2024 in “Veterinary Sciences”
December 2024 in “Veterinary Sciences” Key genes and pathways improve wool quality in Zhexi Angora rabbits.
 3 citations,
October 2007 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
3 citations,
October 2007 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Hair ages due to various factors and treatments like minoxidil and finasteride can help, but more research and better public awareness are needed.
745 citations,
February 1992 in “Trends in genetics” Hair follicles create different cell layers and proteins, controlled by various molecules.
October 2015 in “CRC Press eBooks” Trichoscopy is a useful tool for examining and monitoring hair and scalp conditions.
 12 citations,
June 2006 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
12 citations,
June 2006 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” The study found average numbers for different types of hair follicles in the scalp and observed differences between men and women, suggesting reasons for more common hair shedding in women.


















