 1 citations,
April 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2010 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” The document concludes that early diagnosis and treatment are crucial for managing rare hair loss disorders and that more research is needed to improve treatment strategies.
 4 citations,
May 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology”
4 citations,
May 2015 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology, Venereology and Leprology” Congenital triangular alopecia can occur outside the typical fronto-temporal region.
January 2020 in “International journal of scientific research” Dermoscopy shows that varying hair shaft thickness and single hair follicles are main signs of male pattern baldness, especially in the fronto-temporal region.
January 2021 in “International journal of dermatology, venereology and leprosy sciences” AGA and TE can be differentiated by specific trichoscopic features, with AGA showing more variation in hair thickness in fronto-temporal areas.
 14 citations,
January 2006 in “Australasian journal of dermatology”
14 citations,
January 2006 in “Australasian journal of dermatology” Alopecia areata can look like frontal fibrosing alopecia, making diagnosis hard.
 June 2021 in “Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences”
June 2021 in “Pakistan Journal of Medical and Health Sciences” The study found no link between hair loss, stress, and smoking among men in Lahore.
PRP treatment mildly to moderately improves hair loss in most men with AGA.
 18 citations,
November 2012 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
18 citations,
November 2012 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” A 66-year-old man with a rare case of male frontal fibrosing alopecia did not regrow hair despite treatment.
 49 citations,
January 2003 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
49 citations,
January 2003 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” The document concludes that post-menopausal frontal fibrosing alopecia is a poorly understood condition that does not respond well to common treatments.
April 2023 in “Dohuk medical journal” Trichoscopy effectively differentiates Androgenetic Alopecia from Telogen Effluvium.
 17 citations,
January 2015 in “International Journal of Trichology”
17 citations,
January 2015 in “International Journal of Trichology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia may affect nails and could be a type of lichen planus, treatable with certain medications.
 24 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
24 citations,
September 2014 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Trichoscopy is reliable for diagnosing Temporal Triangular Alopecia and can prevent unnecessary biopsies and wrong treatments.
 1 citations,
February 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation”
1 citations,
February 2014 in “Hair therapy & transplantation” A baby boy had two types of temporary hair loss at birth, which might be two forms of newborn hair loss combined.
 13 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
13 citations,
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” CTA is often mistaken for AA but doesn't respond to steroids and may require hair transplantation.
 58 citations,
April 2009 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
58 citations,
April 2009 in “Dermatologic Surgery” Most women have a widow's peak and specific hairline features useful for designing hair restoration surgery.
 2 citations,
May 2005 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery”
2 citations,
May 2005 in “Seminars in Plastic Surgery” The Juri Temporo-Parieto-Occipital Flap is a good option for scalp reconstruction and hairline restoration with a natural look, despite some risk of necrosis and scarring.
 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Congenital triangular alopecia is a harmless, non-spreading hair loss condition often seen in young children.
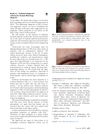 8 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
8 citations,
December 2017 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” The authors updated the criteria for diagnosing frontal fibrosing alopecia, making it easier to diagnose without a biopsy.
14 citations,
January 2014 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology Venereology and Leprology” Frontal fibrosing alopecia can affect men's beards and leads to permanent hair loss.
 33 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
33 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Lack of small, fine hair on the front hairline is a key sign of frontal fibrosing alopecia.
 3 citations,
February 1990 in “Contact Dermatitis”
3 citations,
February 1990 in “Contact Dermatitis” Contact dermatitis may speed up hair loss in some cases.
 2 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
2 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Female pattern hair loss involves thinning hair on crown and frontal scalp, diagnosed by hair ratio, and treated with minoxidil, antiandrogens, or hair transplantation.
 1 citations,
May 2024 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
1 citations,
May 2024 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Frontal Fibrosing Alopecia needs better diagnostics and treatments, with dutasteride showing promise.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The conclusion introduces a new way to classify skin cysts using their shape and genetic markers.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” A new peptide, FOL-005, may help treat excessive hair growth by reducing a hair growth promoter, FGF7.
 April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” 17β-estradiol may help hair growth by increasing cannabinoid receptor type 1.
 April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Removing Lrig1-positive stem cells in mice causes temporary loss of sebaceous glands.
 April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Electrical epilation damages hair follicles and surrounding skin, likely preventing hair regrowth.
 January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology”
January 2011 in “International Journal of Trichology” The document concludes that doctors should recognize congenital triangular alopecia to avoid unnecessary treatments, as it does not respond to steroids like alopecia areata does.
 86 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
86 citations,
July 2002 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” FPHL is a common, age-related, genetic hair loss with unclear causes and limited treatment options.

























