 1 citations,
December 2022 in “BMC Genomics”
1 citations,
December 2022 in “BMC Genomics” The Msx2 gene affects feather development in Hungarian white geese and a specific gene variation could indicate feather quality.
1 citations,
April 2022 in “Applied sciences” Bitter melon extract may help prevent hair loss and can be used in cosmetic products.
[object Object] August 2024 in “Cosmetics” Peanut callus extract helps grow hair and prevent hair loss.
December 2023 in “Asian journal of beauty & cosmetology” Melatonin improves tomato root growth and plant health at certain levels by affecting genes and hormones but can damage roots at high levels.
October 2022 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Fish collagen peptides can significantly promote hair growth.
 81 citations,
May 2007 in “Fertility and Sterility”
81 citations,
May 2007 in “Fertility and Sterility” Testosterone therapy seems safe for postmenopausal women for a few years, but more research is needed for long-term effects.
 11 citations,
December 2010 in “The Journal of Urology”
11 citations,
December 2010 in “The Journal of Urology” Taking oral testosterone with or without dutasteride increases testosterone levels and could be an effective treatment for low testosterone.
 8 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society”
8 citations,
April 2019 in “Journal of the Endocrine Society” Postmenopausal women with hyperandrogenism didn't have better metabolic health even after their testosterone levels became normal.
 7 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Andrology”
7 citations,
May 2012 in “International Journal of Andrology” The new oral testosterone pill normalized testosterone levels and lowered SHBG in men with low testosterone.
 32 citations,
May 2006 in “The Journal of Urology”
32 citations,
May 2006 in “The Journal of Urology” Using finasteride with TIP extends time off period for prostate cancer patients.
 6 citations,
November 2010 in “International Journal of Andrology”
6 citations,
November 2010 in “International Journal of Andrology” New oral testosterone formulations show potential for safer, effective hormone replacement in men with low testosterone.
 118 citations,
May 2003 in “Toxicological Sciences”
118 citations,
May 2003 in “Toxicological Sciences” Exposure to finasteride in the womb caused lasting reproductive issues in male rats.
 67 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
67 citations,
March 1987 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil helps hair growth and prevents hair loss in androgenetic alopecia. It's safe and effective.

A new system for classifying curly hair types using precise measurements can improve hair care products and cultural inclusion.
 32 citations,
May 1995 in “Contact Dermatitis”
32 citations,
May 1995 in “Contact Dermatitis” Minoxidil can cause allergic reactions, but testing helps identify the cause.
 282 citations,
October 2006 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism”
282 citations,
October 2006 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism” The Endocrine Society advised against routine testosterone therapy for women, citing a need for more research on long-term safety and a clear definition of androgen deficiency.
 2 citations,
March 2004 in “Reviews in Gynaecological Practice”
2 citations,
March 2004 in “Reviews in Gynaecological Practice” Hormonal changes and psychological issues can cause sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal women. Behavioral therapy is recommended first, with hormone replacement helping some symptoms but not libido. Testosterone can improve libido, but its effects on overall sexual function are unclear. Emotional and relationship issues should be addressed before using medication, and the benefits and risks of testosterone supplementation should be considered.
 32 citations,
January 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
32 citations,
January 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Hormone therapy affects hair growth in transgender individuals, with testosterone potentially causing hair loss in trans men and estrogen reducing facial/body hair in trans women; treatment options vary.
 31 citations,
January 1989 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
31 citations,
January 1989 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” The study tested a hair treatment and found it can help grow hair, but won't stop baldness. It's safe and works well, but needs more testing.
[object Object]  31 citations,
September 2006 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism”
31 citations,
September 2006 in “The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism” Testosterone therapy may slightly improve sexual function in postmenopausal women, but its long-term safety is unknown.
 1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
July 2018 in “Elsevier eBooks” Many treatments for hair loss show potential, but more testing is needed to confirm their effectiveness. Only minoxidil for women and minoxidil and finasteride for men are FDA approved.
 11 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
11 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Skin reactions to drugs are common and can be deadly, usually requiring stopping the drug and may be better prevented with genetic testing in the future.
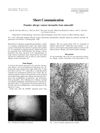 17 citations,
May 1998 in “Contact Dermatitis”
17 citations,
May 1998 in “Contact Dermatitis” Minoxidil can cause pustular allergic reactions on skin.
 43 citations,
May 1986 in “Clinics in Endocrinology and Metabolism”
43 citations,
May 1986 in “Clinics in Endocrinology and Metabolism” Cyproterone acetate is effective for treating hirsutism and acne but less so for hair loss, with side effects similar to birth control pills.
 34 citations,
January 2008 in “International Review of Neurobiology”
34 citations,
January 2008 in “International Review of Neurobiology” Epilepsy and certain epilepsy drugs can lead to reproductive problems in women, but changing medication might improve these issues.
 29 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery”
29 citations,
June 2013 in “Journal of the Saudi Society of Dermatology & Dermatologic Surgery” Alopecia areata is an autoimmune hair loss condition treated with corticosteroids, and histologic confirmation is the best diagnosis method.
 14 citations,
January 2008 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
14 citations,
January 2008 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” High levels of male hormones in women without tumors are linked to metabolic problems and can be treated with metformin.
 10 citations,
March 2019 in “Human Genetics”
10 citations,
March 2019 in “Human Genetics” A genetic mutation in the SGK3 gene causes hairlessness in Scottish Deerhounds and may relate to human hair loss.
 6 citations,
October 2018 in “Endocrinology”
6 citations,
October 2018 in “Endocrinology” Prenatally androgenized ewes can model increased hair diameter in women with PCOS.

























