 7 citations,
June 2015 in “Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology”
7 citations,
June 2015 in “Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology” Some drugs can cause skin reactions, which may improve when the drug is stopped, and rapid diagnosis and stopping the drug is crucial.
 September 2022 in “Polish Hyperbaric Research”
September 2022 in “Polish Hyperbaric Research” Some treatments for hair loss, like finasteride, biotin, and minoxidil, can be effective, but their success varies by individual case.
 11 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
11 citations,
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Skin reactions to drugs are common and can be deadly, usually requiring stopping the drug and may be better prevented with genetic testing in the future.
 6 citations,
October 1997 in “CNS Drugs”
6 citations,
October 1997 in “CNS Drugs” Psychotropic drugs can cause hair loss or excessive hair growth.
 96 citations,
October 1981 in “Drugs”
96 citations,
October 1981 in “Drugs” Minoxidil effectively treats severe hypertension but may cause side effects, so careful monitoring is needed.
 20 citations,
October 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
20 citations,
October 2018 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Some drugs can cause skin and hair color changes, often reversible when the drug is stopped.
 63 citations,
March 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
63 citations,
March 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Some drugs can cause hair loss, and stopping these drugs often leads to hair regrowth.
 December 1990 in “PubMed”
December 1990 in “PubMed” Some drugs can cause hair loss, increase hair growth, or change hair color, but stopping the drug usually reverses these effects.
 1 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2010 in “Elsevier eBooks” Any drug can cause skin reactions, but antibiotics, NSAIDs, and psychotropic drugs are more common, with some reactions being life-threatening.
 4 citations,
July 2018 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice”
4 citations,
July 2018 in “The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice” Four new substances—minoxidil, ferrimanitol ovalbumin, clarithromycin, and glucosamine-hydrochloride—can cause occupational asthma.
 September 2024 in “Current Oncology”
September 2024 in “Current Oncology” Docetaxel often causes hair loss, with limited effective treatments and no cure for permanent hair loss.
 7 citations,
September 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
7 citations,
September 2020 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Low-dose oral minoxidil for hair loss can cause mild excessive hair growth, usually appearing within the first 3 months, but it can be managed by adjusting the dose or removing the unwanted hair, with most people not needing to stop the treatment.
 August 2024 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology”
August 2024 in “Frontiers in Pharmacology” Cyclosporine may cause hair loss, so patients need monitoring.
 28 citations,
March 2017 in “Scientific Reports”
28 citations,
March 2017 in “Scientific Reports” Minoxidil may protect nerves and improve hair quality during paclitaxel treatment.
 15 citations,
November 2002 in “Cardiology in Review”
15 citations,
November 2002 in “Cardiology in Review” Cardiovascular drugs can cause various skin problems, so recognizing these reactions is important.
 63 citations,
May 2003 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
63 citations,
May 2003 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Minoxidil use increases facial hair growth in females, more in older users.
 57 citations,
January 1980 in “Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology”
57 citations,
January 1980 in “Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology” Minoxidil treats high blood pressure and side effects can be managed.
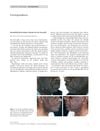 6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology”
6 citations,
May 2012 in “Clinical and experimental dermatology” Oral minoxidil can cause inflamed, ingrown hairs in the beard area.
 32 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
32 citations,
January 2019 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Minoxidil helps treat eyebrow thinning, monilethrix, early hair loss, and shortens chemo-related hair loss.

The document is a detailed guide on skin conditions and treatments for dermatologists.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Side effects of drugs annual”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Side effects of drugs annual” The document concludes that various dermatological treatments and drugs can cause skin reactions and side effects.
 4 citations,
March 2023 in “Current Oncology”
4 citations,
March 2023 in “Current Oncology” Scalp cooling is the only FDA-approved method to prevent hair loss from chemotherapy, but other treatments like minoxidil and PRP are being tested.
 101 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
101 citations,
June 2005 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Very few people experience increased hair growth after laser hair removal, especially those with darker skin and black hair.
 11 citations,
January 1980 in “Southern Medical Journal”
11 citations,
January 1980 in “Southern Medical Journal” Minoxidil effectively treats severe hypertension but has notable side effects.
64 citations,
January 2009 in “Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology” Interferon and ribavirin can cause serious skin reactions and other health issues.

Isotretinoin may cause temporary, reversible facial hair growth in some women.
 10 citations,
February 2016 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia”
10 citations,
February 2016 in “Anais Brasileiros de Dermatologia” Topical minoxidil can cause excessive hair growth in children, so use it carefully.
 45 citations,
November 1979 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
45 citations,
November 1979 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Minoxidil causes excessive hair growth in almost all patients.

Any medication can cause skin reactions, some due to allergies and others due to dosage or genetic factors.
January 2015 in “Annals of dermatology/Annals of Dermatology” Using travoprost for glaucoma may cause extra hair growth and darker skin around the eyes, but these effects can reverse after stopping the drug.




























