 20 citations,
June 2014 in “BMC genomics”
20 citations,
June 2014 in “BMC genomics” Poplar seed hairs grow from the placenta at the ovary base, with endoreduplication playing a key role in their development, and share similar cellulose synthesis processes with cotton fibers.
 May 2019 in “Cytotherapy”
May 2019 in “Cytotherapy” Patients in Australia underwent costly, unproven stem cell treatments due to weak regulations and aggressive marketing.
 28 citations,
January 2011 in “Hearing Research”
28 citations,
January 2011 in “Hearing Research” Gene therapy, especially using atoh1, shows promise for creating functional sensory hair cells in the inner ear, but dosing and side effects need to be managed for clinical application.
[object Object]  1 citations,
November 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
1 citations,
November 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” A woman's hair loss was caused by her husband's testosterone gel and a diabetic man's nail disease led to bone infection, both treated successfully.
 February 2024 in “Planta”
February 2024 in “Planta” TRM21 helps control flavonoid production and root hair growth in Arabidopsis thaliana.
5 citations,
April 2016 in “PubMed” Cetuximab often causes skin problems, but they can be managed without stopping treatment.
 5 citations,
September 2022 in “Molecular pharmacology”
5 citations,
September 2022 in “Molecular pharmacology” KATP channels are important for energy balance and are targeted by drugs for diabetes, hypoglycemia, hypertension, and hair loss.
 1 citations,
May 2019 in “Cytotherapy”
1 citations,
May 2019 in “Cytotherapy” New Australian advertising rules improved stem cell marketing practices but further regulation is needed for consumer safety.

A new mutation in the CYP11B1 gene was found in a woman with mild hyperandrogenemia, a rare cause of non-classic congenital adrenal hyperplasia.
 47 citations,
April 2012 in “The Plant Journal”
47 citations,
April 2012 in “The Plant Journal” Phosphorylation of certain parts of the PIN3 protein is crucial for its role in plant root growth and response to gravity.
 1 citations,
May 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
1 citations,
May 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” The symposium highlighted the importance of understanding disease mechanisms for targeted dermatology treatments.
 April 2012 in “Annals of Neurosciences”
April 2012 in “Annals of Neurosciences” The document concludes that stem cell therapies lack solid proof of effectiveness, except for blood system treatments, and criticizes the ethical issues and commercial exploitation in the field.
 23 citations,
May 2019 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents”
23 citations,
May 2019 in “Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents” New androgen receptor modulators show promise for treating diseases like prostate cancer and muscle wasting.
 139 citations,
February 2010 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology”
139 citations,
February 2010 in “The journal of allergy and clinical immunology/Journal of allergy and clinical immunology/The journal of allergy and clinical immunology” Transplant success has improved with better immunosuppressive drugs and donor matching.
 3 citations,
May 2019 in “Cytotherapy”
3 citations,
May 2019 in “Cytotherapy” ATIR101 improves survival in stem cell transplant patients; Australian stem cell treatment decisions are influenced by regulation changes.
 35 citations,
June 2005 in “The Milbank Quarterly”
35 citations,
June 2005 in “The Milbank Quarterly” The conclusion is that formalizing how past decisions influence current health technology assessments could improve the credibility and defense of coverage decisions.
 223 citations,
September 2018 in “Rheumatology”
223 citations,
September 2018 in “Rheumatology” JAK inhibitors are effective in treating various immune-related diseases, not just rheumatoid arthritis.
 5 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
5 citations,
January 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Skin doctors should know about skin and kidney disease links to prevent serious kidney problems.
 161 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of experimental botany”
161 citations,
August 2013 in “Journal of experimental botany” Certain inhibitors slow down plant growth by causing early cell specialization without changing the cell development pattern.
 7 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Hematology & Oncology”
7 citations,
January 2023 in “Journal of Hematology & Oncology” Using protein degradation to fight cancer drug resistance shows promise but needs more precise targeting and fewer side effects.
 54 citations,
January 2023 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy”
54 citations,
January 2023 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy” New therapies are being developed that target integrin pathways to treat various diseases.
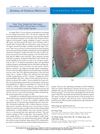 35 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology”
35 citations,
May 2008 in “Journal of Clinical Oncology” A cancer patient died from a severe skin reaction after taking the drug cetuximab.
 11 citations,
September 1999 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
11 citations,
September 1999 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Immunomodulatory therapies are effective for treating cutaneous lymphoma, particularly in early stages.
 7 citations,
September 2013 in “Current Dermatology Reports”
7 citations,
September 2013 in “Current Dermatology Reports” Some skin medications are safe for pregnant women, but others pose risks or should not be used.
 5 citations,
July 2014 in “Acta Crystallographica Section D-biological Crystallography”
5 citations,
July 2014 in “Acta Crystallographica Section D-biological Crystallography” Mutations in the enzyme don't significantly change how it binds to its specific substances.
 27 citations,
December 2015 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings”
27 citations,
December 2015 in “Mayo Clinic Proceedings” The document concludes that lifestyle changes and medical treatments can significantly reduce symptoms of Hidradenitis Suppurativa, a chronic skin condition.
[object Object]  June 2024 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine”
June 2024 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine” CRISPR/Cas9 has improved precision and control but still faces clinical challenges.
 139 citations,
December 2020 in “Cell Stem Cell”
139 citations,
December 2020 in “Cell Stem Cell” Male hormones affect COVID-19 severity and certain drugs targeting these hormones could help reduce the risk.
 1 citations,
April 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
1 citations,
April 2023 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” New CRISPR/Cas9 variants and nanotechnology-based delivery methods are improving cancer treatment, but choosing the best variant and overcoming certain limitations remain challenges.
 15 citations,
April 2011 in “Pediatric Nephrology”
15 citations,
April 2011 in “Pediatric Nephrology” New treatments for lupus show promise, but more research is needed, especially for children.




























