 5 citations,
August 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
5 citations,
August 2003 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Iron deficiency might contribute to hair loss in women.
 35 citations,
August 2001 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
35 citations,
August 2001 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Tacrolimus is effective for various skin conditions with fewer side effects than cyclosporine.
 4 citations,
July 2001 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
4 citations,
July 2001 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Tacrolimus is an effective treatment for several skin conditions with fewer side effects than cyclosporine.
 275 citations,
March 1999 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
275 citations,
March 1999 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Chemotherapy can cause various skin reactions, with hair loss being the most common, and proper diagnosis and treatment of these reactions are important.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Certain drugs can cause skin lupus, but stopping the drug usually helps. Vaccines work against smallpox, genital herpes, and a type of human papillomavirus. More frequent light therapy clears psoriasis faster. Certain treatments work for psoriasis and dermatitis. A specific cream effectively treats a type of skin cancer. Low iron levels aren't directly linked to chronic hair loss.
 49 citations,
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
49 citations,
January 2003 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Effective management of children's hair loss involves accurate diagnosis, various treatments, and supportive care.
 July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
July 2003 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Certain drugs can cause lupus, stopping these drugs is the main treatment. NB-UVB phototherapy clears psoriasis faster when applied three times a week. Monoclonal antibodies and oral pimecrolimus are effective in treating psoriasis. Smoking and drinking are linked to psoriasis in men. No direct link between low iron and hair loss was found. Vaccines are effective against genital herpes and human papillomavirus type 16.
 20 citations,
July 1990 in “Pediatrics in Review”
20 citations,
July 1990 in “Pediatrics in Review” The four main causes of hair loss in children are fungal infections, pulling out hair, autoimmune hair loss, and stress-related hair shedding.
 247 citations,
August 2011 in “European Journal of Epidemiology”
247 citations,
August 2011 in “European Journal of Epidemiology” The Rotterdam Study updated its design and objectives in 2012, providing insights into various diseases in the elderly, including skin cancer, bone health, liver disease, neurological and psychiatric conditions, and respiratory issues.
 74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Minoxidil and finasteride are effective for male hair loss, minoxidil for female hair loss, and various treatments like corticosteroids work for alopecia areata; treatment should be tailored to the individual.
 108 citations,
November 1980 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
108 citations,
November 1980 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Oral retinoids are effective for various skin conditions but have side effects and should not be used during pregnancy.
 27 citations,
September 1992 in “The Lancet”
27 citations,
September 1992 in “The Lancet” ICL is a condition with low CD4+ T cells like AIDS but not caused by HIV, and normal CD4+ T cell counts may vary between men and women.
 10 citations,
January 2014 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal”
10 citations,
January 2014 in “Indian Dermatology Online Journal” Most medical students in the study had skin and hair issues, with acne, hair loss, and sun tan being common, and these issues varied by gender and origin.
4 citations,
January 2014 in “Indian journal of paediatric dermatology” Methotrexate is effective and well-tolerated in children for certain skin conditions but requires careful monitoring.
 August 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
August 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Experts recommend personalized treatment plans for best outcomes in managing Alopecia Areata.
 4 citations,
November 2021 in “Cancers”
4 citations,
November 2021 in “Cancers” The document concludes that understanding and managing hair loss in cancer patients is important, and more research is needed for better treatments.
 4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Various treatments exist for alopecia areata, but none are completely satisfactory; choice depends on age, disease extent, and preference.
 8 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
8 citations,
August 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that doctors should carefully consider off-label drug use in dermatology and always inform patients, while more research is needed on the safety and effectiveness of such practices.
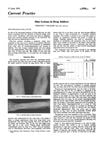 56 citations,
June 1970 in “The BMJ”
56 citations,
June 1970 in “The BMJ” Drug addicts often have scars, skin color changes, blocked veins, and bruising, with severe ulcers from barbiturate injections.
 64 citations,
February 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
64 citations,
February 1995 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Lithium therapy may cause skin problems like hidradenitis suppurativa and other side effects, which can improve after stopping the medication.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
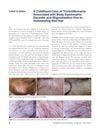 1 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology”
1 citations,
January 2013 in “International Journal of Trichology” A girl with red hair developed hair-pulling and body image disorders after being bullied for her hair color.
13 citations,
May 2014 in “PubMed” Most children with childhood-onset lupus in Baghdad responded well to treatment, but some developed chronic kidney disease or died.
 April 2017 in “Childhood Kidney Diseases”
April 2017 in “Childhood Kidney Diseases” Azathioprine can cause severe blood issues and hair loss, needing careful monitoring and possible discontinuation.
 February 2024 in “Infection and drug resistance”
February 2024 in “Infection and drug resistance” Tinea capitis in a child was caused by a fungus from cats, highlighting the need for accurate diagnosis and treatment.
 1 citations,
June 2023 in “Psychoneuroendocrinology”
1 citations,
June 2023 in “Psychoneuroendocrinology” Childhood sexual trauma, especially between ages 5-7, is linked to lower cortisol levels in adult hair, suggesting long-term stress response changes.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Acne can appear or persist in adulthood due to hormonal changes, external factors, or substance use, and requires appropriate treatment.
4 citations,
August 1971 in “Pediatric clinics of North America/The Pediatric clinics of North America” Childhood hair and scalp disorders can be managed with treatments like cortisone and corticosteroids.
3 citations,
February 2021 in “Pediatric rheumatology online journal” A girl with lupus and trisomy X has a higher risk of bone problems like avascular necrosis and osteoporosis.
 4 citations,
July 2021 in “International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health”
4 citations,
July 2021 in “International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health” Women who lost hair from childhood head radiation are more likely to face mental health issues than men.


























