 1 citations,
November 2019 in “Archives of breast cancer”
1 citations,
November 2019 in “Archives of breast cancer” Some hormone treatments might raise breast cancer risk, while others don't seem to.
 48 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology”
48 citations,
February 2017 in “Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology” The conclusion is to use scalp cooling, gentle hair care, and treatments like minoxidil for managing hair loss from chemotherapy, and stresses the need for more research and collaboration in this area.
 January 2023 in “International Journal of Clinical and Medical Education Research”
January 2023 in “International Journal of Clinical and Medical Education Research” Correct testosterone levels for age to treat prostate cancer, using low dose treatments as necessary.
 62 citations,
April 2009 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
62 citations,
April 2009 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Epidermal stem cells could lead to new treatments for skin and hair disorders.
 4 citations,
October 2002 in “BJUI”
4 citations,
October 2002 in “BJUI” Finasteride treats hair loss but may affect prostate cancer detection.
 January 2022 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny”
January 2022 in “Przegla̧d dermatologiczny” The document concludes that there are various treatments for diseases linked to scarring hair loss, especially for primary scarring alopecia.
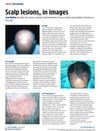 January 2015 in “Independent Nurse”
January 2015 in “Independent Nurse” Different scalp conditions can lead to hair loss or tumors, with treatments varying from creams to surgery; early detection is crucial.
 April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Some blood pressure medications are linked to a higher risk of skin cancer.
5 citations,
January 2018 in “Interdisciplinary sciences: computational life sciences” Accurate protein modeling can help develop new treatments for prostate cancer and other diseases.
69 citations,
January 2002 in “Journal of biomedical optics” Dyes can penetrate human skin and hair follicles up to 1.2 mm deep and the sebaceous gland can store dye; Indocyanine Green lotion was made for safe dyeing and monitoring.
 May 2023 in “Current Medicinal Chemistry”
May 2023 in “Current Medicinal Chemistry” Microneedle patches improve drug delivery for skin treatments and cosmetic enhancements.
 October 2014 in “Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology”
October 2014 in “Journal of Minimally Invasive Gynecology” Genetic testing for cancer risk can lead to early and life-saving treatments in people without symptoms.
 June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
June 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Researchers discovered potential origins and new treatments for skin cancer, including biomarkers for melanoma and therapies that reduce tumor growth.
 April 2022 in “Anti-cancer agents in medicinal chemistry”
April 2022 in “Anti-cancer agents in medicinal chemistry” Some existing medicines show promise as safe treatments to protect against the side effects of radiation therapy.
 2 citations,
November 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
2 citations,
November 2015 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Epidermal stem cells show promise for future dermatology treatments due to ongoing advancements.
February 2024 in “Cancers” New treatments targeting androgen receptors show promise for drug-resistant prostate cancer.
 15 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
15 citations,
October 2014 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” New treatments targeting the Hedgehog pathway can help treat advanced skin cancer but may have side effects and their effectiveness in early stages is unknown.
 6 citations,
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks”
6 citations,
January 2016 in “Springer eBooks” Invasomes effectively deliver drugs through the skin and have potential for improved treatments.
May 2020 in “Authorea (Authorea)” Olfactory receptors found outside the nose may offer new treatments for diseases like cancer and help in wound healing and hair growth.
March 2017 in “Jurnal materi dan pembelajaran fisika” Light diffraction helps in eye surgery, brain treatments, and detecting hair loss and genetic diseases.
 37 citations,
October 2006 in “Steroids”
37 citations,
October 2006 in “Steroids” New sulfur-containing steroid analogs show promise for more targeted medical treatments.
 141 citations,
August 2017 in “Developmental Dynamics”
141 citations,
August 2017 in “Developmental Dynamics” The document concludes that a better understanding of cell changes during wound healing could improve treatments for chronic wounds and other conditions.
19 citations,
December 2008 in “Arthritis Care & Research” The decision board effectively helps lupus nephritis patients in Brazil choose treatments by clearly presenting options and side effects.
 April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2016 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The symposium showed that stem cells are key for understanding and treating skin diseases and for developing new skin models and therapies.
 1 citations,
March 2019 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
1 citations,
March 2019 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” The conference reported improvements in muscle volume, skin cancer diagnosis, facial and vaginal rejuvenation, and hair growth using various laser treatments.
 December 2024 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology”
December 2024 in “Frontiers in Endocrinology” Continued research and awareness are needed to improve treatments for androgen-dependent diseases.
August 2024 in “Steroids” The androgen receptor's shape-changing ability helps it function but can lead to cancer treatment resistance.
 November 1966 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
November 1966 in “British Journal of Dermatology” The meeting discussed various skin conditions, treatments, and unusual cases, highlighting the effectiveness of tetracycline in treating rosacea.
 402 citations,
August 2011 in “Cancer research”
402 citations,
August 2011 in “Cancer research” Prostate cancer cells can make their own androgens to activate the androgen receptor, and treatments like abiraterone may increase this ability, suggesting new therapies should target the entire steroid-making pathway.
 March 2024 in “Frontiers in genetics”
March 2024 in “Frontiers in genetics” Different types of fibroblasts play specific roles in wound healing and cancer, which could help improve treatments.























