 26 citations,
October 2018 in “Clinical & Translational Oncology”
26 citations,
October 2018 in “Clinical & Translational Oncology” Spanish experts provided guidelines for treating skin side effects in cancer patients on new therapies, stressing early action and teamwork.
 15 citations,
January 2003 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
15 citations,
January 2003 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Cold air and a chilled sapphire window both protect the skin during laser treatments, and work better with water or gel, especially for darker skin.
 15 citations,
November 2002 in “Cardiology in Review”
15 citations,
November 2002 in “Cardiology in Review” Cardiovascular drugs can cause various skin problems, so recognizing these reactions is important.
 2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
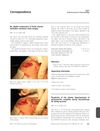
2 citations,
August 2013 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Chemotherapy improved a girl's painful foot condition linked to pachyonychia congenita.
 1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks”
1 citations,
January 2015 in “Springer eBooks” Chemotherapy can cause skin side effects that affect patients' lives, but they can be managed to avoid interrupting cancer treatment.
 February 2020 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology”
February 2020 in “International Journal of Research in Dermatology” EPDS is a rare, chronic scalp condition that's hard to treat and needs better awareness for improved outcomes.
 May 1991 in “Current problems in dermatology”
May 1991 in “Current problems in dermatology” Skin issues can indicate immune system problems.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Deleting the CRIF1 gene in mice disrupts skin and hair formation, certain proteins affect hair growth, a new compound may improve skin and hair health, blood cell-derived stem cells can create skin-like structures, and hair follicle stem cells come from embryonic cells needing specific signals for development.
 April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2017 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Stem cells can create hair follicles, potentially treating permanent hair loss, and healthy skin and hair depend on mitochondrial function and special fats.
 172 citations,
November 1983 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
172 citations,
November 1983 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Chemotherapy can cause skin problems like hair loss, mouth sores, and skin darkening, and recognizing these can affect treatment decisions.
 108 citations,
July 2002 in “Molecular and cellular biology”
108 citations,
July 2002 in “Molecular and cellular biology” Overexpressing Dsg3 in mice skin causes excessive cell growth and abnormal skin development.
 88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
88 citations,
July 2014 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Targeted cancer therapies often cause skin reactions, so dermatologists must manage these effects.
 84 citations,
January 1990 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
84 citations,
January 1990 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Skin grafting can help repigment vitiligo, but it's less effective for widespread cases due to the Koebner phenomenon.
 83 citations,
May 2013 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
83 citations,
May 2013 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Skin development in mammals is controlled by key proteins and signals from underlying cells, involving stem cells for maintenance and repair.
 60 citations,
April 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
60 citations,
April 2006 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Surgical methods like suction blister grafting and split-thickness skin grafting are highly successful for vitiligo repigmentation, but choosing the right patients is crucial for success.
 34 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
34 citations,
March 2015 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” People with pemphigus are more likely to have conditions like hypothyroidism, inflammatory bowel disease, and diabetes.
 10 citations,
March 2021 in “Skin health and disease”
10 citations,
March 2021 in “Skin health and disease” COVID-19 patients often have skin issues like chilblain-like lesions and rashes, which can help in early diagnosis and sometimes indicate severe illness.
 7 citations,
March 2020 in “PloS one”
7 citations,
March 2020 in “PloS one” α-parvin is necessary for skin and hair growth and for the correct orientation of skin cells.
 6 citations,
April 2013 in “Current Dermatology Reports”
6 citations,
April 2013 in “Current Dermatology Reports” Dermatologists are crucial for managing skin side effects in metastatic melanoma patients using vemurafenib and ipilimumab.
 1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks”
1 citations,
May 2017 in “InTech eBooks” The document concludes that alopecia areata is an unpredictable autoimmune hair loss condition with no cure, but various treatments exist that require personalized approaches.
 1 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
January 2013 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The document concludes that stem cells and their environments are crucial for skin and hair health and have potential for medical treatments.
 April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2018 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Androgens increase growth factors in skin cells, which may lead to acne.

COVID-19 can cause skin problems and affect dermatology treatments, with recommendations for skin care and cautious use of certain drugs.
 27 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
27 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Dermatology” COVID-19 can cause skin issues like chilblains and rashes, which may help in early detection, especially in patients without other symptoms.
 3 citations,
March 2008 in “Medical laser application”
3 citations,
March 2008 in “Medical laser application” Lasers have become safer and more effective for treating skin problems and hair removal.
 2 citations,
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
2 citations,
October 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Cancer treatments can cause skin-related side effects that may affect patient quality of life and require changes in treatment.
 April 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology”
April 2016 in “The journal of investigative dermatology/Journal of investigative dermatology” Applying the anti-cancer drug Bortezomib to skin can promote hair growth and increase hair proteins through the GATA-3 factor.
 January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks” New treatments for skin and hair repair show promise, but further improvements are needed.
 273 citations,
May 2017 in “The Lancet”
273 citations,
May 2017 in “The Lancet” Some drugs can cause rare but potentially deadly skin reactions, and early treatment and avoiding the drug again are key.
 5 citations,
September 2015 in “Nepalese journal of ophthalmology”
5 citations,
September 2015 in “Nepalese journal of ophthalmology” An 11-year-old girl with a rare skin disorder also had cornea issues and dry eye, needing careful management.





























