 16 citations,
June 2017 in “JAMA Dermatology”
16 citations,
June 2017 in “JAMA Dermatology” Thalidomide works best for skin lupus not helped by antimalarials, but has many side effects; other treatments are less effective, especially if patients also have systemic lupus.
 60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology”
60 citations,
September 2015 in “Expert Review of Clinical Immunology” Lymphocytes, especially CD8+ T cells, play a key role in causing alopecia areata, and targeting them may lead to new treatments.
 14 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
14 citations,
November 2020 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” Advanced therapies like gene, cell, and tissue engineering show promise for hair regrowth in alopecia, but their safety and effectiveness need more verification.
 4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology”
4 citations,
September 2011 in “Expert Review of Dermatology” Various treatments exist for alopecia areata, but none are completely satisfactory; choice depends on age, disease extent, and preference.
 3 citations,
May 2018 in “InTech eBooks”
3 citations,
May 2018 in “InTech eBooks” Animal models, especially mice, are essential for advancing hair loss research and treatment.
48 citations,
April 2021 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Topical corticosteroids are the best initial treatment for children's alopecia areata.
31 citations,
July 2021 in “ImmunoTargets and therapy” Alopecia areata is an incurable autoimmune condition causing hair loss, with research aiming for better treatments.
 4 citations,
May 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences”
4 citations,
May 2018 in “International Journal of Molecular Sciences” The research showed how melanocytes develop, move, and respond to UV light, and their stem cells' role in hair color and skin cancer risk.
 3 citations,
March 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology”
3 citations,
March 2021 in “Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dermatology” Early treatment of Lupus Erythematosus Alopecia can prevent permanent hair loss, and various medications are effective.
 May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine”
May 2023 in “Journal of Clinical Medicine” New understanding and treatments for hair loss are improving, but more research is needed.
 45 citations,
January 1992 in “Dermatology”
45 citations,
January 1992 in “Dermatology” Half of the patients treated with a specific drug for skin cancer experienced hair loss not related to the drug's dosage.
 147 citations,
April 1994 in “Drug Safety”
147 citations,
April 1994 in “Drug Safety” Some drugs can cause hair loss or increase hair growth, but these effects are usually reversible when the drug is stopped.
 63 citations,
March 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
63 citations,
March 1995 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Some drugs can cause hair loss, and stopping these drugs often leads to hair regrowth.
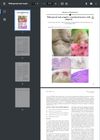 November 2022 in “JAAD case reports”
November 2022 in “JAAD case reports” A man with skin and hair symptoms improved partially with specific treatment.
 9 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatology Online Journal”
9 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatology Online Journal” A patient with Crohn's disease grew back their hair after stopping Adalimumab, which had caused hair loss.
 April 2020 in “Rheumatology”
April 2020 in “Rheumatology” Rituximab therapy successfully treated a patient's complete body hair loss and was effective for six years.
 64 citations,
July 2016 in “Journal of Immunology”
64 citations,
July 2016 in “Journal of Immunology” Blocking the CXCR3 receptor reduces T cell accumulation in the skin and prevents hair loss in mice.
 April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2023 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Booster shots of mRNA vaccines for COVID-19 increased protective antibodies without worsening autoimmune skin conditions in patients.
 72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology”
72 citations,
February 2011 in “The American Journal of Dermatopathology” Anti-TNF therapy can cause a unique type of hair loss that may get better with topical treatments without stopping the therapy.
 36 citations,
September 2009 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine”
36 citations,
September 2009 in “Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine” New treatments targeting skin stem cells show promise for skin repair, anti-aging, and cancer therapy.
 19 citations,
October 2008 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
19 citations,
October 2008 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Anti-cancer treatments can cause reversible hair loss, skin sensitivity, pigmentation changes, nail damage, and skin reactions, with a need for more research on managing these side effects.
 17 citations,
January 2011 in “The Korean Journal of Hepatology”
17 citations,
January 2011 in “The Korean Journal of Hepatology” Vogt-Koyanagi-Harada disease can develop during interferon therapy for chronic hepatitis C.
 10 citations,
September 2014 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
10 citations,
September 2014 in “European Journal of Dermatology” A woman's hair loss worsened after starting hepatitis C treatment due to immune changes in her hair follicles.
 7 citations,
January 2009 in “Immunological investigations”
7 citations,
January 2009 in “Immunological investigations” A 3-year-old boy lost all his hair due to a rare reaction to phenobarbital, but it grew back after steroid treatment.
 4 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal of clinical and translational research”
4 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal of clinical and translational research” Chitosan-based dressings reduce inflammation and speed up skin wound healing.
 209 citations,
March 1989 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
209 citations,
March 1989 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Interferon alfa-2a is effective for treating cutaneous T cell lymphoma but has significant side effects.
 34 citations,
April 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
34 citations,
April 2008 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Skin problems like itching, dry skin, and hair loss are more common in hepatitis C patients after interferon treatment, but lichen planus is not linked to the infection.
 26 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica”
26 citations,
January 2017 in “Acta dermato-venereologica” Antidepressants might help with skin inflammation and improve conditions like psoriasis and eczema.
 July 2023 in “Journal of skin and stem cell”
July 2023 in “Journal of skin and stem cell” Interferon beta treatment in MS patients can cause skin reactions and increased hair loss.
 April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Hydroxychloroquine may cause false results in tuberculosis tests for patients with autoimmune skin diseases.



























