 15 citations,
January 1996 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine”
15 citations,
January 1996 in “Lasers in Surgery and Medicine” Lasers in hair transplantation may have potential but require caution due to possible damage and reduced graft survival.
 13 citations,
April 2023 in “Nature communications”
13 citations,
April 2023 in “Nature communications” Long COVID patients have more health issues than non-infected people.
 9 citations,
June 1998 in “Dermatologic Surgery”
9 citations,
June 1998 in “Dermatologic Surgery” The Rapid Fire Hair Implanter Carousel may allow faster hair transplants with less bleeding and similar healing and growth compared to manual methods.
 8 citations,
January 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology”
8 citations,
January 2019 in “Experimental Dermatology” The 3D skin model is better for hair growth research and testing treatments.
 8 citations,
June 2001 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Surgery and Aesthetic Dermatology”
8 citations,
June 2001 in “International Journal of Cosmetic Surgery and Aesthetic Dermatology” Use shallow cuts, small tissue removal, careful suturing, and keep the area moist to reduce scarring in hair transplants.
 February 2024 in “Journal of ayurveda and integrated medical sciences”
February 2024 in “Journal of ayurveda and integrated medical sciences” Ayurvedic medicine helped increase a young woman's hemoglobin levels and improved her anemia symptoms.
 January 2024 in “Theranostics”
January 2024 in “Theranostics” HDAC6 helps keep ovarian follicles dormant, extending female fertility.
 September 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
September 2021 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Not having enough or having too much of the protein Grainyhead-like 3 leads to various developmental problems.

Low Level Laser Therapy may improve noise-induced hearing loss.
 3 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of nutritional health & food science”
3 citations,
May 2018 in “Journal of nutritional health & food science” Nutritional supplements can help manage hair loss and promote hair growth by strengthening hair roots and countering harmful effects of pollution, smoking, and deficiencies in vitamins and minerals.
 1 citations,
January 2016
1 citations,
January 2016 Learn how to do hair restoration surgery.
October 2020 in “M/C Journal” Society's view of "freaks" has shifted from natural deformities to extreme plastic surgery, reflecting changing beauty standards and pressures.
 July 2015 in “Hair transplant forum international”
July 2015 in “Hair transplant forum international” The document's conclusion cannot be determined.
Hair loss in women can be caused by genetics, menopause, certain health conditions, and emotional stress, and it often results in thinner hair and a changing hairline.
11 citations,
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” The book helps surgeons improve hair transplants for Asian patients.
 5 citations,
December 2022 in “Toxins”
5 citations,
December 2022 in “Toxins” Neurotoxins can affect neurotransmitter release and have potential in treating muscle, pain, and cancer conditions, but more research is needed on how they work.
 47 citations,
September 2022 in “European Heart Journal”
47 citations,
September 2022 in “European Heart Journal” Women may need different blood pressure guidelines than men for heart disease prevention.
34 citations,
February 2015 in “Frontiers in Cellular Neuroscience” Zebrafish helped find new ways to prevent drug-induced hair cell death and potential treatments for hearing loss.
17 citations,
January 2018 in “Journal of cutaneous and aesthetic surgery” The article discusses debates on hair transplant techniques, safe donor areas, PRP use, and practitioner qualifications in hair restoration.
12 citations,
November 2020 in “Transplant international” Hand and forearm transplants can be successful long-term, but they come with challenges like rejection and side effects from immunosuppression.
4 citations,
August 2023 in “Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy” Ivacaftor can protect against noise-induced hearing loss by reducing oxidative stress.
 1 citations,
January 2024
1 citations,
January 2024 CaBP1 and CaBP2 are necessary for proper hearing and neurotransmission in the ear's inner hair cells.
 1 citations,
February 2018 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research”
1 citations,
February 2018 in “Plastic and Aesthetic Research” The KD spreader makes hair transplants safer and easier, especially for beginners, by reducing damage to hair follicles.
January 2024 in “Diagnostics” Long COVID causes a wide range of long-lasting symptoms that change over time and are hard to diagnose and treat.

CaBP1 and 2 are important for maintaining the activity of calcium channels necessary for hearing in inner ear cells.

CaBP1 and 2 are necessary for maintaining calcium currents and hearing in inner ear cells.

CaBP1 and CaBP2 are important for continuous hearing by preventing inactivation of calcium currents in ear cells, with CaBP2 also able to restore hearing when reintroduced.

CaBP1 and CaBP2 are necessary for proper hearing and neurotransmission in the ear's inner hair cells.

CaBP1 and CaBP2 are important for maintaining hearing by supporting continuous calcium currents and nerve signaling in the ear.
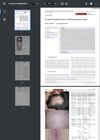 December 2023 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy”
December 2023 in “Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy” A man developed myasthenia gravis after alopecia areata, and treatment improved his symptoms and stopped hair loss.























