 38 citations,
January 1997 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
38 citations,
January 1997 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” Finasteride and flutamide effectively reduce hirsutism in PCOS women, with flutamide also lowering hormone levels.
 5 citations,
October 2014 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
5 citations,
October 2014 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” Triptorelin helps evaluate hormone production in Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors.
 June 2023 in “Oriental Journal of Chemistry/Oriental journal of chemistry”
June 2023 in “Oriental Journal of Chemistry/Oriental journal of chemistry” New compounds may help treat prostate cancer by reducing cell growth.
 49 citations,
November 2019 in “Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics”
49 citations,
November 2019 in “Egyptian Journal of Medical Human Genetics” Certain gene variants may contribute to high androgen levels in women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
 37 citations,
January 2008 in “Gynecological Endocrinology”
37 citations,
January 2008 in “Gynecological Endocrinology” Shorter CAG repeats in a specific gene may increase male hormone activity and symptoms like acne and excess hair in women with PCOS.
 6 citations,
October 2018 in “Endocrinology”
6 citations,
October 2018 in “Endocrinology” Prenatally androgenized ewes can model increased hair diameter in women with PCOS.
 July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks”
July 2015 in “Cambridge University Press eBooks” The document concludes that treatments for female hair loss and excess body hair are available, but managing expectations is important.
 153 citations,
March 2017 in “Endocrine”
153 citations,
March 2017 in “Endocrine” Male pattern baldness involves genetics, hormones, and needs better treatments.
 85 citations,
June 2008 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences”
85 citations,
June 2008 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” PCOS starts in adolescence with hormonal issues, leading to adult health problems, and early treatment is crucial.
 67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy”
67 citations,
September 2008 in “Dermatologic therapy” Hirsutism is excessive hair growth in women often caused by polycystic ovarian syndrome, and identifying the cause is important for managing associated health risks.
 60 citations,
May 2015 in “Archives of dermatological research”
60 citations,
May 2015 in “Archives of dermatological research” PPAR agonists show promise for skin conditions but need more research before being a main treatment.
 56 citations,
October 1983 in “Archives of Dermatology”
56 citations,
October 1983 in “Archives of Dermatology” Some women with acne have higher levels of free testosterone, which might suggest using hormonal treatments for acne.
 37 citations,
February 2013 in “Maturitas”
37 citations,
February 2013 in “Maturitas” Testosterone therapy is beneficial for women's health and does not cause masculinization or liver damage, and it protects the heart and breasts.
 14 citations,
March 2010 in “Gynecological endocrinology”
14 citations,
March 2010 in “Gynecological endocrinology” New treatments for excessive hair growth in women include insulin modulators and enzyme inhibitors.
 10 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine”
10 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine” The article explains how to identify and treat excessive hair growth in women, which can be distressing and may signal other health problems.
 10 citations,
April 2000 in “Archives of Oral Biology”
10 citations,
April 2000 in “Archives of Oral Biology” Minocycline may cause hair loss by increasing DHT levels, but finasteride can help counteract this effect.
 1 citations,
January 1996 in “Gynecological endocrinology”
1 citations,
January 1996 in “Gynecological endocrinology” Non-invasive imaging helped diagnose a woman's severe hormone imbalance and diabetes, and medication successfully treated her condition.
 January 2008 in “Pratique médicale & chirurgicale de l'animal de compagnie”
January 2008 in “Pratique médicale & chirurgicale de l'animal de compagnie” Alopecia X in dogs is a cosmetic issue, not a hormonal disorder, and harmful treatments should be avoided.
 January 1986 in “Journal of Steroid Biochemistry”
January 1986 in “Journal of Steroid Biochemistry” Lower testosterone levels in men may be linked to a higher risk of severe coronary artery disease.
 60 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
60 citations,
September 2001 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Insulin resistance contributes to hormone imbalances in many women with polycystic ovary syndrome.
 28 citations,
April 2013 in “Fertility and Sterility”
28 citations,
April 2013 in “Fertility and Sterility” Caucasian and Asian women with PCOS generally show similar symptoms, except Asian women have less chest hair.
 21 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine”
21 citations,
January 2003 in “Seminars in reproductive medicine” The document concludes that various drugs can manage symptoms and metabolic issues in women with PCOS.
 20 citations,
September 1978 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
20 citations,
September 1978 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Hair growth is influenced by factors like genetics and nutrition, and more research is needed to understand hair loss and growth mechanisms.
 14 citations,
May 2011 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America”
14 citations,
May 2011 in “Facial Plastic Surgery Clinics of North America” Laser hair removal is effective for dark hair but needs improvement for nonpigmented or fine hairs.
 157 citations,
April 1994 in “Clinical endocrinology”
157 citations,
April 1994 in “Clinical endocrinology” Androgens can cause hair growth in some areas and hair loss on the scalp.
 65 citations,
July 2013 in “International Clinical Psychopharmacology”
65 citations,
July 2013 in “International Clinical Psychopharmacology” Mood stabilizers like lithium and anticonvulsants have side effects that can lead to patients stopping their medication, and managing these effects is important for treatment adherence.
 42 citations,
February 1985 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
42 citations,
February 1985 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Excessive hair growth can be assessed by history, exam, and blood tests, and treated with medication like dexamethasone, birth control pills, and spironolactone.
 29 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
29 citations,
September 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Hair disorders are caused by a complex mix of biology, genetics, hormones, and environmental factors, affecting hair growth and leading to conditions like alopecia.
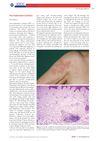 October 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
October 2012 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Post-implantation erythema is a red skin condition after medical device implantation that sometimes goes away on its own.
 86 citations,
March 1993 in “Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology”
86 citations,
March 1993 in “Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology” Finasteride affects male rat genitalia development, causing abnormalities during specific pregnancy days.






























