 December 2024 in “Journal of Skin and Stem Cell”
December 2024 in “Journal of Skin and Stem Cell” Trichoscopy helps diagnose and manage different types of hair loss in the Indian population.
 11 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft”
11 citations,
January 2022 in “Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Alopecia areata is a chronic condition causing hair loss, with new treatments targeting the immune system showing promise.
 November 2023 in “Aktualʹnì problemi sučasnoï medicini”
November 2023 in “Aktualʹnì problemi sučasnoï medicini” The guidelines suggest using various treatments, including antidepressants and steroids, for alopecia areata and discuss the condition's genetic and immune aspects.
 August 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
August 2023 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Experts recommend personalized treatment plans for best outcomes in managing Alopecia Areata.
 March 2022 in “Wound practice & research”
March 2022 in “Wound practice & research” New treatments for alopecia areata show promise, but standardized guidelines are needed.
 January 2020 in “Archives of Medicine and Health Sciences”
January 2020 in “Archives of Medicine and Health Sciences” Certain immune molecules and stress affect hair loss, and while genes play a role, more research is needed to fully understand and treat it.
 3 citations,
January 2024 in “Signal transduction and targeted therapy”
3 citations,
January 2024 in “Signal transduction and targeted therapy” Lymphatic vessels are essential for health and can be targeted to treat various diseases.
 156 citations,
September 2014 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement”
156 citations,
September 2014 in “British journal of dermatology/British journal of dermatology, Supplement” Accurate diagnosis and effective oral treatment are key to managing tinea capitis and preventing its spread.
125 citations,
May 2010 in “Pediatric dermatology” Systemic treatment is necessary for tinea capitis in children, with griseofulvin preferred for Microsporum infections.
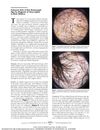 108 citations,
March 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology”
108 citations,
March 2011 in “Archives of Dermatology” Corkscrew hair may be a new sign for quickly diagnosing scalp fungus in black children.
 89 citations,
May 1999 in “Pediatric Dermatology”
89 citations,
May 1999 in “Pediatric Dermatology” New antifungal treatments for a children's scalp infection are effective and safe, but it's not decided if they will become the preferred option over the old treatment.
 65 citations,
January 2005 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
65 citations,
January 2005 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Children with scalp fungal infections need proper diagnosis and treatment, usually with antifungal medications, and newer drugs may offer quicker recovery.
 62 citations,
June 2015 in “Sexually Transmitted Infections”
62 citations,
June 2015 in “Sexually Transmitted Infections” Sexual activity can spread T. interdigitale, needing quick antifungal treatment to avoid permanent scarring.
46 citations,
January 2002 in “Paediatric drugs” Tinea capitis, a scalp fungal infection in children, is best treated with newer antifungal agents for shorter periods.
 41 citations,
September 2007 in “Pediatric emergency care”
41 citations,
September 2007 in “Pediatric emergency care” Oral medication is necessary to treat scalp fungus in children, with griseofulvin being the usual choice.
 38 citations,
July 2010 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology”
38 citations,
July 2010 in “Clinical, cosmetic and investigational dermatology” To treat tinea capitis in children, oral antifungal medication is necessary, with newer drugs offering shorter treatment times than the traditional griseofulvin.
37 citations,
October 2010 in “JDDG Journal der Deutschen Dermatologischen Gesellschaft” Griseofulvin is the best treatment for tinea capitis in children, but more research is needed on other treatments and safety.
 37 citations,
August 1991 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
37 citations,
August 1991 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Most tinea capitis cases in southern Taiwan were in adult women, mainly caused by Trichophyton violaceum.
 36 citations,
October 2016 in “Medical mycology”
36 citations,
October 2016 in “Medical mycology” PCR-ELISA is better for identifying the fungus causing scalp infections in Ugandan children than traditional methods.
 35 citations,
January 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics”
35 citations,
January 1996 in “Dermatologic clinics” Tinea capitis is a common scalp infection causing hair loss, mostly in young children.
 33 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology”
33 citations,
December 2013 in “Journal of cutaneous pathology” A fungal infection can look like a different scalp condition in teens, leading to wrong treatment until proper tests are done.
 33 citations,
February 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
33 citations,
February 1996 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Treat scalp and beard fungal infections early with oral antifungal medication and sometimes topical therapy, avoiding unnecessary allergy tests and surgery.
 32 citations,
August 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
32 citations,
August 2003 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Tinea capitis can be misdiagnosed as bacterial infection in adult women but is treatable with antifungal medication.
 29 citations,
April 2013 in “Mycoses”
29 citations,
April 2013 in “Mycoses” A young man was initially misdiagnosed with a scalp condition but was found to have a fungal infection, which improved with antifungal treatment.
26 citations,
January 1990 in “Mycoses” Most tinea capitis cases in Rotterdam were caused by Trichophyton violaceum, mainly affecting Moroccan immigrant children.
24 citations,
January 2012 in “Journal of natural science, biology and medicine” Tinea capitis is common among Kolkata school children, especially boys, and hygiene doesn't greatly impact infection rates.
24 citations,
July 2009 in “Mycoses” A scalp infection was treated successfully, leading to full hair regrowth.
24 citations,
August 2007 in “Journal of pediatric surgery” Surgery is not the right treatment for a fungal scalp infection; proper medical treatment is needed.
 22 citations,
January 2009 in “Medical mycology”
22 citations,
January 2009 in “Medical mycology” A family got a fungal infection from a boy who had contact with rabbits, but they all recovered with treatment.
 21 citations,
February 2009 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology”
21 citations,
February 2009 in “Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology” Some cases of tinea capitis, a fungal scalp infection, can look like scarring hair loss due to the body's immune response and the fungus itself.























