 1 citations,
January 1989 in “Handbook of experimental pharmacology”
1 citations,
January 1989 in “Handbook of experimental pharmacology” Anti-androgens can help reduce the effects of male hormones on the skin.
35 citations,
October 2000 in “Dermatologic clinics” A scarring hair loss condition mainly affects middle-aged women of African descent, impacting their quality of life, with treatments more effective when started early.
 May 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology”
May 2024 in “Indian Journal of Dermatology” Androgenetic alopecia in men is genetic and linked to health issues like obesity and heart disease, with treatments including minoxidil, finasteride, and hair transplants.
January 2024 in “Cosmetics” Menopause worsens skin, hair, and nails, affecting self-esteem and quality of life.
84 citations,
February 2015 in “Experimental Dermatology” PPARγ is crucial for skin health but can have both beneficial and harmful effects.
May 2024 in “Journal of Fungi” Tinea capitis in adults, especially postmenopausal Black women, needs prompt treatment with oral antifungals to avoid scarring.
 50 citations,
December 1999 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
50 citations,
December 1999 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Finasteride improves hidradenitis suppurativa but not for child-bearing women.
 56 citations,
August 1981 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
56 citations,
August 1981 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Minoxidil helps hair regrowth in alopecia areata safely.
 9 citations,
December 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
9 citations,
December 1981 in “International Journal of Dermatology” The document concludes that early diagnosis is key for treating common baldness in women, but reassurance is often the best approach as hair thinning can be a normal part of aging.
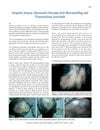 53 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery”
53 citations,
January 2014 in “Journal of Cutaneous and Aesthetic Surgery” Microneedling combined with triamcinolone can safely stimulate faster hair regrowth in people with Alopecia Areata.
 5 citations,
February 2004 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
5 citations,
February 2004 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” The book provides updated knowledge on hair disorders and new treatments for hair loss.
 5 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
5 citations,
March 2001 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Diagnose and manage hair issues in women by checking medical conditions and using personalized treatments.
 3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
3 citations,
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” AGA is a genetic, hormonal hair loss treated with finasteride, minoxidil, and supplements, but new compounds are being developed.

 January 2018 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2018 in “Springer eBooks” Hidradenitis Suppurativa is likely an autoinflammatory disease, and better understanding its causes could improve treatments.
 January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology”
January 2012 in “The Year book of dermatology” Many treatments for alopecia areata have inconsistent results; for under 10s, use minoxidil with a corticosteroid, and for over 10s, add ILC and consider diphenylcyclopropenone for widespread cases.

Chemotherapy can cause skin issues and hair loss, and this guide explains how to manage them.
 89 citations,
November 2014 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine”
89 citations,
November 2014 in “International Journal of Nanomedicine” Using nanostructured lipid carriers to deliver spironolactone could improve treatment for hair loss.
 34 citations,
July 2010 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery”
34 citations,
July 2010 in “Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery” The document concludes that there is no agreed-upon best method for measuring drug delivery within hair follicles and more research is needed to validate current techniques.
 October 2023 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences”
October 2023 in “Benha Journal of Applied Sciences” Insulin resistance may contribute to hair loss in people with androgenic alopecia.
 November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
November 1999 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Treatments for hair loss include hormone modifiers, minoxidil, and hair transplant surgery.
 170 citations,
December 2009 in “Histopathology”
170 citations,
December 2009 in “Histopathology” The conclusion is that accurate diagnosis of different types of hair loss requires good teamwork between skin doctors and lab experts.
 143 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
143 citations,
October 1996 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Too much androgen can cause hair loss; finasteride may help.
 129 citations,
October 2007 in “The New England Journal of Medicine”
129 citations,
October 2007 in “The New England Journal of Medicine” Over one-third of women experience hair loss, with female-pattern hair loss being most common, and treatments include minoxidil and possibly hair transplantation.
 72 citations,
July 2014 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
72 citations,
July 2014 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Some treatments, like corticosteroids and sensitizing agents, can help with alopecia areata, but more high-quality research is needed.
 52 citations,
March 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
52 citations,
March 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy” The CLASI is a reliable tool for measuring the severity of cutaneous lupus erythematosus.
 50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology”
50 citations,
March 2000 in “American Journal of Clinical Dermatology” Alopecia Areata has no guaranteed treatment for hair regrowth, but options like corticosteroids and minoxidil are used, with future research focusing on genetic and immune therapies.
 42 citations,
April 2011 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy”
42 citations,
April 2011 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy” Flutamide effectively treats female pattern hair loss with low doses showing good liver tolerance.
 36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy”
36 citations,
May 2011 in “Dermatologic therapy” No treatments fully cure or prevent alopecia areata; some help but have side effects or need more research.
 29 citations,
April 2004 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy”
29 citations,
April 2004 in “Annals of Pharmacotherapy” Finasteride reduces hirsutism effectively with fewer side effects but is a second-choice treatment due to safety concerns.


























