 38 citations,
August 2005 in “Veterinary dermatology”
38 citations,
August 2005 in “Veterinary dermatology” A disease causing skin issues in young adult German short-haired pointers is hereditary, with most affected dogs not responding to treatment.
 27 citations,
July 2017 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
27 citations,
July 2017 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Certain microRNAs are linked to various skin diseases and could be used to diagnose and treat these conditions.
 5 citations,
January 2014 in “Current Dermatology Reports”
5 citations,
January 2014 in “Current Dermatology Reports” Many adult women suffer from persistent or late-onset acne, and while various treatments exist, finding the right one can be challenging.
 1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2016 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” A man developed a rare skin condition and drug-induced lupus, highlighting the need for biopsy in diagnosing skin issues caused by sunlight.
 May 2019 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology”
May 2019 in “Australasian Journal of Dermatology” The conclusion is that managing hair loss conditions like FFA and melanoma requires individualized approaches, considering new findings and balancing treatment benefits with potential risks.
 3 citations,
May 2022 in “JAAD case reports”
3 citations,
May 2022 in “JAAD case reports” A woman developed alopecia after her second Pfizer vaccine but regrew her hair with treatment and had no issues after a booster shot.
 24 citations,
July 2019 in “Cochrane library”
24 citations,
July 2019 in “Cochrane library” Some treatments like methotrexate with prednisone might help juvenile morphea, but more research is needed to confirm.
8 citations,
February 2022 in “Frontiers in Medicine” COVID-19 may trigger severe skin flare-ups in people with autoimmune conditions like lupus.
 1 citations,
October 1996 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery”
1 citations,
October 1996 in “Journal of Cutaneous Medicine and Surgery” Gene therapy shows promise for treating skin disorders and cancer, but faces technical challenges.
 125 citations,
September 2001 in “The FASEB Journal”
125 citations,
September 2001 in “The FASEB Journal” Stress can cause hair loss by negatively affecting hair follicles and this effect might be reversed with specific treatments.
 119 citations,
January 2012 in “Nutrition & Metabolism”
119 citations,
January 2012 in “Nutrition & Metabolism” Modern lifestyles, including poor diet, stress, and long-term use of certain medications, hinder the body's ability to heal from inflammation, leading to chronic diseases.
 489 citations,
November 2021 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy”
489 citations,
November 2021 in “Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy” The JAK/STAT pathway is important in cell processes and disease, and JAK inhibitors are promising for treating related conditions.
 1 citations,
January 2010 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology”
1 citations,
January 2010 in “Serbian Journal of Dermatology and Venereology” The document concludes that effective acne treatment requires a personalized combination of therapies and long-term commitment, with retinoids being important for maintenance.
 April 2019 in “Radiotherapy and oncology”
April 2019 in “Radiotherapy and oncology” HPV infection is linked to better survival in advanced anal cancer, higher radiation doses improve survival, especially in HPV-negative patients, and prostaglandin E₂ pretreatment can protect mouse hair follicles from radiation damage.
82 citations,
May 2010 in “PLoS neglected tropical diseases” Secondary syphilis in Cali, Colombia, shows high Treponema pallidum presence and challenges in early diagnosis, needing better public health strategies.
 September 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology”
September 2016 in “British Journal of Dermatology” Doctors need more training in skin cancer screening, a new treatment is effective for a skin condition, better diagnosis methods for skin cancer are available, hair loss in women may be linked to hormones and cholesterol, certain skin care products might cause hair loss, babies' skin gets weaker after birth, and a gene mutation might be linked to eczema.
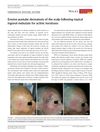 9 citations,
July 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
9 citations,
July 2017 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Two elderly men developed scalp inflammation after using a gel for skin lesions, which healed with treatment except for some permanent hair loss.
 December 2024 in “Brazilian Journal of Health Review”
December 2024 in “Brazilian Journal of Health Review” Early diagnosis of alopecia frontal fibrosante is crucial, but treatment remains controversial and varies.
 February 2008 in “Experimental dermatology”
February 2008 in “Experimental dermatology” Oxidative stress plays a significant role in vitiligo, and both skin and non-skin cells may be involved.
 May 2024 in “Journal of drug delivery science and technology”
May 2024 in “Journal of drug delivery science and technology” Exosomes show promise for treating skin diseases and improving skin regeneration.
701 citations,
August 2014 in “Nature medicine” Alopecia areata can be reversed by JAK inhibitors, promoting hair regrowth.
 August 2023 in “Medical Hypotheses”
August 2023 in “Medical Hypotheses” Metformin, usually used for diabetes, can also help treat hair loss from alopecia areata due to its ability to reduce inflammation and stimulate new hair growth.
 1 citations,
July 2015 in “Cytokine”
1 citations,
July 2015 in “Cytokine” Finasteride improves immune response and reduces organ damage after trauma hemorrhage in mice.
 22 citations,
June 2012 in “PLOS ONE”
22 citations,
June 2012 in “PLOS ONE” Cholesterol-related compounds can stop hair growth and cause inflammation in a type of scarring hair loss.
 18 citations,
November 2007 in “Annals of Surgery”
18 citations,
November 2007 in “Annals of Surgery” Finasteride reduces inflammation and improves immune response after trauma by altering hormone levels.
 9 citations,
November 2020 in “Medical Hypotheses”
9 citations,
November 2020 in “Medical Hypotheses” Hair loss may link to weaker COVID-19 immunity, suggesting possible need for extra vaccine boost.
 125 citations,
August 2020 in “Frontiers in Immunology”
125 citations,
August 2020 in “Frontiers in Immunology” Men generally have more severe COVID-19 cases and higher death rates than women due to biological differences.
 21 citations,
January 2021 in “Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism”
21 citations,
January 2021 in “Therapeutic Advances in Endocrinology and Metabolism” Testosterone may have a dual role in COVID-19, potentially worsening outcomes in men, and testosterone therapy could help some patients, but more research is needed.
 June 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
June 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Jagged-1 in skin Tregs is crucial for timely wound healing by recruiting specific immune cells.
 April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2021 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The new skin-targeted COVID-19 vaccine creates strong immune responses and could improve vaccination methods.


























