20 citations,
January 2003 in “Dermatology online journal” Prostaglandin analogs like Latanoprost might help grow hair on the scalp and body.
[object Object]  9 citations,
December 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
9 citations,
December 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Certain drugs are effective for skin conditions like psoriasis, vitiligo, and hair loss.
 6 citations,
July 2008 in “Clinical and experimental optometry”
6 citations,
July 2008 in “Clinical and experimental optometry” Prostaglandin eye drops for glaucoma can rarely cause too much cheek hair growth.
 5 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
5 citations,
May 2019 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Prostaglandin analogue may help with eyebrow loss in frontal fibrosing alopecia.
 31 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
31 citations,
January 2015 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” Prostaglandin F2α analogs show promise for treating certain types of hair loss but need more research for other skin conditions.
 1 citations,
March 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine”
1 citations,
March 2023 in “Frontiers in Medicine” Topical prostaglandin analogs may help with hair growth but more research is needed.
[object Object]  162 citations,
August 2002 in “Survey of Ophthalmology”
162 citations,
August 2002 in “Survey of Ophthalmology” Latanoprost can make eyelashes longer, thicker, and darker.
 9 citations,
August 2014 in “European journal of ophthalmology”
9 citations,
August 2014 in “European journal of ophthalmology” PGF2α receptors in human eyelids are found in specific parts of hair follicles, explaining eyelash changes with glaucoma treatment.
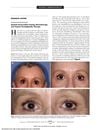 3 citations,
July 2010 in “Archives of internal medicine”
3 citations,
July 2010 in “Archives of internal medicine” A woman kept her eyelashes during chemotherapy possibly because of her glaucoma eye drops.
 January 2024 in “Vestnik oftalʹmologii”
January 2024 in “Vestnik oftalʹmologii” Stopping minoxidil and using prostaglandin analogues improved the man's eye condition.
 20 citations,
March 2013 in “Journal of Lipid Research”
20 citations,
March 2013 in “Journal of Lipid Research” The research explains how a human enzyme binds and processes its substrate, which could relate to its role in biological functions and hair loss.
 September 2024 in “Egyptian Journal of Dermatology and Venerology”
September 2024 in “Egyptian Journal of Dermatology and Venerology” Combining TRA and latanoprost is most effective for treating localized alopecia areata.
 June 2012 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature”
June 2012 in “Faculty Opinions – Post-Publication Peer Review of the Biomedical Literature” Prostaglandin D2, found in higher levels in bald scalps, stops hair growth and could be a target for treating hair loss.
 100 citations,
April 2010 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy”
100 citations,
April 2010 in “Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy” Hair loss in men treated best with early medication or transplant, new treatments researched.
 85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
85 citations,
October 2012 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune condition often starting before age 20, with varied treatment success and a need for personalized treatment plans.
 85 citations,
April 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
85 citations,
April 2007 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Some drugs can cause hair loss, change hair color and shape, or increase hair growth, and treatment may involve stopping the drug or using specific hair growth treatments.
 72 citations,
July 2014 in “American journal of clinical dermatology”
72 citations,
July 2014 in “American journal of clinical dermatology” Some treatments, like corticosteroids and sensitizing agents, can help with alopecia areata, but more high-quality research is needed.
 66 citations,
June 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology”
66 citations,
June 2018 in “International Journal of Women's Dermatology” No cure for female pattern hair loss, but various effective treatments exist.
 57 citations,
October 2013 in “international journal of endocrinology and metabolism”
57 citations,
October 2013 in “international journal of endocrinology and metabolism” Female pattern hair loss is common, linked to polycystic ovarian syndrome, and treated with topical Minoxidil.
 48 citations,
April 2013 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs”
48 citations,
April 2013 in “Expert Opinion on Investigational Drugs” Possible new treatments for common hair loss include drugs, stem cells, and improved transplants.
 36 citations,
June 2012 in “PubMed”
36 citations,
June 2012 in “PubMed” There are potential treatments for pattern baldness, but more research is needed to confirm their effectiveness.
 33 citations,
November 2006 in “Survey of Ophthalmology”
33 citations,
November 2006 in “Survey of Ophthalmology” Madarosis is the loss of eyelashes and eyebrows due to various health issues and requires thorough examination to diagnose and treat the underlying cause.
 30 citations,
May 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology”
30 citations,
May 2018 in “Experimental Dermatology” The conclusion is that future hair loss treatments should target the root causes of hair thinning, not just promote hair growth.
 22 citations,
September 2004 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
22 citations,
September 2004 in “Journal of The European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Bimatoprost can cause longer, thicker, darker eyelashes and eyebrows.
 22 citations,
April 2003 in “Eye”
22 citations,
April 2003 in “Eye” Applying latanoprost on skin can stimulate hair growth with minimal side effects.
 21 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
21 citations,
January 2015 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Latanoprost may cause scalp inflammation and delayed healing.
 20 citations,
January 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas”
20 citations,
January 2017 in “Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas” Recent advances in hair loss treatments show significant progress.
 16 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
16 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” Intralesional corticosteroids work best for mild alopecia areata, and DPCP works best for moderate to severe cases.
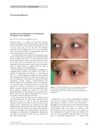 15 citations,
November 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology”
15 citations,
November 2009 in “Clinical and Experimental Dermatology” Bimatoprost helped a girl grow her eyelashes back quickly and without serious side effects.
14 citations,
September 2015 in “PubMed” Alopecia areata can be managed with various treatments, and severe cases should be referred to dermatologists.



























