 122 citations,
May 2010 in “Plant Physiology”
122 citations,
May 2010 in “Plant Physiology” Different PIN proteins affect plant root hair growth by changing how auxin is transported.
[object Object]  84 citations,
June 2010 in “The Plant Cell”
84 citations,
June 2010 in “The Plant Cell” Phospholipase A2 is necessary for the correct placement of PIN proteins in plant roots, affecting root growth.
 20 citations,
January 2021 in “Plants”
20 citations,
January 2021 in “Plants” High energy boosts root hair growth in plants, while low energy stops it.
 47 citations,
April 2012 in “The Plant Journal”
47 citations,
April 2012 in “The Plant Journal” Phosphorylation of certain parts of the PIN3 protein is crucial for its role in plant root growth and response to gravity.
 4 citations,
October 2014 in “Springer eBooks”
4 citations,
October 2014 in “Springer eBooks” Ethylene and auxin hormones interact in complex ways that are essential for plant growth and development.
 28 citations,
December 2018 in “Plant, cell & environment/Plant, cell and environment”
28 citations,
December 2018 in “Plant, cell & environment/Plant, cell and environment” A protein called PLC2 is important for the growth and development of plant roots influenced by auxin.
 356 citations,
March 2012 in “Trends in Plant Science”
356 citations,
March 2012 in “Trends in Plant Science” Auxin and ethylene hormones both work together and against each other to control plant growth.
 33 citations,
February 2016 in “Journal of Experimental Botany”
33 citations,
February 2016 in “Journal of Experimental Botany” ROOT HAIR SPECIFIC 10 (RHS10) reduces the length of root hairs in Arabidopsis plants.
August 2024 in “Scientia Horticulturae” AMF initially inhibits but later promotes citrus root hair growth by regulating auxin levels.
[object Object]  6 citations,
February 2023 in “Plant and Soil”
6 citations,
February 2023 in “Plant and Soil” Bacillus subtilis strain WM13-24 helps plant root growth through volatile compounds.
 October 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
October 2022 in “Research Square (Research Square)” The conclusion is that certain chemicals from Bacillus subtilis help improve plant root growth through a hormone-related process.
 80 citations,
April 2011 in “Plant physiology”
80 citations,
April 2011 in “Plant physiology” White lupin uses specific genes to grow root hairs and access phosphorus when it's scarce.
 35 citations,
September 2012 in “PloS one”
35 citations,
September 2012 in “PloS one” Two distinct pathways direct proteins to vacuoles in Arabidopsis, affecting root hair growth and protein targeting.
 52 citations,
April 2013 in “Developmental Cell”
52 citations,
April 2013 in “Developmental Cell” Brg1 is crucial for hair growth and skin repair by maintaining stem cells and promoting regeneration.

Plant roots respond to fungus smells by possibly using certain proteins and a plant hormone to change root growth, but more research is needed.
 178 citations,
May 2006 in “Developmental Dynamics”
178 citations,
May 2006 in “Developmental Dynamics” Jumonji genes are important for development and their mutations can cause abnormalities, especially in the heart and brain.
28 citations,
December 2016 in “Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A” Bone-forming cells grow well in 3D polymer scaffolds with 35 µm pores.
January 2023 in “Pharmaceutics” AA–TF#15 significantly promotes hair regrowth and could be an effective treatment for androgenic alopecia.
October 2024 in “Cosmetics” ATG effectively reduces hair frizz without damaging hair strength.
 131 citations,
March 2004 in “The American journal of pathology”
131 citations,
March 2004 in “The American journal of pathology” Modulating BMP activity changes the number, size, shape, and type of ectodermal organs.
 66 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Molecular Biology”
66 citations,
July 2015 in “Journal of Molecular Biology” The document concludes that for hair and feather growth, it's better to target the environment around stem cells than the cells themselves.
 13 citations,
December 2018 in “Development, Growth & Differentiation”
13 citations,
December 2018 in “Development, Growth & Differentiation” Sex hormones, especially estradiol, can change chicken feather shapes and colors.
 61 citations,
June 2018 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America”
61 citations,
June 2018 in “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America” Light can turn on hair growth cells through a nerve path starting in the eyes.
 4 citations,
March 2019 in “Experimental Biology and Medicine”
4 citations,
March 2019 in “Experimental Biology and Medicine” Exposure to 50 Hz electromagnetic fields may help mice grow hair faster.
 191 citations,
November 1959 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences”
191 citations,
November 1959 in “Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences” Hair and wool have complex microscopic structures with microfibrils and varying cystine content.
 43 citations,
December 2013 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology”
43 citations,
December 2013 in “Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology” Genetic mutations can cause hair growth disorders by affecting key genes and signaling pathways.
 15 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of circadian rhythms”
15 citations,
October 2012 in “Journal of circadian rhythms” RNA from horse hair follicles can track circadian rhythms non-invasively.
 57 citations,
May 2014 in “Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution”
57 citations,
May 2014 in “Molecular Phylogenetics and Evolution” The research found how GPCR Class A Rhodopsin receptors are related and suggested possible substances they interact with.
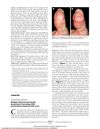 11 citations,
December 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology”
11 citations,
December 2010 in “Archives of Dermatology” A man with rare skin changes on his fingers was diagnosed with multiple myeloma-linked amyloidosis.
 September 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)”
September 2023 in “bioRxiv (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory)” The mTurq2-Col4a1 mouse model shows that cells can divide while attached to stable basement membranes during development.


























