 1 citations,
July 2014 in “Nepal journal of dermatology, venereology & leprology”
1 citations,
July 2014 in “Nepal journal of dermatology, venereology & leprology” Patients with chronic kidney disease on hemodialysis often have skin problems.
 August 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)”
August 2024 in “Research Square (Research Square)” Using 5-alpha reductase inhibitors may lower the risk of breast cancer in females.
 July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ”
July 2023 in “The Egyptian Journal of Hospital Medicine ” The conclusion is that emotional support and a variety of treatments are important for alopecia areata, but more research is needed.
 April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
April 2019 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” The research found that certain characteristics like age, sex, race, marital status, and education level can influence whether alopecia patients stick to their hair loss treatment with topical minoxidil.
 January 2019 in “Springer eBooks”
January 2019 in “Springer eBooks” Platelet-rich plasma therapy may have benefits and is generally safe, but more research is needed to confirm its effectiveness and safety.
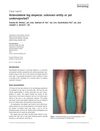 September 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology”
September 2018 in “International Journal of Dermatology” Anterolateral leg alopecia is a benign, nonprogressive hair loss condition on the lower legs that is not well understood and may resolve on its own.
 May 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
May 2007 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Hair care practices like using relaxers and tight braiding can lead to permanent hair loss in black women.
 November 2020 in “Skin Research and Technology”
November 2020 in “Skin Research and Technology” Videodermoscopy better identifies female hair loss than clinical diagnosis.
 145 citations,
November 2018 in “Nature Communications”
145 citations,
November 2018 in “Nature Communications” The Sonic hedgehog pathway is crucial for new hair growth during mouse skin healing.
 86 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology”
86 citations,
August 2014 in “Journal of The American Academy of Dermatology” To diagnose hair loss, use a systematic approach including history, exams, and tests.
 74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics”
74 citations,
April 2005 in “Dermatologic Clinics” Minoxidil and finasteride are effective for male hair loss, minoxidil for female hair loss, and various treatments like corticosteroids work for alopecia areata; treatment should be tailored to the individual.
 68 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Dermatology”
68 citations,
May 2011 in “European Journal of Dermatology” Acne is caused by genetics, diet, hormones, and bacteria, with treatments not yet curative.
 37 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in pharmacology”
37 citations,
August 2022 in “Frontiers in pharmacology” Oral JAK inhibitors are effective and safe for treating alopecia areata but may need ongoing use to keep results.
 27 citations,
December 2016 in “Dermatology and Therapy”
27 citations,
December 2016 in “Dermatology and Therapy” Certain skin conditions can indicate insulin resistance and should prompt lifestyle changes and medical treatment to manage underlying health issues.
 21 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology”
21 citations,
September 2015 in “Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology” Yellow and orange colors are important for diagnosing certain skin conditions.
 17 citations,
December 2004 in “The Journal of Men's Health & Gender”
17 citations,
December 2004 in “The Journal of Men's Health & Gender” Male pattern baldness involves hormone-related hair thinning, shorter hair, and inflammation.
 15 citations,
November 2019 in “Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology”
15 citations,
November 2019 in “Cutaneous and Ocular Toxicology” Minoxidil tretinoin liposomal based hydrogel shows promise for effective treatment of hair loss by delivering both drugs at the same time.
 15 citations,
January 2011 in “Annals of Dermatology”
15 citations,
January 2011 in “Annals of Dermatology” The study concluded that neonatal occipital alopecia is common, not caused by physical friction, and usually resolves on its own without treatment.
 14 citations,
August 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy”
14 citations,
August 2020 in “Dermatologic Therapy” Low-dose oral minoxidil is a safe treatment for hair loss, with the main side effect being excessive hair growth. Other side effects like foot swelling, low blood pressure when standing, and heart rate changes are rare.
 13 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in oncology”
13 citations,
April 2022 in “Frontiers in oncology” Melanoma development can be linked to the breakdown of skin's melanin-producing units.
 9 citations,
May 1989 in “Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine”
9 citations,
May 1989 in “Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine” An elderly woman's swollen, painful foot was found to be caused by a rare type of bone lymphoma, which improved with radiation treatment.
 5 citations,
January 2017 in “Clinics in Dermatology”
5 citations,
January 2017 in “Clinics in Dermatology” Skin symptoms without a medical cause often reflect psychological stress and are influenced by culture, requiring a team approach for treatment.
 4 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders”
4 citations,
January 2019 in “Skin appendage disorders” The new Follicular Map method could help assess hair treatment effectiveness but has some limitations.
 1 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology”
1 citations,
April 2018 in “Journal of Investigative Dermatology” Tofacitinib helped most patients with alopecia areata regrow hair and changes in immune cells were linked to the treatment's effectiveness.
 May 2024 in “Scientific reports”
May 2024 in “Scientific reports” Twist2 is essential for scarless skin healing and hair growth in mouse fetuses.
 October 2023 in “Animal production science”
October 2023 in “Animal production science” Vitamin A deficiency changes cattle hair structure, while pregnancy may improve it, suggesting hair can indicate cattle health.
 March 2023 in “Revista română de reumatologie”
March 2023 in “Revista română de reumatologie” Skin problems are common in lupus, often appearing first, with various types and treatments, and careful monitoring is important for diagnosis and management.
 November 2015 in “European Journal of Inflammation”
November 2015 in “European Journal of Inflammation” Cicatricial alopecia, a permanent hair loss condition, is mainly caused by damage to specific hair follicle stem cells and abnormal immune responses, with gene regulator PPAR-y and lipid metabolism disorders playing significant roles.
 January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks”
January 2012 in “Elsevier eBooks” Hair loss can cause emotional and social issues, and various treatments, including medication, surgery, and psychological support, are needed.
 April 2008 in “Medical & surgical dermatology”
April 2008 in “Medical & surgical dermatology” Certain hairstyles can cause scalp diseases, smoking is linked to hair loss, 5% minoxidil foam is effective for hair loss treatment, and various factors influence wound healing and hair growth.






























